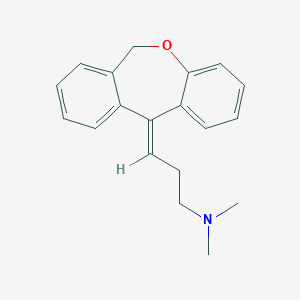
Doxepin
1668-19-5
1229-29-4 (hydrochloride), 4698-39-9 ((E)-isomer); 25127-31-5 ((Z)-isomer)
Launched – 1964
| Doxepin Hydrochloride | 3U9A0FE9N5 | 1229-29-4 |
NSC-108160
P-3693A
SO-101
Aponal
Quitaxon
Silenor
Sinequan
Sinquan
Xepin
Zonalon
USP
USP32/pub/data/v32270/usp32nf27s0_m28110
N,N-Dimethyldibenz[b,e]oxepin-D11(6H),![]() -propylamine hydrochloride
-propylamine hydrochloride ![]()
![]()
![]() [1229-29-4; 4698-39-9 ((E)-isomer); 25127-31-5 ((Z)-isomer)].
[1229-29-4; 4698-39-9 ((E)-isomer); 25127-31-5 ((Z)-isomer)].
DESCRIPTION
SINEQUAN® (doxepin hydrochloride) is one of a class of psychotherapeutic agents known as dibenzoxepin tricyclic compounds. The molecular formula of the compound is C19H21NO•HCl having a molecular weight of 316. It is a white crystalline solid readily soluble in water, lower alcohols and chloroform.
Inert ingredients for the capsule formulations are: hard gelatin capsules (which may contain Blue 1, Red 3, Red 40, Yellow 10, and other inert ingredients); magnesium stearate; sodium lauryl sulfate; starch.
Inert ingredients for the oral concentrate formulation are: glycerin; methylparaben; peppermint oil; propylparaben; water.
Chemistry
SINEQUAN (doxepin HCl) is a dibenzoxepin derivative and is the first of a family of tricyclic psychotherapeutic agents. Specifically, it is an isomeric mixture of: 1-Propanamine, 3-dibenz[b,e]oxepin-11(6H)ylidene-N,N-dimethyl-, hydrochloride.
 |
For Consumers
WHAT ARE THE POSSIBLE SIDE EFFECTS OF DOXEPIN (SINEQUAN) (SINEQUAN)?
Get emergency medical help if you have any of these signs of an allergic reaction: hives; difficulty breathing; swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Report any new or worsening symptoms to your doctor, such as: mood or behavior changes, anxiety, panic attacks, trouble sleeping, or if you feel impulsive, irritable, agitated, hostile, aggressive, restless, hyperactive (mentally or physically), more depressed, or have thoughts about suicide or hurting yourself.
Synthesis Reference
Luigi Schioppi, Brian Talmadge Dorsey, Michael Skinner, John Carter, Robert Mansbach, Philip Jochelson, Roberta L. Rogowski, Cara Casseday, Meredith Perry, Bryan Knox, “LOW-DOSE DOXEPIN FORMULATIONS AND METHODS OF MAKING AND USING THE SAME.” U.S. Patent US20090074862, issued March 19, 2009.

DOI: 10.1007/BF00904459
DOI: 10.1007/BF00901313 US 3420851
DE 1232161
SYN 2
Synth Commun 1989, 19(19): 3349, US 3438981

Condensation of dibenzo-oxepinone (I) with 3-(dimethylamino)propylmagnesium chloride (II), followed by a dehydration of the resultant tertiary alcohol with hot HCl gives the target 3-(dimethylamino)propylidene derivative.
SYN 3

Chlorination of 2-(phenoxymethyl)benzoic acid (I) with SOCl2 at 50 °C gives 2-(phenoxymethyl)benzoyl chloride (II), which undergoes cyclization in the presence of FeCl3 in toluene to furnish dibenzo[b,e]oxepin-11-one (III)
Grignard reaction of intermediate (III) with tert-butyl 3-chloropropyl ether (IV) using Mg in refluxing THF or Et2O provides 11-(3-tert-butoxypropyl)-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[b,e]oxepin-11-ol (V), which upon elimination by means of HCl in refluxing EtOH affords alkene (VI).
Treatment of tert-butyl ether (VI) with SOCl2 in refluxing toluene gives 11-(3-chloropropylidene)-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[b,e]oxepine (VII), which is then coupled with dimethylamine (VIII) in the presence of Ni(OAc)2, PPh3 and K2CO3 in DMF or in EtOH at 100 °C to furnish doxepin (VII) .
Finally, treatment of tertiary amine (VII) with HCl at 140 °C yields the target doxepin hydrochloride .
US 2014309437, CN 102924424
Doxepin is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) used as a pill to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic hives, and for short-term help with trouble remaining asleep after going to bed (a form of insomnia).[8][7][9] As a cream it is used for short term treatment of itchiness due to atopic dermatitis or lichen simplex chronicus.[10]
At doses used to treat depression, doxepin appears to inhibit the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine and to have antihistamine, adrenergic and serotonin receptor antagonistic, and anticholinergic activities; at low doses used to treat insomnia it appears to be selective for the histamine H1 receptor.[11]
It was introduced under the brand names Quitaxon and Aponal by Boehringer, which discovered it, and as Sinequan by Pfizer,[12] and has subsequently been marketed under many other names worldwide.[2]
Medical uses
Doxepin is used as a pill to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic hives, and for short-term help with trouble remaining asleep after going to bed (a form of insomnia).[8][7][9] As a cream it is used for short term treatment of itchiness to due atopic dermatitis or lichen simplex chronicus.[10]
In 2016 the American College of Physicians advised that insomnia be treated first by treating comorbid conditions, then with cognitive behavioral therapy and behavioral changes, and then with drugs; doxepin was among those recommended for short term help maintaining sleep, on the basis of weak evidence.[13][14] The 2017 American Academy of Sleep Medicine recommendations focused on treatment with drugs were similar.[13] A 2015 AHRQ review of treatments for insomnia had similar findings.[15]
A 2010 review found that topical doxepin is useful to treat itchiness.[16]
A 2010 review of treatments for chronic hives found that doxepin had been superseded by better drugs but was still sometimes useful as a second line treatment.[17]
Chemistry
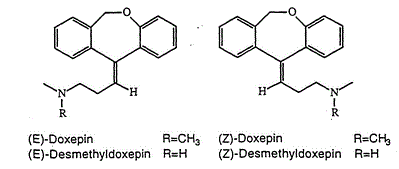
Doxepin is a tricyclic compound, specifically a dibenzoxepin, and possesses three rings fused together with a side chain attached in its chemical structure.[38] It is the only TCA with a dibenzoxepin ring system to have been marketed.[64] Doxepin is a tertiary amine TCA, with its side chain–demethylated metabolite nordoxepin being a secondary amine.[40][41] Other tertiary amine TCAs include amitriptyline, imipramine, clomipramine, dosulepin (dothiepin), and trimipramine.[65][66] Doxepin is a mixture of (E) and (Z) stereoisomers (the latter being known as cidoxepin or cis-doxepin) and is used commercially in a ratio of approximately 85:15.[3][67] The chemical name of doxepin is (E/Z)-3-(dibenzo[b,e]oxepin-11(6H)-ylidene)-N,N-dimethylpropan-1-amine[38][68] and its free base form has a chemical formula of C19H21NO with a molecular weight of 279.376 g/mol.[68] The drug is used commercially almost exclusively as the hydrochloride salt; the free base has been used rarely.[3][69] The CAS Registry Number of the free base is 1668-19-5 and of the hydrochloride is 1229-29-4.[3][69]

clip
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040402007016079

History
Doxepin was discovered in Germany in 1963 and was introduced in the United States as an antidepressant in 1969.[38] It was subsequently approved at very low doses in the United States for the treatment of insomnia in 2010.[44][69]
Society and culture
Generic names
Doxepin is the generic name of the drug in English and German and its INN and BAN, while doxepin hydrochloride is its USAN, USP, BANM, and JAN.[3][69][70][2] Its generic name in Spanish and Italian and its DCIT are doxepina, in French and its DCF are doxépine, and in Latin is doxepinum.[2]
The cis or (Z) stereoisomer of doxepin is known as cidoxepin, and this is its INN while cidoxepin hydrochloride is its USAN.[3]
Brand names
It was introduced under the brand names Quitaxon and Aponal by Boehringer and as Sinequan by Pfizer.[12]
As of October 2017, doxepin is marketed under many brand names worldwide: Adnor, Anten, Antidoxe, Colian, Dofu, Doneurin, Dospin, Doxal, Doxepini, Doxesom, Doxiderm, Flake, Gilex, Ichderm, Li Ke Ning, Mareen, Noctaderm, Oxpin, Patoderm, Prudoxin, Qualiquan, Quitaxon, Sagalon, Silenor, Sinepin, Sinequan, Sinequan, Sinquan, and Zonalon.[2] It is also marketed as a combination drug with levomenthol under the brand name Doxure.[2]
Approvals
The oral formulations of doxepin are FDA-approved for the treatment of depression and sleep-maintenance insomnia and its topical formulations are FDA-approved the short-term management for some itchy skin conditions.[71] Whereas in Australia and the United Kingdom, the only licensed indication(s) is/are in the treatment of major depression and pruritus in eczema, respectively.[20][72]
Research
Antihistamine
As of 2017 there was no good evidence that topical doxepin was useful to treat localized neuropathic pain.[73] Cidoxepin is under development by Elorac, Inc. for the treatment of chronic urticaria (hives).[74] As of 2017, it is in phase II clinical trials for this indication.[74] The drug was also under investigation for the treatment of allergic rhinitis, atopic dermatitis, and contact dermatitis, but development for these indications was discontinued.[74]
Headache
Doxepin was under development by Winston Pharmaceuticals in an intranasal formulation for the treatment of headache.[75] As of August 2015, it was in phase II clinical trials for this indication.[75]
PATENT
https://patents.google.com/patent/US9486437B2/en
Doxepin:
Doxepin HCl is a tricyclic compound currently approved and available for treatment of depression and anxiety. Doxepin has the following structure:
For all compounds disclosed herein, unless otherwise indicated, where a carbon-carbon double bond is depicted, both the cis and trans stereoisomers, as well as mixtures thereof are encompassed.
Doxepin belongs to a class of psychotherapeutic agents known as dibenzoxepin tricyclic compounds, and is currently approved and prescribed for use as an antidepressant to treat depression and anxiety. Doxepin has a well-established safety profile, having been prescribed for over 35 years.
Doxepin, unlike most FDA approved products for the treatment of insomnia, is not a Schedule IV controlled substance. U.S. Pat. Nos. 5,502,047 and 6,211,229, the entire contents of which are incorporated herein by reference, describe the use of doxepin for the treatment chronic and non-chronic (e.g., transient/short term) insomnias at dosages far below those used to treat depression.
It is contemplated that doxepin for use in the methods described herein can be obtained from any suitable source or made by any suitable method. As mentioned, doxepin is approved and available in higher doses (75-300 milligrams) for the treatment of depression and anxiety. Doxepin HCl is available commercially and may be obtained in capsule form from a number of sources. Doxepin is marketed under the commercial name SINEQUAN® and in generic form, and can be obtained in the United States generally from pharmacies in capsule form in amounts of 10, 25, 50, 75, 100 and 150 mg dosage, and in liquid concentrate form at 10 mg/mL. Doxepin HCl can be obtained from Plantex Ltd. Chemical Industries (Hakadar Street, Industrial Zone, P.O. Box 160, Netanya 42101, Israel), Sifavitor S.p.A. (Via Livelli 1—Frazione, Mairano, Italy), or from Dipharma S.p.A. (20021 Baranzate di Bollate, Milano, Italy). Also, doxepin is commercially available from PharmacyRx (NZ) (2820 1st Avenue, Castlegar, B.C., Canada) in capsule form in amounts of 10, 25, 50, 75, 100 and 150 mg. Furthermore, Doxepin HCl is available in capsule form in amounts of 10, 25, 50, 75, 100 and 150 mg and in a 10 mg/ml liquid concentrate from CVS Online Pharmacy Store (CVS.com).
Also, doxepin can be prepared according to the method described in U.S. Pat. No. 3,438,981, which is incorporated herein by reference in its entirety. It should be noted and understood that although many of the embodiments described herein specifically refer to “doxepin,” other doxepin-related compounds can also be used, including, for example, pharmaceutically acceptable salts, prodrugs, metabolites, in-situ salts of doxepin formed after administration, and solid state forms, including polymorphs and hydrates.
Metabolites:
In addition, doxepin metabolites can be prepared and used. By way of illustration, some examples of metabolites of doxepin can include, but are not limited to, desmethyldoxepin, hydroxydoxepin, hydroxyl-N-desmethyldoxepin, doxepin N-oxide, N-acetyl-N-desmethyldoxepin, N-desmethyl-N-formyldoxepin, quaternary ammonium-linked glucuronide, 2-O-glucuronyldoxepin, didesmethyldoxepin, 3-O-glucuronyldoxepin, or N-acetyldidesmethyldoxepin. The metabolites of doxepin can be obtained or made by any suitable method, including the methods described above for doxepin.
Desmethyldoxepin has the following structure:
Desmethyldoxepin is commercially available as a forensic standard. For example, it can be obtained from Cambridge Isotope Laboratories, Inc. (50 Frontage Road, Andover, Mass.). Desmethyldoxepin for use in the methods discussed herein can be prepared by any suitable procedure. For example, desmethyldoxepin can be prepared from 3-methylaminopropyl triphenylphosphonium bromide hydrobromide and 6,11-dihydrodibenz(b,e)oxepin-11-one according to the method taught in U.S. Pat. No. 3,509,175, which is incorporated herein by reference in its entirety.
Hydroxydoxepin has the following structure:
2-Hydroxydoxepin can be prepared by any suitable method, including as taught by Shu et al. (Drug Metabolism and Disposition (1990) 18:735-741), which is incorporated herein by reference in its entirety.
Hydroxyl-N-desmethyldoxepin has the following structure:
2-Hydroxy-N-desmethyldoxepin can be prepared any suitable method.
Doxepin N-oxide has the following structure:
Doxepin N-oxide can be prepared by any suitable method. For example, doxepin N-oxide can be prepared as taught by Hobbs (Biochem Pharmacol (1969) 18:1941-1954), which is hereby incorporated by reference in its entirety.
N-acetyl-N-desmethyldoxepin has the following structure:
N-acetyl-N-desmethyldoxepin can be prepared by any suitable means. For example, (E)-N-acetyl-N-desmethyldoxepin has been produced in filamentous fungus incubated with doxepin as taught by Moody et al. (Drug Metabolism and Disposition (1999) 27:1157-1164), hereby incorporated by reference in its entirety.
N-desmethyl-N-formyldoxepin has the following structure:
N-desmethyl-N-formyldoxepin can be prepared by any suitable means. For example, (E)-N-desmethyl-N-formyldoxepin has been produced in filamentous fungus incubated with doxepin as taught by Moody et al. (Drug Metabolism and Disposition (1999) 27:1157-1164), hereby incorporated by reference in its entirety.
N-acetyldidesmethyldoxepin has the following structure:
N-acetyldidesmethyldoxepin can be prepared by any suitable means. For example, (E)-N-acetyldidesmethyldoxepin has been produced in filamentous fungus incubated with doxepin as taught by Moody et al. (Drug Metabolism and Disposition (1999) 27:1157-1164), hereby incorporated by reference in its entirety.
Didesmethyldoxepin has the following structure:
Didesmethyldoxepin can be prepared by any suitable means. For example, (Z)- and (E)-didesmethyldoxepin have been isolated from plasma and cerebrospinal fluid of depressed patients taking doxepin, as taught by Deuschle et al. (Psychopharmacology (1997) 131:19-22), hereby incorporated by reference in its entirety.
3-O-glucuronyldoxepin has the following structure:
3-O-glucuronyldoxepin can be prepared by any suitable means. For example, (E)-3-O-glucuronyldoxepin has been isolated from the bile of rats given doxepin, as described by Shu et al. (Drug Metabolism and Disposition (1990) 18:1096-1099), hereby incorporated by reference in its entirety.
2-O-glucuronyldoxepin has the following structure:
2-O-glucuronyldoxepin can be prepared by any suitable means. For example, (E)-2-O-glucuronyldoxepin has been isolated from the bile of rats given doxepin, and also in the urine of humans given doxepin, as described by Shu et al. (Drug Metabolism and Disposition (1990) 18:1096-1099), hereby incorporated by reference in its entirety.
Quaternary ammonium-linked glucuronide of doxepin (doxepin N+-glucuronide) has the following structure:
N+-glucuronide can be obtained by any suitable means. For example, doxepin N+-glucuronide can be prepared as taught by Luo et al. (Drug Metabolism and Disposition, (1991) 19:722-724), hereby incorporated by reference in its entirety.
PATENT
https://patents.google.com/patent/CN105330638A/en
doxepin hydrochloride, the chemical name is N, N- dimethyl-3-dibenzo (b, e) _ oxepin -11 (6H) -1-propanamine salt subunit cistron iso the mixture body configuration. CAS Number 1229-29-4 thereof, of the formula
[0003]
[0004] Doxepin hydrochloride is a drug for the treatment of depression and anxiety neurosis that act to inhibit the central nervous system serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake, such that these two synaptic cleft neurotransmitter concentration increased and antidepressant effect, but also has anti-anxiety and sedative effects. Doxepin hydrochloride oral absorption, bioavailability of 13-45%, half-life (Shu 1/2) is 8-12 hours, to apparent volume of distribution (1) ^ 9-33171.Primarily metabolized in the liver to active metabolites thereof demethylation.Metabolite excretion from the kidney, elderly patients decline of metabolism and excretion ability of this product
[0005] Chinese Patent CN102924486A discloses a method for preparing a hydrochloride of doxepin. The method comprises the coupling reaction CN, i.e., the use of Ni (0Α〇) 2 / ΡΡ1 ^ φ to the amine-based compound. Although Ni catalyst the reaction step (OAc) 2 is more readily available and inexpensive, but the low yield of this step, and low product purity.
SUMMARY
[0006] Accordingly, the present invention provides a method of o-toluic acid synthesized multi doxepin hydrochloride, the higher the yield and purity of the obtained product was purified by this method.
[0007] – o-methylbenzoate method for the synthesis of doxepin hydrochloride, comprising the steps of:
[0008] (1) o-methylbenzoic acid with N- halosuccinimide benzylation halogenation reaction occurs in an acetonitrile solvent in the light conditions, to give o-halo-methylbenzoic acid (Compound J), the following reaction formula,
[0009]
[0010] (2) Compound J celite load cesium fluoride intramolecular substitution reaction, to give phthalide (Compound H) in an acetonitrile solvent and as a catalyst, the following reaction formula,
[0011]
[0012] (3) The phenol compound J with sodium methoxide in an alcohol solvent substitution reaction, to give a compound I, the following reaction formula,
[0013]
[0014] (4) The cyclization reaction of Compound I in a solvent in the catalytic DMS0 anhydrous aluminum chloride to give 6, 11-dihydro-dibenzo [b, e] oxepin -11- one (compound A), the following reaction formula,
[0015]
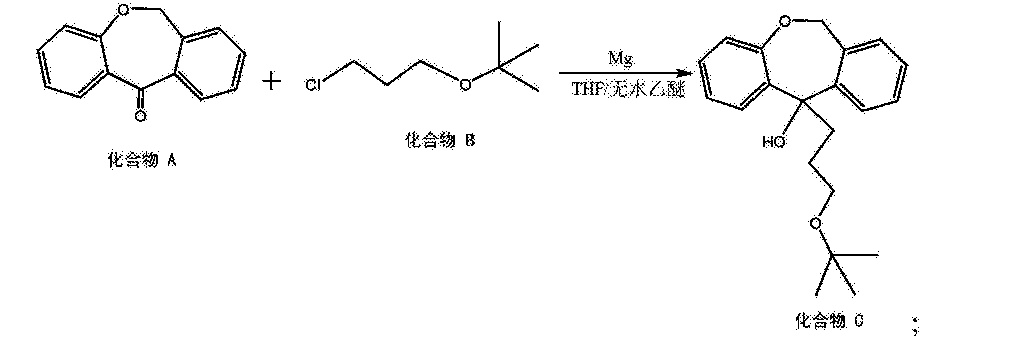
[0016] (5) 6, 11-dihydro-dibenzo [b, e] oxepin-11-one (Compound A) and 3-chloropropyl alkyl tert-butyl ether (compound B) is added magnesium powder and with THF and / or a nucleophilic addition of anhydrous diethyl ether under the conditions of the reaction solvent to give the hydroxy compound (compound C), the following reaction formula,
[0017]
[0018] (6) heating elimination reaction to give an olefin compound (Compound D) in a strong base in an alcoholic solvent to the hydroxy compound, the following reaction formula,
[0019]
[0020] (7) to the olefinic compound in the nucleophilic substitution reaction of a hydrogen halide acid, to give halide (Compound E), the following reaction formula,
[0022] wherein the compound E X is a C1, Br, or a a I;
[0023] (8) the halide with dimethylamine in a solvent under an organic lithium compound is added in ether to nucleophilic substitution reaction to yield doxepin (Compound F.), The following reaction formula,
[0024]
[0025] (9) the doxepin neutralization reaction with hydrochloric acid to give sulfasalazine (Compound G), the following reaction formula,
Example 1
[0043] placed in a 20L reaction vessel acetonitrile, o-methylbenzoic acid, N- bromosuccinimide, using a water bath temperature controlled at 10 ° C, under stirring for 4h. A known separation method, separation of o-bromomethyl-benzoic acid. This compound is named J.
[0044] placed in a 20L reaction container, Compound J, diatomaceous earth in an amount of 0.05 to load cesium fluoride (compound J as a mass basis), acetonitrile in an amount of 2.5 (in Compound J 1 is a mass basis), and the temperature was adjusted to 30 ° C, with stirring under reflux for 20h adjustment. Then, a known means for separating the reaction phthalide.
After [0045] placed in a 20L reaction vessel phthalide, 3 an amount of sodium methoxide in ethanol solvent (total mass of phenol phthalide and 1 meter), the reaction solution temperature adjusted to 50 ° C, was added dropwise start phenol was 1.05 mass (in mass was 1 meter phthalide), dropwise over lh. After the dropwise addition, the reaction temperature after 5h using known separation methods, to give o-methyl benzyl phenyl ether, this compound is named I.
[0046] The above compound I, in an amount of 10% anhydrous aluminum chloride (mass of Compound I was 100% basis), the amount of DMS0 3 (mass basis Compound I 1) into a reaction vessel , the temperature was adjusted to 95 ° C. The reaction time is to be 12h. Using known separation means for separating the 6, 11-dihydro-dibenzo [b, e] oxepin-11-one.
[0047] placement 6, 11-dihydro-dibenzo in a reaction vessel and 20L [b, e] oxepin-11-one, 1.1-dihydro-fold of the mole of diphenyl at 6, 11 and [ b, e] oxepin-11-one 3-chloropropyl alkyl tert-butyl ether, 2 times the mass 6, 11-dihydro-dibenzo [b, e] oxepin-11-one magnesium in , taking all of fifths THF (5 to 6 times by mass, 11-dihydro-dibenzo [b, e] THF oxepin-11-one) and heated to 35 ° C and allowed to react. After the reaction started, the remaining 3/5 of THF was added dropwise.Was added dropwise to the system to be completed into hydrogen, reflux. After a total reaction 5h, the reaction was stopped. After the system was cooled and then poured into saturated ammonium chloride solution, extracted twice with ethyl acetate was added, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate 5h, the resulting crude product was recrystallized from acetonitrile to give hydroxy compound.
[0048] placed in a 20L reaction vessel above hydroxy compound, an ethanol solution of 1.5 times the mass of hydroxy compound class of sodium hydroxide (concentration l〇wt mass%), was heated to 65 ° C, 2h elimination reaction after the reaction was stopped, cooled, the solvent was distilled off more of the obtained crude product was crystallized from acetonitrile to give the olefinic compounds.
[0049] placed in a 20L reaction vessel of the olefin compound, in an aqueous solution plus 1 times the mass of the olefinic compound hydrochloride (concentration of 5wt%), and heated to 50 ° C, so that a nucleophilic substitution reaction . The reaction time is to be after 4h, the reaction was stopped, cooled, the solvent was distilled off more of the obtained crude product was crystallized from acetonitrile to give the halides.
[0050] placed in a 20L reaction vessel above halide, 0.1 times the mass of methyl lithium halides to 2 times the mass of the halide in diethyl ether, heated to 40 ° C, so that the nucleophilic substitution reaction. The reaction time is to be after 5h, the reaction was stopped, reaction was complete and extracted with ethylacetate three times, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate 5h, the resulting crude product was recrystallized from acetonitrile to obtain doxepin.
[0051] 20L is placed in a pressure reactor above doxepin, 1.05 times the mass of material in the doxepin hydrochloride (concentration of 30wt%), the control pressure to 3 ~ 4MPa, and heated to 130 ° C , and among the responses. Time after to be reacted for 20 h, cooled to room temperature and should be finished by filtration, and dried to give doxepin hydrochloride. In this embodiment overall yield 37.9%, measured by HPLC obtaining 99.2% purity.
[0052] Example 2
[0053] placed in a 20L reaction vessel acetonitrile, o-methylbenzoic acid, N- bromosuccinimide, using a water bath temperature controlled at 20 ° C, under stirring for 2h. A known separation method, separation of o-toluic acid halide.
[0054] placed in a 20L reaction container, Compound J, an amount of load of cesium fluoride Celite ~ 0.05 0.15 (in mass Compound J is 1 meter), in an amount of 2.5 to 8 acetonitrile (compound J as a mass basis), and the temperature was adjusted to 30 ~ 50 ° C, 12 ~ 20h at reflux with stirring under regulation. Then, a known means for separating the reaction phthalide.
After [0055] phthalide placed in 20L reaction vessel, an amount of sodium methoxide in 10 ethanol solvent (total mass of phenol phthalide and 1 meter), adjusting the temperature of the reaction solution was 60 ° C, was added dropwise start phenol was 1.15 mass (in mass was 1 meter phthalide), dropwise over lh.After the dropwise addition, the reaction temperature after 5h using known separation methods, to give o-methyl benzyl phenyl ether, this compound is named I.
[0056] The above compound I, in an amount of 40% anhydrous aluminum chloride (mass of Compound I was 100% basis), in an amount of DMS0 8 (in compound I is a mass basis) into a reaction vessel , the temperature was adjusted to 105 ° C. The reaction time is to be for 6h. Using known separation means for separating the 6, 11-dihydro-dibenzo [b, e] oxepin-11-one.
[0057] placement 6, 11-dihydro-dibenzo in a reaction vessel and 20L [b, e] oxepin-11-one, 1.5-dihydro-fold of the mole of diphenyl at 6, 11 and [ b, e] oxepin-11-one 3-chloropropyl alkyl tert-butyl ether, 2.4 times the mass in 6, 11-dihydro-dibenzo [b, e] oxepin-11-one of magnesium, taking all fifths THF (5 to 7 times the mass in 6, 11-dihydro-dibenzo [b, e] THF oxepin-11-one) is to make, and heated to 40 ° C reaction.After the reaction started, the remaining 3/5 of THF was added dropwise. Was added dropwise to the system to be completed into hydrogen, reflux. When the total reaction 2h, the reaction was stopped. After the system was cooled and then poured into saturated ammonium chloride solution, extracted twice with ethyl acetate was added, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate 5h, the resulting crude product was recrystallized from acetonitrile to give hydroxy compound.
[0058] placed in a 20L reaction vessel above hydroxy compound, an ethanol solution of 5 times the mass of hydroxy compound class of sodium hydroxide (concentration of 70wt%), was heated to 80 ° C, the reaction was stopped after the elimination reaction LH, cooling, the solvent was distilled off more of the obtained crude product was crystallized from acetonitrile to give the olefinic compounds.
[0059] placed in a 20L reaction vessel of the olefin compound, in an aqueous solution of 2 times the mass of the olefinic compound added hydrobromic acid (concentration of 30wt%), and heated to 60 ° C, so that nucleophilic Substitution reaction. The reaction time is to be after the 1. 5h, the reaction was stopped, cooled, the solvent was distilled off more of the obtained crude product was crystallized from acetonitrile to give the halides.
[0060] placed in a 20L reaction vessel above halide, 0.8 times the mass of phenyl lithium halide to 8 times the mass of the halide in diethyl ether, heated to 50 ° C, so that the nucleophilic substitution reaction. The reaction time is to be after 2h, the reaction was stopped, reaction was complete and extracted with ethylacetate three times, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate 5h, the resulting crude product was recrystallized from acetonitrile to obtain doxepin.
[0061] 20L is placed in a pressure reactor above doxepin, 1.2 times the mass of material in the doxepin hydrochloride (concentration of 38wt%), the control pressure to 3 ~ 4MPa, and heated to 150 ° C , and among the responses. Time after to be reacted for 16 h, cooled to room temperature and should be finished by filtration, and dried to give doxepin hydrochloride. In this embodiment overall yield 39.7%, measured by HPLC obtaining 99.4% purity.
[0062] Example 3
[0063] placed in a 20L reaction vessel acetonitrile, o-methylbenzoic acid, N- bromosuccinimide, using a water bath temperature controlled at 15 ° C, under stirring for 3h. A known separation method, separation of o-bromomethyl-benzoic acid.
[0064] placed in a 20L reaction container, Compound J, an amount of load of cesium fluoride Celite ~ 0.05 0.15 (in mass Compound J is 1 meter), in an amount of 2.5 to 8 acetonitrile (compound J as a mass basis), and the temperature was adjusted to 30 ~ 50 ° C, 12 ~ 20h at reflux with stirring under regulation. Then, a known means for separating the reaction phthalide.
After [0065] phthalide placed in 20L reaction vessel, an amount of sodium methoxide in ethanol solvent 6 (total mass of phenol phthalide and 1 meter), adjusting the temperature of the reaction solution was 55 ° C, was added dropwise start phenol was 1.10 mass (in mass was 1 meter phthalide), dropwise over lh.After the dropwise addition, the reaction temperature after 3. 5h using known separation methods, to give o-methyl benzyl phenyl ether, this compound is named I.
[0066] Anhydrous aluminum above compound I, in an amount of 25% of the chloride (compound I mass is 100% basis), in an amount of DMS0 6. 5 (in compound I is a mass basis) into the reaction vessel temperature is adjusted to 100 ° C. The reaction time is to be 9h. Using known separation means for separating the 6, 11-dihydro-dibenzo [b, e] oxepin-11-one.
[0067] placement 6, 11-dihydro-dibenzo in a reaction vessel and 20L [b, e] oxepin-11-one, 1.3-dihydro-fold of the mole of diphenyl at 6, 11 and [ b, e] oxepin-11-one 3-chloropropyl alkyl tert-butyl ether, 2.2 times the mass in 6, 11-dihydro-dibenzo [b, e] oxepin-11-one of magnesium, taking all fifths THF (5 to 7 times the mass in 6, 11-dihydro-dibenzo [b, e] THF oxepin-11-one) is to make, and heated to 38 ° C reaction.After the reaction started, the remaining 3/5 of THF was added dropwise. Was added dropwise to the system to be completed into hydrogen, refluxed for 2h. After a total reaction 3. 5h, the reaction was stopped. After the system was cooled and then poured into saturated ammonium chloride solution, extracted twice with ethyl acetate was added, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate 5h, the resulting crude product was recrystallized from acetonitrile to give hydroxy compound.
[0068] placed in a 20L reaction vessel above hydroxy compound, an ethanol solution of 3-hydroxysteroid times the mass of the compound of sodium hydroxide (concentration of 40wt%), and heated to 75 ° C, 1. 5h the reaction stopped after elimination the reaction was cooled, the solvent was distilled off more of the obtained crude product was crystallized from acetonitrile to give the olefinic compounds.
[0069] placed in a 20L reaction vessel of the olefin compound, an aqueous solution of 1.5-fold increase in the mass of hydroiodic olefinic compounds (concentration of 18wt%), was heated to 55 ° C, so nucleophilic substitution reaction. The reaction time is to be after 2h, the reaction was stopped, cooled, the solvent was distilled off more of the obtained crude product was crystallized from acetonitrile to give the halides.
[0070] placed in a 20L reaction vessel above halide, 0.4 times the mass of the halide in n-butyllithium, in diethyl ether five times the mass of halide and heated to 45 ° C, so that a nucleophilic substitution reaction . The reaction time is to be 3. After 5h, the reaction was stopped, reaction was complete and extracted with ethylacetate three times, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate 5h, the resulting crude product was recrystallized from acetonitrile to obtain doxepin.
[0071] 20L is placed in a pressure reactor above doxepin, 1.12 times the mass of material in the doxepin hydrochloride (concentration of 34wt%), the control pressure to 3 ~ 4MPa, and heated to 140 ° C , and among the responses. Time after to be reacted for 18 h, cooled to room temperature and should be finished by filtration, and dried to give doxepin hydrochloride. In this embodiment overall yield 40.2%, measured by HPLC obtaining 99.5% purity.
[0072] Example 4
[0073] placed in a 20L reaction vessel acetonitrile, o-methylbenzoic acid, N- bromosuccinimide, using a water bath temperature controlled at 15 ° C, under stirring for 4h. A known separation method, separation of o-toluic acid halide.
[0074] placed in a 20L reaction container, Compound J, an amount of load of cesium fluoride Celite ~ 0.05 0.15 (in mass Compound J is 1 meter), in an amount of 2.5 to 8 acetonitrile (compound J as a mass basis), and the temperature was adjusted to 30 ~ 50 ° C, 12 ~ 20h at reflux with stirring under regulation. Then, a known means for separating the reaction phthalide.
After [0075] phthalide placed in 20L reaction vessel, 5 an amount of sodium methoxide in ethanol solvent (total mass of phenol phthalide and 1 meter), adjusting the temperature of the reaction solution was 55 ° C, was added dropwise start phenol was 1.15 mass (in mass was 1 meter phthalide), dropwise over lh.After the dropwise addition, the reaction temperature after 5h using known separation methods, to give o-methyl benzyl phenyl ether, this compound is named I.
[0076] The above compound I, in an amount of 25% anhydrous aluminum chloride (mass of Compound I was 100% basis), in an amount of DMS0 8 (in compound I is a mass basis) into a reaction vessel , the temperature was adjusted to 100 ° C. The reaction time is to be 12h. Using known separation means for separating the 6, 11-dihydro-dibenzo [b, e] oxepin-11-one.
[0077] placement 6, 11-dihydro-dibenzo in a reaction vessel and 20L [b, e] oxepin-11-one, 1.3-dihydro-fold of the mole of diphenyl at 6, 11 and [ b, e] oxepin-11-one 3-chloropropyl alkyl tert-butyl ether, 2.4 times the mass in 6, 11-dihydro-dibenzo [b, e] oxepin-11-one of magnesium, taking all fifths THF (5 to 7 times the mass in 6, 11-dihydro-dibenzo [b, e] THF oxepin-11-one) is to make, and heated to 40 ° C reaction.After the reaction started, the remaining 3/5 of THF was added dropwise. Was added dropwise to the system to be completed into hydrogen, reflux. When the total reaction 2h, the reaction was stopped. After the system was cooled and then poured into saturated ammonium chloride solution, extracted twice with ethyl acetate was added, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate 5h, the resulting crude product was recrystallized from acetonitrile to give hydroxy compound.
[0078] placed in a 20L reaction vessel above hydroxy compound, an ethanol solution of 5 times the mass of hydroxy compound class of sodium hydroxide (concentration of 70wt%), was heated to 80 ° C, the reaction was stopped after the elimination reaction LH, cooling, the solvent was distilled off more of the obtained crude product was crystallized from acetonitrile to give the olefinic compounds.
[0079] placed in a 20L reaction vessel of the olefin compound, an aqueous solution of 1.5-fold increase in the mass of hydroiodic olefinic compounds (concentration of 30wt%), and heated to 60 ° C, so nucleophilic substitution reaction. The reaction time is to be after the 1. 5h, the reaction was stopped, cooled, the solvent was distilled off more of the obtained crude product was crystallized from acetonitrile to give the halides.
[0080] placed in a 20L reaction vessel above halide, 0.8 times in mass n-butyl lithium halide, eight times the mass of the halide in diethyl ether, heated to 50 ° C, so that a nucleophilic substitution reaction . The reaction time is to be after 2h, the reaction was stopped, reaction was complete and extracted with ethylacetate three times, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate 5h, the resulting crude product was recrystallized from acetonitrile to obtain doxepin.
[0081] 20L is placed in a pressure reactor above doxepin, 1.2 times the mass of material in the doxepin hydrochloride (concentration of 38wt%), the control pressure to 3 ~ 4MPa, and heated to 150 ° C , and among the responses. Time after to be reacted for 16 h, cooled to room temperature and should be finished by filtration, and dried to give doxepin hydrochloride. In this embodiment overall yield 41.6%, measured by HPLC obtaining 99.7% purity.
[0082] Example 5
[0083] placed in a 20L reaction vessel acetonitrile, o-methylbenzoic acid, N- bromosuccinimide, using a water bath temperature controlled at 15 ° C, the reaction 2. 5h under stirring. A known separation method, separation of o-bromomethyl-benzoic acid.
[0084] placed in a 20L reaction vessel o-bromomethyl benzoic acid, diatomaceous earth in an amount of load of cesium fluoride 0.05 ~ 0.15 (in mass Compound J is 1 meter), in an amount of 2. 5-8 acetonitrile (compound J as a mass basis), and the temperature was adjusted to 30 ~ 50 ° C, 12 ~ 20h at reflux with stirring under regulation. Then, a known means for separating the reaction phthalide.
After [0085] phthalide placed in 20L reaction vessel, 5 an amount of sodium methoxide in ethanol solvent (total mass of phenol phthalide and 1 meter), adjusting the temperature of the reaction solution was 55 ° C, was added dropwise start was 1.08 mass of phenol (mass was phthalide 1 meter), dropwise over lh.After the dropwise addition, the reaction temperature after 3h using known separation methods, to give o-methyl benzyl phenyl ether, this compound is named I.
[0086] Anhydrous aluminum above compound I, in an amount of 25% of the chloride (compound I mass is 100% basis), in an amount of DMS0 5 (in compound I is a mass basis) into a reaction vessel , the temperature was adjusted to 100 ° C.The reaction time is to be 8h. Using known separation means for separating the 6, 11-dihydro-dibenzo [b, e] oxepin-11-one.
[0087] placement 6, 11-dihydro-dibenzo in a reaction vessel and 20L [b, e] oxepin-11-one, 1.2-dihydro-fold of the mole of diphenyl at 6, 11 and [ b, e] oxepin-11-one 3-chloropropyl alkyl tert-butyl ether, 2.2 times the mass in 6, 11-dihydro-dibenzo [b, e] oxepin-11-one of magnesium, taking all fifths THF (5 to 7 times the mass in 6, 11-dihydro-dibenzo [b, e] THF oxepin-11-one) is to make, and heated to 38 ° C reaction.After the reaction started, the remaining 3/5 of THF was added dropwise. Was added dropwise to the system to be completed into hydrogen, reflux. When the total reaction 2h, the reaction was stopped. After the system was cooled and then poured into saturated ammonium chloride solution, extracted twice with ethyl acetate was added, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate 5h, the resulting crude product was recrystallized from acetonitrile to give hydroxy compound.
[0088] placed in a 20L reaction vessel above hydroxy compound, an ethanol solution of 2 times the mass of hydroxy compound class of sodium hydroxide (concentration of 40wt%), was heated to 70 ° C, the reaction was stopped after the elimination reaction 2h, cooling, the solvent was distilled off more of the obtained crude product was crystallized from acetonitrile to give the olefinic compounds.
[0089] placed in a 20L reaction vessel of the olefin compound, an aqueous solution of 1.5-fold increase in the mass of hydroiodic olefinic compounds (concentration of 15wt%), and heated to 50 ° C, so nucleophilic substitution reaction. The reaction time is to be after 4h, the reaction was stopped, cooled, the solvent was distilled off more of the obtained crude product was crystallized from acetonitrile to give the halides.
[0090] placed in a 20L reaction vessel above halide, 0.4 times the mass of the halide in n-butyl lithium, 2 to 8 times the mass of the halide in diethyl ether, heated to 45 ° C, so that nucleophilic Substitution reaction. The reaction time is to be after 3h, the reaction was stopped, reaction was complete and extracted with ethylacetate three times, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate 5h, the resulting crude product was recrystallized from acetonitrile to obtain doxepin.
[0091] 20L is placed in a pressure reactor above doxepin, 1.12 times the mass of material in the doxepin hydrochloride (mass concentration 37. 6wt%), the control pressure to 3 ~ 4MPa, heated to 140 ° C, allowing the reaction among. Time after to be reacted for 20 h, cooled to room temperature and should be finished by filtration, and dried to give doxepin hydrochloride. In this embodiment overall yield 43.9%, measured by HPLC obtaining 99.9% purity.
PATENTS
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Sinequan, many others[2] |
| Synonyms | NSC-108160[3] |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682390 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
By mouth, topical, intravenous, intramuscular injection[1] |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 13–45% (mean 29%)[5][6] |
| Protein binding | 76%[7] |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (CYP2D6, CYP2C19)[4][5] |
| Metabolites | Nordoxepin, glucuronide conjugates[4] |
| Elimination half-life | Doxepin: 8–24 hours (mean 17 hours)[7] Nordoxepin: 31 hours[7] |
| Excretion | Urine: ~50%[4][5] Feces: minor[5] |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H21NO |
| Molar mass | 279.376 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
- Virtanen R, Iisalo E, Irjala K: Protein binding of doxepin and desmethyldoxepin. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh). 1982 Aug;51(2):159-64. [PubMed:7113722]
- Virtanen R, Scheinin M, Iisalo E: Single dose pharmacokinetics of doxepin in healthy volunteers. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh). 1980 Nov;47(5):371-6. [PubMed:7293791]
- Negro-Alvarez JM, Carreno-Rojo A, Funes-Vera E, Garcia-Canovas A, Abellan-Aleman AF, Rubio del Barrio R: Pharmacologic therapy for urticaria. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 1997 Jan-Feb;25(1):36-51. [PubMed:9111875]
- Sansone RA, Sansone LA: Pain, pain, go away: antidepressants and pain management. Psychiatry (Edgmont). 2008 Dec;5(12):16-9. [PubMed:19724772]
- Kirchheiner J, Meineke I, Muller G, Roots I, Brockmoller J: Contributions of CYP2D6, CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 to the biotransformation of E- and Z-doxepin in healthy volunteers. Pharmacogenetics. 2002 Oct;12(7):571-80. [PubMed:12360109]
- ZONALON® (doxepin hydrochloride) CREAM, 5% [Link]
- FDA Label: SilenorTM (doxepin) tablets for oral administration [Link]
//////////////Doxepin, ドキセピン , NSC-108160 , P-3693A , SO-101
[H]C(CCN(C)C)=C1C2=CC=CC=C2COC2=CC=CC=C12
N,N-Dimethyldibenz[b,e]oxepin-D11(6H),
USP Doxepin Hydrochloride RS.
USP Doxepin Related Compound A RS
 .
. USP Doxepin Related Compound B RS
 .
. USP Doxepin Related Compound C RS.
Identification—
Related compounds—
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography ![]() 621
621![]() )— The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 215-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains 5-µm packing L1. The flow rate is about 1 mL per minute. The column temperature is maintained at 30
)— The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 215-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains 5-µm packing L1. The flow rate is about 1 mL per minute. The column temperature is maintained at 30![]() . Chromatograph about 20 µL of the Standard solution, and record the peak areas as directed for Procedure: the resolution, R, between doxepin related compound A and doxepin related compound C is not less than 1.5; the resolution between doxepin related compound C and doxepin related compound B is not less than 1.5; and the signal-to-noise ratio for all the peaks is not less than 10. [NOTE—Use the approximate relative retention times given in Table 1 for the purpose of peak identification. The doxepin related compound C peak will be the largest peak in the Standard solution chromatogram.]
. Chromatograph about 20 µL of the Standard solution, and record the peak areas as directed for Procedure: the resolution, R, between doxepin related compound A and doxepin related compound C is not less than 1.5; the resolution between doxepin related compound C and doxepin related compound B is not less than 1.5; and the signal-to-noise ratio for all the peaks is not less than 10. [NOTE—Use the approximate relative retention times given in Table 1 for the purpose of peak identification. The doxepin related compound C peak will be the largest peak in the Standard solution chromatogram.]
| Name | Relative Retention Time (RRT) |
Limit (%) |
| Doxepin related compound A | 0.48 | 0.10 |
| Doxepin related compound C | 0.55 | 0.20 |
| Doxepin related compound B | 0.63 | 0.10 |
| Doxepin hydrochloride | 1.0 | — |
| Unknown impurity | — | 0.10 each |
Procedure— Inject a volume (about 20 µL) of the Test solution into the chromatograph, record the chromatogram for up to 2.2 times the retention time of doxepin, and measure the peak responses. Calculate the percentage of each individual doxepin related compound in the portion of Doxepin Hydrochloride taken by the formula:
in which rU is the individual peak response for each doxepin related compound obtained from the Test solution; rS is the response of the corresponding peak in theStandard solution; CS is the concentration, in mg per mL, of each doxepin related compound in the Standard solution; and CT is the concentration, in mg per mL, of Doxepin Hydrochloride in the Test solution. The related substance limits are listed in Table 1. [NOTE—Discard any peak with a relative retention time less than 0.25. This method is not intended to resolve the E- and Z-isomers of doxepin hydrochloride. Minor variations in the mobile phase composition could result in a shoulder in the trailing edge of doxepin. In cases where there may be separation, both the E- and Z-isomers should be used in the appropriate calculations.] Use the response of the doxepin peak obtained from the Standard solution and the concentration of doxepin hydrochloride in the Standard solution to calculate the percentage of unknown individual impurities.
Assay—
Procedure— Separately inject equal volumes (about 20 µL) of the Standard preparation and the Assay preparation into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the responses for the major peaks. Calculate the quantity, in mg, of C19H21NO·HCl in the portion of Doxepin Hydrochloride taken by the formula:
in which C is the concentration, in µg per mL, of USP Doxepin Hydrochloride RS in the Standard preparation, and rU(Z) and rU(E) are the respective peak responses of the (Z)- and (E)-isomers obtained from the Assay preparation, and rS(Z) and rS(E) are the respective peak responses of the (Z)- and (E)-isomers obtained from the Standard preparation. Calculate the percentage of the (Z)-isomer in the Assay preparation taken by the formula:
in which WS is the weight, in mg, of USP Doxepin Hydrochloride RS in the Standard preparation, WT is the weight, in mg, in the portion of Doxepin Hydrochloride taken, and PZ is the labeled percentage of (Z)-isomer in USP Doxepin Hydrochloride RS. Similarly calculate the percentage of (E)-isomer in the Assay preparationtaken by the formula:
in which PE is the labeled percentage of (E)-isomer in USP Doxepin Hydrochloride RS.
Auxiliary Information— Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
| Monograph | Ravi Ravichandran, Ph.D. Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8330 |
(MDPP05) Monograph Development-Psychiatrics and Psychoactives |
| Reference Standards | Lili Wang, Technical Services Scientist 1-301-816-8129 RSTech@usp.org |
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 32(2) Page 330
Chromatographic Column—