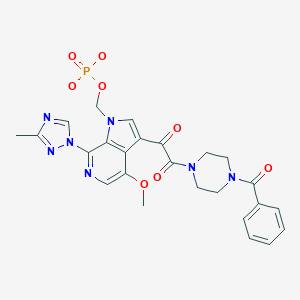
FOSTEMSAVIR ,фостемсавир , فوستيمسافير , 磷坦姆沙韦 ,ホステムサビル;
Fostemsavir
GSK3684934
CAS 864953-29-7
- Molecular FormulaC25H26N7O8P
- Average mass583.490 Da
- ホステムサビル;
[3-[2-(4-benzoylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-oxoacetyl]-4-methoxy-7-(3-methyl-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-1-yl]methyl dihydrogen phosphate
- BMS 663068
- BMS663068
- Fostemsavir tromethamine
- UNII-2X513P36U0

Fostemsavir tromethamine [USAN],
CAS 864953-39-9,
MW 704.6303
Prodrug of BMS-626529, an HIV-1 attachment inhibitor.

Fostemsavir (GSK3684934/BMS-663068) is an experimental HIV entry inhibitor and a prodrug of temsavir (BMS-626529). It is under development by [ViiV Healthcare / GlaxoSmithKline]] for use in the treatment of HIV infection. By blocking the gp120 receptor of the virus, it prevents initial viral attachment to the host CD4+ T cell and entry into the host immune cell; its method of action is a first for HIV drugs.[1] Because it targets a different step of the viral lifecycle, it offers promise for individuals with virus that has become highly resistant to other HIV drugs.[2] Since gp120 is a highly conserved area of the virus, the drug is unlikely to promote resistance to itself via generation of CD4-independent virus.[3]


Example 6Preparation of Compound I from Compound D′ (Example 5)
N-Benzoylpiperazine HCl, Compound Db, (11.73 g, 51.74 mmol) was added to a mixture of Compound D′ (14.83 g, 47.03 mmol) (prepared in Example 5) in dry THF (265 mL) and dry DMF (29.5 mL). NaOt-Bu, 30% w/w (52.3 mL, 147 mmol) was added dropwise (30 min.) keeping the temperature at 17-21° C. The resulting yellow slurry was stirred at 17-20° for 1 h more, then cooled to about 5° C. The mixture was slowly poured into cold water (90 mL) and the flask rinsed with additional water (10 mL). The pH of the resulting yellow solution was adjusted to 6-7 with slow addition (˜20 min., 5-12° C.) of 1 N HCl (105 mL). The resulting slurry was warmed and stirred at room temperature for 1.5 h. The slurry was filtered and the cake washed with water (2×60 mL) then dried in vacuo at 65-70° C. for 5 h giving 18.4 g Compound I as a white solid (82.6%), HPLC AP 99.4. 1H NMR (400 MHz, d6-DMSO): δ 2.48 (s, 3H), 3.43 (b, 4H), 3.67 (b, 4H), 3.99 (s, 3H), 7.45 (s, 5H), 7.88 (s, 1H), 8.24 (s, 1H), 9.22 (s, 1H), 12.39 (s, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, d6-DMSO): 13.85, 40.65, 45.22, 56.85, 114.19, 121.02, 122.78, 123.65, 127.06, 128.42, 129.61, 129.70, 135.51, 138.59, 142.18, 149.23, 161.38, 166.25, 169.30, 185.51.
If necessary, the product could be further purified by recrystallization from acetic acid-water-ethanol, ethanol-water, or acetone-water. For example: A mixture of Compound I (25.0 g), glacial acetic acid (260 mL) and DI water (13.8 mL) was heated to 80° C. and held with stirring (overhead) until a solution was obtained (40 min.). The batch was cooled to 70° C. and seeded (0.5 g). With slow agitation (100 rpm), EtOH (300 mL) was added slowly (1 h), keeping the temperature at 70° C. The resulting slurry was kept at 70° C. for 1 h more with very slow stirring. The slurry was cooled to 20° C. over 2 hours and held at 20° C. for over 4 hours. The slurry was filtered, the wet cake washed with EtOH (125 mL), and the solid dried in vacuo at 70° C. (≧16 h), giving 22.6 g Compound I as a white solid (88.4%).

The development of a short and efficient synthesis of a complex 6-azaindole, BMS-663068, is described. Construction of the 6-azaindole core is quickly accomplished starting from a simple pyrrole, via a regioselective Friedel–Crafts acylation, Pictet–Spengler cyclization, and a radical-mediated aromatization. The synthesis leverages an unusual heterocyclic N-oxide α-bromination to functionalize a critical C–H bond, enabling a highly regioselective copper-mediated Ullmann–Goldberg–Buchwald coupling to install a challenging triazole substituent. This strategy resulted in an efficient 11 step linear synthesis of this complex clinical candidate

Attachment inhibitor BMS-663068 is currently in clinical development for the treatment of HIV infection. Key steps in the synthesis depicted are (1) a radical-mediated redox-aromatization to generate the 6-azaindole (B → C) and (2) the regioselective bromination of an N-oxide using PyBroP (D → E).
High regioselectivity was observed in the copper(I)-mediated Ullmann–Goldberg–Buchwald coupling (H → K) using the diamine ligand J (N1/N2 = 22:1), whereas a thermal SNAr reaction gave N1/N2 = 1:1. Alternative conditions for the bromination of the N-oxide D led mainly to deoxygenation.
………………………………….
http://www.google.com/patents/US20050209246
Preparation of Compound IVc
Procedure: To a solution of the acid 6-81 (3.01 g, 10 mmol) and benzoylpiperazine hydrochloride (3.39 g, 15 mmol) in DMF (50 mL) was added triethylamine (10.1 g, 100 mmol, 10 eq.), followed by 1-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC; 5.75 g, 30 mmol) under N2 and the mixture stirred at room temperature for 22 h after sonication and at 40° C. for 2 h. The mixture was concentrated in vacuo to remove DMF and TEA, and to the residual solution was added water (200 mL) under stirring and sonication. The precipitates formed were collected, washed with water and dried in vacuo to obtain 2.8 g (5.9 mmol, Y. 59%) of the title compound IVc as off-white solid. The filtrate was extracted with CH2Cl2 (x2). The CH2Cl2 extracts were dried (Na2SO4), filtered and concentrated to gum which was triturated with Et2O to obtain a solid. This solid was suspended and triturated with MeOH to obtain 400 mg of the title compound IVc as off-white solid. Total yield: 3.2 g (6.8 mmol, Y. 68%): MS m/z 474 (MH); HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C24H24N7O4 (M+H) 474.1890, found 474.1884 (Δ-1.2 ppm); 1H NMR (DMSO-d6) δ ppm 2.50 (3H, s, overlapped with DMSO peaks), 3.43 (4H, br, CH2N), 3.68 (4H, br, CH2N), 3.99 (3H, s, CH3O), 7.46 (5H, br. s, Ar—Hs), 7.88 (1H, s, indole-H-5), 8.25 (1H, s, indole-H-2), 9.25 (1H, s, triazole-H-5), 12.40 (1H, s, NH); 13C-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ ppm 13.78 ,40.58, 45.11, 56.78, 114.11, 120.95, 122.71, 123.60, 126.98, 128.34, 129.6, 135.43, 138.52, 142.10, 149.15, 161.29, 166.17, 169.22, 185.42; UV (MeOH) λ max 233.6 nm (ε 3.43×104), 314.9 nm (ε 1.73×104); Anal: Calc for C24H24N7O4.1/5H2O; C, 60.42; H, 4.94; N, 20.55, Found; C 60.42, H 5.03, N 20.65; KF (H2O) 0.75%.
This reaction can also be performed by use of HATU and DMAP to provide more consistent yield of the title compound: To a suspension of the acid 6-81 (15.6 mmol) and HATU [O-(7-azabenzotriazol-1-yl)-N,N,N′,N′-tetramethyluronium hexafluorophos phonate] (8.90 g, 23.4 mmol; 1.5 eq.) in DMF (60 mL) and CH2Cl2 (60 mL) was added a mixture of DMAP (5.72 g, 46.8 mmol, 3 eq.) and benzoylpiperazine hydrochloride (5.30 g, 23.4 mmol; 1.5 eq.) in DMF (60 mL) at room temperature and the mixture was stirred under nitrogen atmosphere for 4 hrs. The mixture was concentrated in vacuo to remove CH2Cl2 and most of DMF, and to the residual solution was added water under stirring and sonication. The precipitates formed were collected, washed with water and dried in vacuo to obtain 5.38 g (11.4 mmol, Y. 72.8%) of the title compound IVc as off-white solid: HPLC >95% (AP, uv at 254 nm)
EXAMPLE 5Preparation of Ica, (Disodium Salt)
General Procedure: A suspension of IVc (0.24 g, 0.5 mmol) in anhydrous THF (4 mL) under nitrogen atmosphere was treated with sodium hydride (60% oil dispersion, 0.08 g, 2.0 mmol), and stirred until gas evolution ceased (approximately 5 minutes). The reaction mixture was treated with iodine (0.13 g, 0.5 mmol) and stirred for 2-3 minutes followed by addition of di-tert-butyl chloromethyl phosphate (1.6 g, 6.0 mmol, crude). A stream of nitrogen was allowed to pass over the reaction to facilitate the removal of much or all of the THF. The reaction mixture was stirred overnight. HPLC analysis of crude indicated starting IVc (ca. 56%) and desired adduct (ca. 32%).
Several crude reaction mixtures (a total of 6.7 mmol based on starting material IVc) were re-dissolved in dichloromethane, combined, concentrated in vacuo to remove any remaining THF. The residue was suspended in dichloromethane and TFA (1:1, approximately 40 mL total volume). The mixture was stirred for 1.5-2 hours and then solvent was removed in vacuo. The residue was suspended in dichloromethane and extracted into water (approximately 60 mL) made weakly basic with solid or aqueous sodium bicarbonate. The aqueous layer was reduced in volume by rotary evaporator if required and the solution was loaded onto a C-18 reverse phase column (approximately 80 g of C-18, YMC ODS-Aq, 50 micron) and eluted with water, followed by water containing 2.5% acetonitrile. Fractions containing pure product were pooled and organic solvent was removed by rotary evaporator. Purified product was recovered after lyophilization to give 1.00 g (1.30 mmol, 19% over 2 steps) of the title compound Ica (disodium salt) as an off-white powder: HPLC purity>99% AP at 254 nm (gradient 0-100% B/A; A 10% CH3CN-90% H2O-0.1% TFA, B 90% CH3CN-10% H2O-0.1 % TFA, gradient time 4 min, column YMC ODS-Aq 4.6×50 mm 3 micron); MS-ESI— m/z 482 (M−H minus 2Na)−; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C25H27N7O8P (M+H minus 2Na)+584.1659, found 584.1651 (Δ-1.3 ppm); 1H NMR (D2O, 500 MHz) δ ppm 2.53, 2.54 (3H, 2s), 3.56 (2H, s, CH2N), 3.72 (2H, br.s, CH2N), 3.78, 3.83 (2H, 2br.s, CH2N), 3.94, 3.96 (2H, 2br.s, CH2N), 4.14 (3H, s, CH3O), 5.38, 5.40 (2H, 2d, J=11 Hz), 7.45-7.59 (5H, m, Ar—Hs), 8.07, 8.09 (1H, 2s, indole-H-5), 8.64, 8.67 (1H, 2s, indole-H-2), 8.87, 8.89 (1H, 2s, triazole-H-5); 13C NMR (125.7 MHz, D2O) δ ppm 15.43 (N-Me), 44.03, 44.47, 44.66, 45.05, 48.20, 48.82, 49.60, 50.23, 59.78 (OMe), 75.81 (NCH2O), 115.6, 126.0, 127.2, 129.6, 131.0, 131.7, 132.1, 133.5, 136.8, 147.6, 150.1, 154.2, 164.8, 170.4, 175.8, 189.2; UV (H2O) λmax 220 nm (ε 3.91×104), 249 nm (ε 2.00×104), 303 nm (ε 1.60×104); Anal: Calc for C25H24N7O8PNa2. 8H2O. 0.2NaHCO3; C, 38.39; H, 5.14; N, 12.44, P, 3.93, Na, 6.42 Found; C, 38.16; H, 4.81; N, 12.43, P, 3.72, Na, 6.05; KF (H2O) 17.3%. A less pure fractions were collected to obtain 0.22 g (0.29 mmol, Y. 4%) of the title compound Ica (disodium salt): HPLC purity>95% (AP at 254 nm).
EXAMPLE 7Preparation of Crystalline Ic (Free Acid Mono-Hydrate)
To a mixture of IVc (600 mg, 1.27 mmol) in anhydrous THF (10 ml) in an oven-dried round bottle flask under nitrogen at r.t. was added NaH (153 mg, 6.38 mmol, dry powder, 95%), and the white suspension stirred until no gas evolution was observed. The mixture was then added I2 (375 mg, 1.48 mmol), and stirred at r.t. for 3 h. To the reaction mixture was added NaH (153 mg, 6.38 mmol, dry powder, 95%), and the mixture stirred for about 5 to 10 min. The crude chloromethyl di-tert-butylphosphate (2.0 g, about 1.6 ml, 7.79 mmol) was added to the mixture, which was then stirred at r.t. for 15 h. LCMS analysis of the reaction showed a >97% conversion of the starting material. After evaporation of the volatiles, the residue was added CH2Cl2 (10 ml), cooled in an ice-water bath, slowly added TFA (10 ml) and stirred at r.t. for 3 h. The reaction mixture was then evaporated, and the residue partitioned between CH2Cl2 (50 ml) and H2O (50 ml). The CH2Cl2 layer was poured into the reaction flask that contained some undissolved brownish solid, and this mixture was extracted with a dilute aqueous NaHCO3 solution (50 ml). The aqueous mixture was purified by reverse phase preparative HPLC (solvent A: 10% MeOH-90% H2O-0.1% TFA; solvent B: 90% MeOH-10% H2O-0.1% TFA; start % B=0, final % B=100; gradient time=6 min; flow rate=45 ml/min; column: phenomenex-Luna 30×50 mm, S5; fraction collected: 3.65 to 4.05 min). The fractions collected were evaporated to dryness, and the residue dried under high vacuum to obtain the acid Ic as a pale yellow solid (356.6 mg); 1H NMR: (500 MHz, CD3OD) δ 9.05 (s, 1H), 8.46 (s, 1H), 8.04 (s, 1H), 7.47 (b s, 5H), 5.93 (d, J=12, 2H), 4.10 (s, 3H), 4.00-3.40 (b s, 8H), 2.53 (s, 3H); 19F NMR analysis showed that the material contained residual TFA, (the percentage was not quantified); Analytical HPLC method: Start % B=0, Final % B=100, Gradient time=2 min, Flow Rate=5 mL/min, Column: Xterra MS C18 7u 3.0×50 mm, LC/MS: (ES+) m/z (M+H)+=584, HPLC Rt=0.983.
172.2 mg of the purified acid Ic was dissolved in 1 ml of H2O and then about 0.3 ml of absolute EtOH (200 proof) was added. The mixture was left standing in a refrigerator (temperature about 3° C.) overnight, after which time, crystalline material was observed. The mixture was then warmed to ambient temperature, diluted with H2O to a volumn of 3 mL, and then 20 mL of MeCN was added slowly. Following the completion of addition, the mixture was stirred at r.t. for 2 h and then filtered. The solid collected (90 mg) was dried in vacuo, and then under high vacuum. This material was shown by powder x-ray studies to be crystalline; Elemental Analysis calculated for C25H26N7O8P.H2O: C 49.92; H 4.69; N 16.30; observed: C 49.66; H 4.62; N 15.99; mp=205° C. (measured by differential scanning calorimetry). The 1H NMR pattern for crystalline material was compared with that from the purified acid and both were consistent with the structure.
EXAMPLE 10Preparation of Icb (mono tromethamine salt): [3-[(4-benzoylpiperazin-1-yl)(oxo)acetyl]-4-methoxy-7-(3-methyl-1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-1H-pyrrolo[2, 3-c]pyridin-1-yl]methyl dihydrogen phosphate, 2-amino-2-(hydroxymethyl)propane-1,3-diol salt (1:1). The sequence of reactions is described in Scheme for Example 10.
Scheme for Example 10
Preparation of di-tert-butyl chloromethyl phosphate
A mixture of tetrabutylammonium di-tert-butyl phosphate (57 g, 0.126 mol, Digital Specialty Chemicals) and chloroiodomethane (221 g, 1.26 mol) was stirred at room temperature for four hours before the volatiles were removed under vacuum. 500 ml of ethyl ether was added to the residue and insoluble solid was filtered away. Concentration of the filtrate in vacuo and removal of remaining volatiles using a vacuum pump provided di-tert-butyl chloromethyl phosphate as a light brown or yellow oil, which was utilized in the next step without further purification.
Preparation of IIc: (3-(2-(4-benzoylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-oxoacetyl)-4-methoxy-7-(3-methyl-1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-1-yl)methyl di-tert-butyl phosphate
NaH (2.6 g, 10.3 mmol, 95% in oil, Seq.) was added slowly into a suspension of IVc (10.0 g, 21.1 mmol) in dry THF (100 ml) and the mixture was allowed to stir for 0.5 hour at room temperature. A solution of iodine (5.27 g, 20.8 mmol) dissolved in dry THF (10 ml) was added slowly into the stirring solution at a rate which prevented foaming or a violent reaction. The resultant mixture was stirred for an additional 3 hours before a second 2.6 g portion of NaH was introduced. After 15 minutes at ambient temperature di-tert-butyl chloromethyl phosphate, the entire batch of di-tert-butyl chloromethyl phosphate, obtained from step one, was added. After stirring for 16 hours, the reaction mixture was poured into iced NH4OAc (30%) (120 ml), followed by extraction with EtOAc (3×300 ml). The combined organic extracts were washed with water (100 ml) and then brine (100 ml), dried over Na2SO4, and concentrated under vacuum to afford a residue, which was purified by silica gel chromatography (elution with EtOAc/Et3N (50/1) and then EtOAc/MeOH (100/1)) to give 8.0 g (˜75% AP, ˜41% yield) of diester IIc as a light yellow solid.
1H NMR (500 MHz, CD3OD) δ8.82 (s, 1H), 8.41 (s, 1H), 8.04 (s, 1H), 7.47 (b, 5H), 6.00 (d, 2H, J=14.5 Hz), 4.10 (s, 3H), 4.00-3.40 (b, 8H), 2.49 (s, 3H), 1.28 (s, 18H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CD3OD) δ18.6, 176.4, 172.9, 168.0, 162.6, 152.6, 147.5, 144.0, 136.5, 131.5, 130.8, 129.9, 129.1, 128.3, 126.1, 124.0, 116.2, 85.8, 75.4, 61.6, 57.7, 30.1, 22.2, 13.7; HRMS m/z: (M+H)+ calcd for C33H43N7O8P 696.29, found 696.34.
Preparation of Icb (mono L tromethamine salt): [3-[(4-benzoylpiperazin-1-yl)(oxo)acetyl]-4-methoxy-7-(3-methyl-1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-1-yl]methyl dihydrogen phosphate, 2-amino-2-(hydroxymethyl)propane-1,3-diol salt (1:1)
500 mg (˜p75 AP, 0.54 mmol) of diester IIc was dissolved in a mixture of water (2.5 ml) and acetone (2.5 ml). The resulting mixture was stirred at 40° C. for 16 hours to complete the solvolysis. To this reaction mixture was added 3.0M aqueous TRIS (mono tromethamine) solution to adjust pH to 3.32. Acetone (30 ml) was slowly added to the reaction mixture in 1 hour.* After complete addition of acetone, the solution was stirred overnight to complete the crystallization of Icb. The solid was collected by filtration and rinsed with 20:1 acetone-water (2×5 mL). The white crystalline solid was dried under house vacuum under nitrogen atomosphere at 50° C. for 24 h to afford 290 mg of Icb (>98.5 AP).
*After adding about 15 and 20 ml of acetone, the reaction mixture was seeded with crystalline Icb.
Icb obtained in the above operation: 1H NMR (500 MHz, CD3OD) δ8.83 (s, 1H), 8.52 (s, 1H), 8.02 (s, 1H) 7.49 (b, 5H), 5.469 (d, 2H, J=13 Hz), 4.11 (s, 3H), 4.00-3.40 (m, 8H), 3.66 (s, 6H), 2.50 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CD3OD) δ185.6, 171.9, 167.4, 161.4, 151.7, 146.9, 143.8, 135.4, 130.3, 129.7, 128.8, 127.2, 124.9, 122.6, 114.3, 73.5, 61.8, 59.9, 56,5, 46.0, 41.7, 12.6. HRMS m/z: (M-trisamine+H)+ calcd for C25H27N7O8P 584.1659, found 584.1664. Anal. Calcd. C, 49.43; H, 5.29; N, 15.90; P, 4.39; found: C, 49.18; H, 5.38; N, 15.59; P, 4.26. Melting Point 203° C.
Obtained via other process (hydrolysis with TFA in methylene chloride), salt Icb is ˜1 molar mono tromethamine salt with 0.47% of water, 0.1% of acetone and 0.05% of methanol. 1H NMR (500 MHz, d6-DMSO, 30° C.) δ8.77 (s, 1H), 8.48 (s, 1H), 8.00 (s, 1H) 7.44 (b, 5H), 5.42 (d, 2H, J=15 Hz), 4.02 (s, 3H), 3.70-3.30 (m, 8H), 3.41 (s, 6H), 2.38 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3, 30° C.) δ184.8, 169.0, 165.8, 160.3, 150.4, 146.2, 143.2, 135.4, 129.4, 128.9, 128.2, 127.7, 126.9, 123.2, 122.2, 112.9, 72.3, 60.7, 59.0, 56.7, 13.4. MS m/z: (M-trisamine+H)+ calcd for C25H27N7O8P 584.2, found 584.0. Anal. Calcd. C, 49.11; H, 5.37; N, 15.76; P, 4.32; found: C, 48.88; H, 5.28; N, 15.71; P, 4.16. M.P. 201-205° C.
EXAMPLE 13Alternate preparation of Icb (Pro-drug of IVc)
To a 10 L reactor equipped with an overhead stirrer, thermocouple, distillation apparatus, and nitrogen inlet was charged IVc (200.00 g, 422.39 mmol), Cs2CO3 (344.06 g, 1.06 mol), KI (140.24 g, 844.81 mmol) and NMP (1.00 L, 10.38 mol). The reaction was stirred at room temperature resulting in a light brown heterogeneous suspension. Di-tert-butyl chloromethyl phosphate (273.16 g, 1.06 mol) was added via addition funnel and the reaction mixture was heated to 30° C. for 16-24 hours with stirring after which time the reaction was cooled to 5° C. To the reaction was added DCM (1.5 L) then the reaction was slowly quenched with water (3.5 L) maintaining the reaction temperature under 20° C. resulting in a biphasic mixture. The product rich bottom layer was separated, washed with water (3.5 L×3), then transferred back to the reactor. The solution was concentrated under vacuum to a volume of 1 L keeping the temperature below 25° C. IPA was added (2 L) then the reaction was concentrated under vacuum to a volume of 2 L keeping the temperature below 25° C. The reaction was then seeded with IIc (0.200 g), stirred overnight at room temperature resulting in a slurry. The slurry was filtered and the wet cake was washed with MTBE (1 L), dried in a vacuum oven at 50° C. overnight resulting in a yellow/white powder (207.1 g, 70%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.54 (s, 1H), 8.18 (s, 1H), 7.91 (s, 1H), 7.42 (s, 5H), 5.95 (d, J=14.2 Hz, 2H), 4.06 (s, 3H), 3.97-3.36 (m, 8H), 2.50 (s, 3H), 1.27 (s, 18H); 3C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 184.64, 170.65, 165.91, 161.60, 150.82, 145.38, 141.89, 134.96, 130.20, 129.59, 128.68, 127.58, 127.10, 124.77, 122.64, 115.22, 83.90, 83.83, 73.69, 73.63, 56.95, 46.04, 41.66, 29.61, 29.56, 13.90; ES+ MS m/z (rel. intensity) 696 (MH+,10), 640 (MH+-isobutylene, 30), 584 (MH+-2 isobutylene, 100).
To a 10 L 4 neck reactor equipped with a thermocouple, overhead stirrer, condenser and nitrogen inlet was added IIc (200.24 g, 287.82 mmol), acetone (800.00 ml, 10.88 mol) and water (800.00 ml, 44.41 mol). The reaction was heated to 40° C. and stirred for 18-24 hours. The reaction was cooled to 20° C. then tromethamine (33.62 g, 277.54 mmol) was added. The reaction was heated to 40° C. then stirred for an additional hour until all solids were dissolved. The reaction was cooled to 20° C. then filtered through a 10 micron cuno filter into a 10 L 4 neck reactor equipped with a thermocouple, overhead stirrer, and nitrogen inlet. Acetone (3 L) was added rapidly, followed by seeding with Icb (0.500 g), then additional acetone (3 L) was added. The reaction was stirred at room temperature overnight resulting in a slurry then filtered. The wet cake was washed with acetone (800 ml) then dried in a vacuum oven at 50° C. overnight resulting in a fluffy white powder (165.91 g, 82%).
Supplementary Information:
Isolation of the Free-Acid Intermediate IC:
In a 250 mL 3 neck reactor equipped with a thermocouple, overhead stirrer, condenser and nitrogen inlet was added IIc (10.0 g, 14.37 mmol), acetone (40.00 ml, 544.15 mmol) and water (40.00 ml, 2.22 mol). The reaction was heated to 40° C. and stirred for 14-24 hours. The reaction was cooled to 20° C. then stirred for three hours, resulting in a slurry. The slurry was filtered, then the wet cake washed with acetone (40.00 ml) then dried in a vacuum oven at 50° C. overnight resulting in a fluffy white powder (7.00 g, 83%). NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.84 (s, 1H), 8.47 (s, 1H), 8.06 (s, 1H), 7.45 (s, 5H), 5.81 (d, J=12.3 Hz, 2H), 4.03 (s, 3H), 3.91-3.19 (m, 8H), 2.39 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 185.20, 169.32, 165.85, 160.75, 150.51, 146.30, 143.24, 135.53, 129.74, 129.22, 128.46, 127.34, 127.09, 123.67, 122.73, 113.94, 72.90 (d, 2JC-P=5 Hz), 57.01, 45.2 (bs), 40.8 (bs), 13.66. ES+ MS m/z (rel. intensity) 486 (MH+−H3PO4, 100).
References
- ^ HIV Attachment Inhibitor BMS-663068 Looks Good in Early Studies
- ^ HIV attachment inhibitor BMS-663068 shows good safety and efficacy in phase 2b study
- ^ Activity of the HIV-1 attachment inhibitor BMS-626529, the active component of the prodrug BMS-663068, against CD4-independent viruses and HIV-1 envelopes resistant to other entry inhibitors
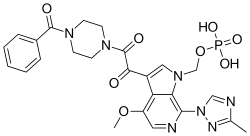 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
{3-[(4-Benzoyl-1-piperazinyl)(oxo)acetyl]-4-methoxy-7-(3-methyl-1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-1-yl}methyl dihydrogen phosphate
|
|
| Other names
BMS-663068, GSK3684934
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| Properties | |
| C25H26N7O8P | |
| Molar mass | 583.498 g·mol−1 |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
////////////////фостемсавир , فوستيمسافير , 磷坦姆沙韦 ,BMS 663068, Fostemsavir, GSK 3684934, PHASE 3, ホステムサビル;
COc1cnc(c2c1c(cn2COP(=O)