Phytomenadione,
PHYTONADIONE, Phylloquinone
| Molecular Formula: | C31H46O2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight: | 450.707 g/mol |
| Optical Rotatory Power | -0.28 ° | Solv: 1,4-dioxane (123-91-1); Wavlen: 589.3 nm; Temp: 25 °C |
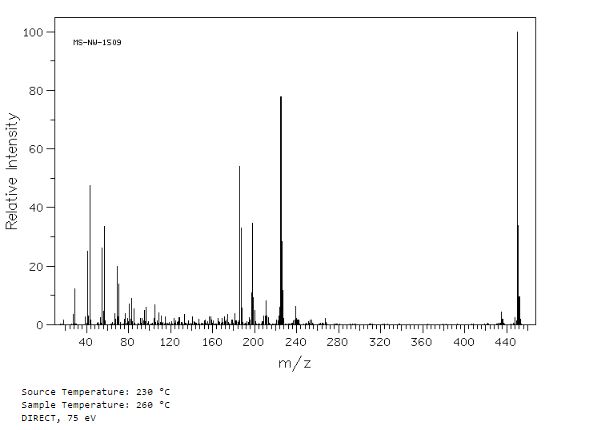
MASS
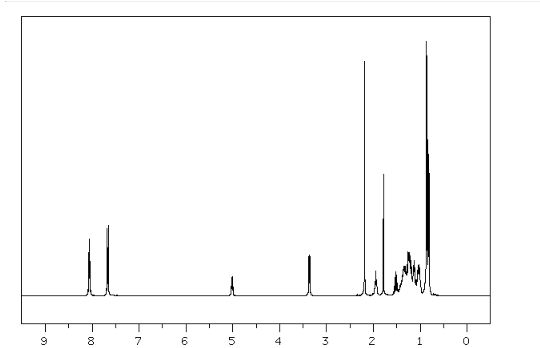
1H NMR
400 MHZ CDCL3
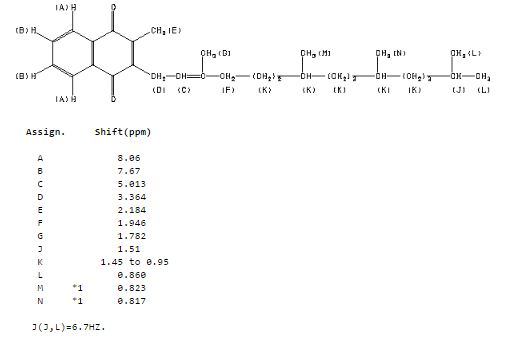
13C NMR
- Murahashi, Shun-ichi; European Journal of Organic Chemistry 2011, VOL2011(27), P5355-5365
- Huang, Zhihong; Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis 2007, VOL349(4+5), PG539-545
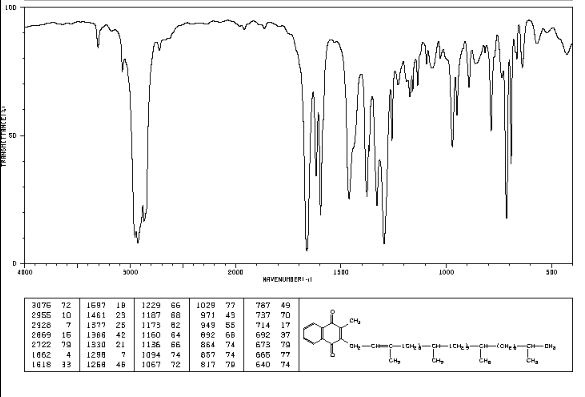
IR LIQ FILM
Phytomenadione, also known as vitamin K1 or phylloquinone, is a vitamin found in food and used as a dietary supplement.[1][2] As a supplement it is used to treat certain bleeding disorders.[2] This includes in warfarin overdose, vitamin K deficiency, and obstructive jaundice.[2] It is also recommended to prevent and treat hemorrhagic disease of the newborn.[2] Use is typically recommended by mouth or injection under the skin.[2] Use by injection into a vein or muscle is recommended only when other routes are not possible.[2] When given by injection benefits are seen within two hours.[2]
Common side effects when given by injection include pain at the site of injection and altered taste.[2] Severe allergic reactions may occur with injected into a vein or muscle.[2] It is unclear if use during pregnancy is safe; however, use is likely okay during breastfeeding.[3] It works by supplying a required component for making a number of blood clotting factors.[2] Found sources include green vegetables, vegetable oil, and some fruit.[4]
Phytomenadione was first isolated in 1939.[5] It is on the World Health Organization’s List of Essential Medicines, the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system.[6] The wholesale cost in the developing world is about 0.11 to 1.27 USD for a 10 mg vial.[7]In the United States a course of treatment costs less than 25 USD.[8] In 1943 Edward Doisy and Henrik Dam were given a Nobel Prizefor its discovery.[5]
Terminology
Phytomenadione is often called phylloquinone or vitamin K,[9] phytomenadione or phytonadione. Sometimes a distinction is made between phylloquinone, which is considered to be a natural substance, and phytonadione, which is considered to be a synthetic substance.[10]
A stereoisomer of phylloquinone is called vitamin k1 (note the difference in capitalization).
Chemistry
Vitamin K is a fat-soluble vitamin that is stable in air and moisture but decomposes in sunlight. It is a polycyclic aromatic ketone, based on 2-methyl–1,4-naphthoquinone, with a 3-phytyl substituent. It is found naturally in a wide variety of green plants, particularly in leaves, since it functions as an electron acceptor during photosynthesis, forming part of the electron transport chain of photosystem I.
Phylloquinone is an electron acceptor during photosynthesis, forming part of the electron transport chain of Photosystem I.
The best-known function of vitamin K in animals is as a cofactor in the formation of coagulation factors II (prothrombin), VII, IX, and X by the liver. It is also required for the formation of anticoagulant factors protein C and S. It is commonly used to treat warfarin toxicity, and as an antidote for coumatetralyl.
Vitamin K is required for bone protein formation.
SYN
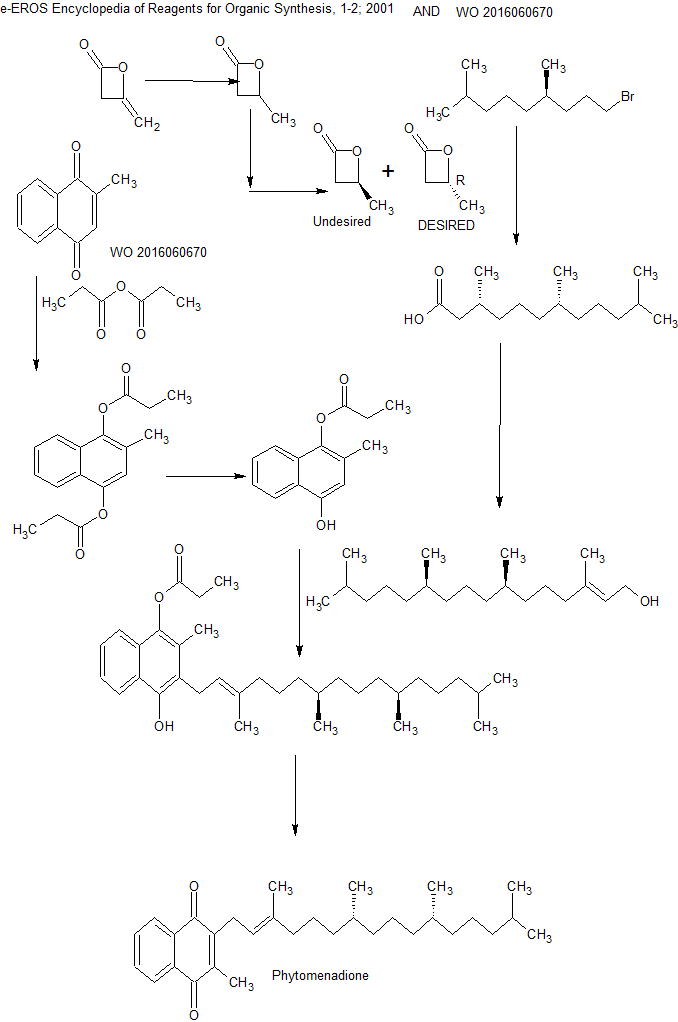
e-EROS Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis, 1-2; 2001
WO2016060670
PAPERS
Helvetica Chimica Acta (1944), 27, 317-19.
PATENT
US 2683176
CN 105399615
WO 2016060670
References
- Jump up^ Watson, Ronald Ross (2014). Diet and Exercise in Cystic Fibrosis. Academic Press. p. 187. ISBN 9780128005880.
- ^ Jump up to:a b c d e f g h i j “Phytonadione”. The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Retrieved 8 December 2016.
- Jump up^ “Phytonadione Use During Pregnancy”. Drugs.com. Retrieved 29 December 2016.
- Jump up^ “Office of Dietary Supplements – Vitamin K”. ods.od.nih.gov. 11 February 2016. Retrieved 30 December 2016.
- ^ Jump up to:a b Sneader, Walter (2005). Drug Discovery: A History. John Wiley & Sons. p. 243. ISBN 9780471899792.
- Jump up^ “WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (19th List)” (PDF). World Health Organization. April 2015. Retrieved 8 December 2016.
- Jump up^ “Vitamin K1”. International Drug Price Indicator Guide. Retrieved 8 December 2016.
- Jump up^ Hamilton, Richart (2015). Tarascon Pocket Pharmacopoeia 2015 Deluxe Lab-Coat Edition. Jones & Bartlett Learning. p. 229. ISBN 9781284057560.
- Jump up^ Haroon, Y.; Shearer, M. J.; Rahim, S.; Gunn, W. G.; McEnery, G.; Barkhan, P. (June 1982). “The content of phylloquinone (vitamin K1) in human milk, cows’ milk, and infant formula foods determined by high-performance liquid chromatography”. J. Nutr. 112 (6): 1105–1117. PMID 7086539.
- Jump up^ “Vitamin K”. Retrieved 2009-03-18.
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Mephyton, others |
| Synonyms | Vitamin K1, phytonadione, phylloquinone |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
by mouth, subQ, IM, IV |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.422 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C31H46O2 |
| Molar mass | 450.70 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
/////////////PHYTONADIONE, фитоменадион ,فيتوميناديون , PHYTONADIONE, Phylloquinone
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
| MELTING POINT | : | Yellow viscous oil (Ref. 0001) |
|
|
||
|
|
||
| REFRACTIVE INDEX | : | n20D=1.5263(Ref. 0010) |
|
|
||
| OPTICAL ROTATION | : | [a]25D=-28 [Table ] (Ref. 0010)  |
|
|
||
| SOLUBILITY | : | Insol in water. Sparingly sol in methanol; sol in ethanol, acetone, benzene, petr ether, hexane, dioxane, chloroform, ether, other fat solvents and in vegetable oils(Ref. 0001) |
| SPECTRAL DATA |
| UV SPECTRA | : | Uv max (petr ether) 242, 248, 260, 269, 325 nm (E1%1cm396, 419, 383, 387, 68) (Ref. 0001). Uv max (ethanol) 243, 248, 262, 270, 330 nm (Ref. 0002). (UV Ref. 0010)Em at 248 nm (EtOH) =18,900 (Ref. 0002/0006).  |
|
|
||
| IR SPECTRA | : | (liquid) : 6.05m (CO), 6.21, 6.28m (aromatic nucleus) (Ref. 0008) (IR Ref. 0010) [Table 0002] (Ref. 0010)  |
|
|
||
| NMR SPECTRA | : | at 60 MHz in CDCl3, i nternal standard Si(CH3)4: multiplet at 453-486 Hz (4 aromatic H), triplet at 302 Hz (J=7 Hz) (olefinic H at C2. , doublet at 201 Hz ) (J=7 Hz) (CH2.-1), singlet at 130 Hz (CH3-2), signal at 107 Hz (trans-methyl group at C3. .(Ref. 0008) ( NMR Ref. 0010) Proton magnetic resonance data   |
|
|
||
| MASS SPECTRA | : | [Spectrum (Ref. 0005) |
| REFERENCES |
| AUTHOR | : | Anonym. (1989) Vitamin K1 in The Merck Index , 11th edition (Budavari, S., O’Neil, M. J., Smith, A., and Heckelman, P.E., eds), pp1580, Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, N. J. |
| TITLE | : | |
| JOURNAL | : | |
| VOL | : | PAGE : – () |
| AUTHOR | : | Dunphy,P.J., and Brodie,A.F. |
| TITLE | : | The structure and function of quinones in respiratory metabolism. |
| JOURNAL | : | Methods in Enzymology |
| VOL | : | 18 PAGE : 407 -461 (1971) |
| AUTHOR | : | Di Mari, S. J., Supple, J. H., and Rapoport, H. |
| TITLE | : | Mass spectra of naphthoquinones. Vitamin K1(20) PubMed ID:5910960 |
| JOURNAL | : | J Am Chem Soc. |
| VOL | : | 88 PAGE : 1226-1232 (1966) |
| AUTHOR | : | Suttie,W.J. (1991) Vitamin K, in Handbook of Vitamins (2nd ed., Machlin,L.J., ed) , pp145-194, Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York |
| TITLE | : | |
| JOURNAL | : | |
| VOL | : | PAGE : – () |
| AUTHOR | : | Kodaka,K., Ujiie,T.,Ueno,T., and Saito,M. |
| TITLE | : | Contents of Vitamin K1 and Chlorophyll in Green Vegetables. |
| JOURNAL | : | J Jpn Soc Nutr Food Sci |
| VOL | : | 39 PAGE : 124 -126 (1986) |
| AUTHOR | : | Mayer,H., and Isler,O . |
| TITLE | : | Synthesis of Vitamin K. |
| JOURNAL | : | Methods in Enzymology |
| VOL | : | 18 PAGE : 491 -547 (1971) |
| AUTHOR | : | Naruta,Y., and Maruyama,K. |
| TITLE | : | Regio- and sterocontrolled polyprenylation of quinones. A new synthetic method of vitamin K series. |
| JOURNAL | : | Chemistry Lett |
| VOL | : | PAGE : 881 -884 (1979) |
| AUTHOR | : | Sommer,P., and Kofler,M. |
| TITLE | : | Physicochemical Properties and Methods of Analysis of Phylloquinones, Menaquinones, Ubiquinones, and Related Compounds. PubMed ID:5340867 |
| JOURNAL | : | Vitamins and Hormones |
| VOL | : | 24 PAGE : 349 -399 (1966) |
| AUTHOR | : | Bristol, J. A., Ratcliffe, J. V., Roth, D. A., Jacobs, M. A., Furie, B. C., and Furie, B. |
| TITLE | : | Biosynthesis of prothrombin: intracellular localization of the vitamin K-dependent carboxylase and the sites of gamma-carboxylation PubMed ID:8839851 |
| JOURNAL | : | Blood. |
| VOL | : | 88 PAGE : 2585-2593 (1996) |
| AUTHOR | : | Usui, Y., Nishimura, N., Kobayashi, N., Okanoue, T., Kimoto, M., and Ozawa, K. |
| TITLE | : | Measurement of vitamin K in human liver by gradient elution high-performance liquid chromatography using platinum-black catalyst reduction and fluorimetric detection PubMed ID:2753953 |
| JOURNAL | : | J Chromatogr. |
| VOL | : | 489 PAGE : 291-301 (1989) |
//////////////














