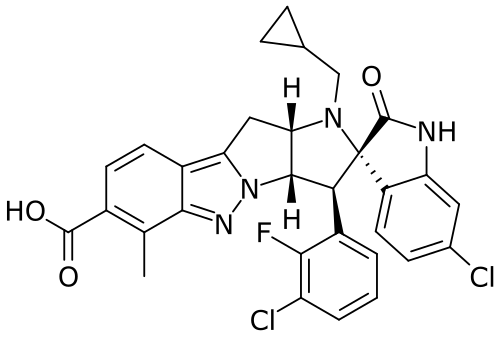
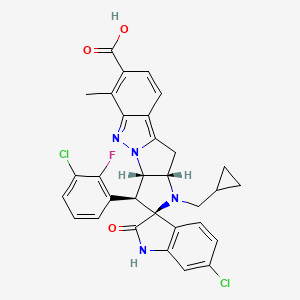
BRIGIMADLIN
Cas 2095116-40-6
WeightAverage: 591.46
Monoisotopic: 590.1287742
Chemical FormulaC31H25Cl2FN4O3
Spiro[3H-indole-3,2′(1′H)-pyrrolo[2′,3′:4,5]pyrrolo[1,2-b]indazole]-7′-carboxylic acid, 6-chloro-3′-(3-chloro-2-fluorophenyl)-1′-(cyclopropylmethyl)-1,2,3′,3′a,10′,10′a-hexahydro-6′-methyl-2-oxo-, (2′S,3′S,3′aS,10′aS)-
(2′S,3′S,3′aS,10′aS)-6-Chloro-3′-(3-chloro-2-fluorophenyl)-1′-(cyclopropylmethyl)-1,2,3′,3′a,10′,10′a-hexahydro-6′-methyl-2-oxospiro[3H-indole-3,2′(1′H)-pyrrolo[2′,3′:4,5]pyrrolo[1,2-b]indazole]-7′-carboxylic acid (
- (3S,10’S,11’S,14’S)-6-chloro-11′-(3-chloro-2-fluorophenyl)-13′-(cyclopropylmethyl)-6′-methyl-2-oxospiro[1H-indole-3,12′-8,9,13-triazatetracyclo[7.6.0.02,7.010,14]pentadeca-1,3,5,7-tetraene]-5′-carboxylic acid
- (3S,3’S,3a’S,10a’S)-6-chloro-3′-(3-chloro-2-fluorophenyl)-1′-(cyclopropylmethyl)-6′-methyl-2-oxo-1,2,3′,3a’,10′,10a’-hexahydro- 1’H-spiro[indole-3,2′-pyrrolo[2′,3′:4,5]pyrrolo[1,2-b]indazole]-7′- carboxylic acid
- (3S,3’S,3a’S,10a’S)-6-Chloro-3′-(3-chloro-2-fluorophenyl)-1′-(cyclopropylmethyl)-6′-methyl-2-oxo-1,2,3′,3a’,10′,10a’-hexahydro1’H-spiro[indole-3,2′-pyrrolo[2′,3′:4,5]pyrrolo[1,2-b]indazole]-7′-carboxylic acid
- Spiro[3H-indole-3,2′(1’H)-pyrrolo[2′,3′:4,5]pyrrolo[1,2-b]indazole]-7′-carboxylic acid, 6-chloro-3′-(3-chloro-2-fluorophenyl)-1′-(cyclopropylmethyl)-1,2,3′,3’a,10′,10’a-hexahydro-6′-methyl-2-oxo-, (2’S,3’S,3’aS,10’aS)-
Brigimadlin (BI-907828) is a small molecule MDM2–TP53 inhibitor developed for liposarcoma.[2][3][4][5][6]
Brigimadlin is an orally available inhibitor of murine double minute 2 (MDM2), with potential antineoplastic activity. Upon oral administration, brigimadlin binds to MDM2 protein and prevents its binding to the transcriptional activation domain of the tumor suppressor protein p53. By preventing MDM2-p53 interaction, the transcriptional activity of p53 is restored. This leads to p53-mediated induction of tumor cell apoptosis. Compared to currently available MDM2 inhibitors, the pharmacokinetic properties of BI 907828 allow for more optimal dosing and dose schedules that may reduce myelosuppression, an on-target, dose-limiting toxicity for this class of inhibitors.
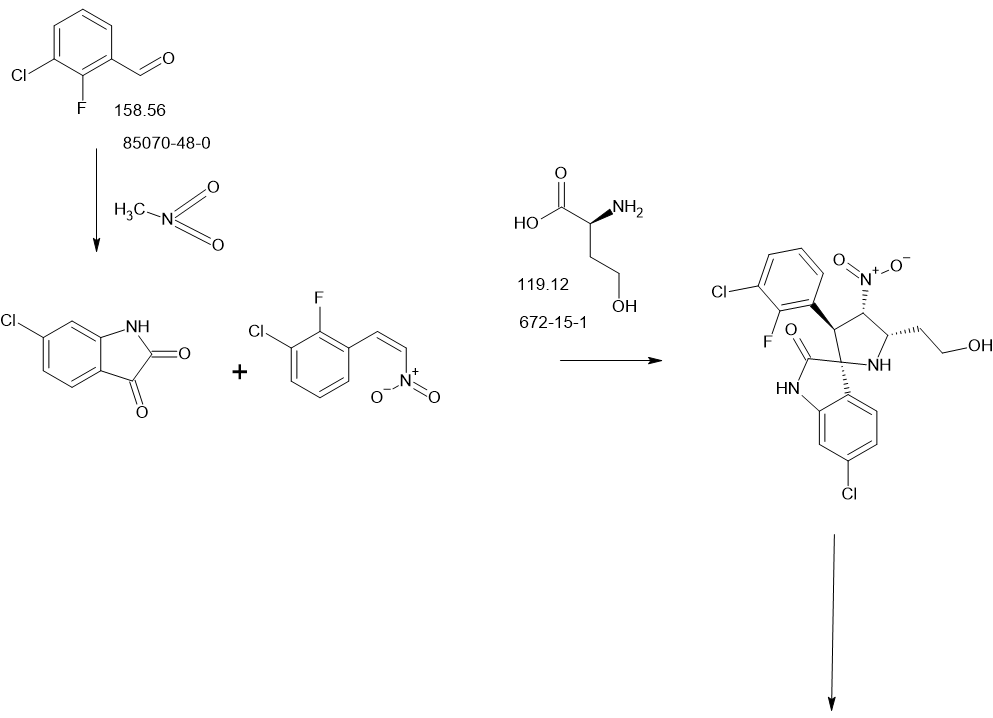
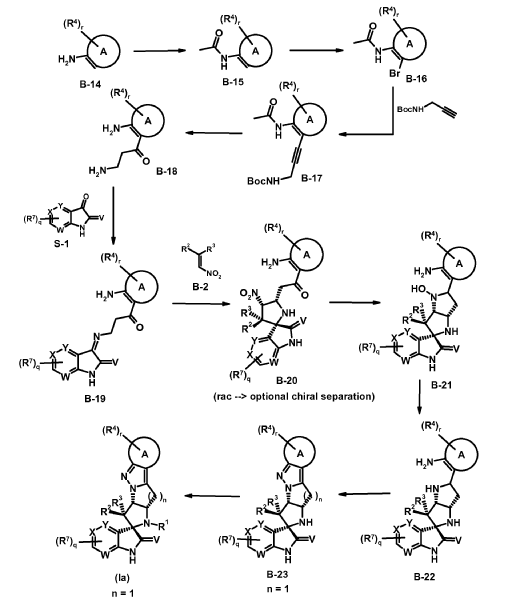
SCHEME
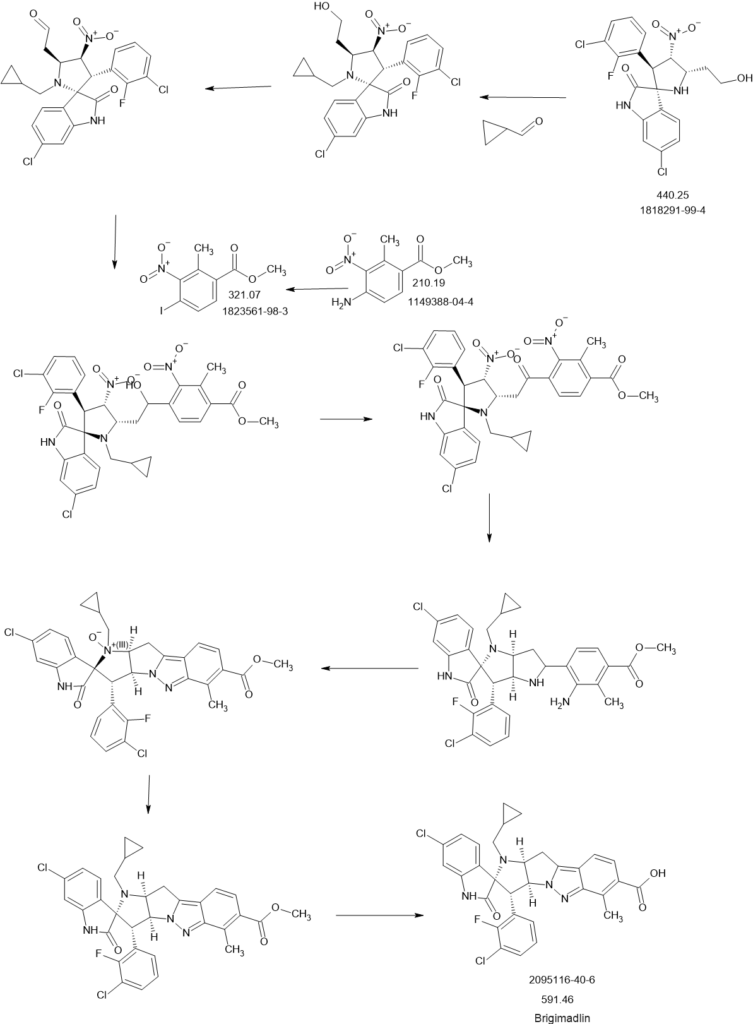
PATENT
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=US231206177&_cid=P10-MA0ULZ-04263-1
PATENT
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=WO2017060431&_cid=P10-MA0TY5-76812-1
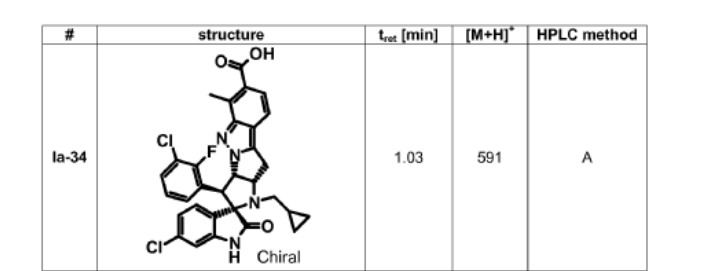
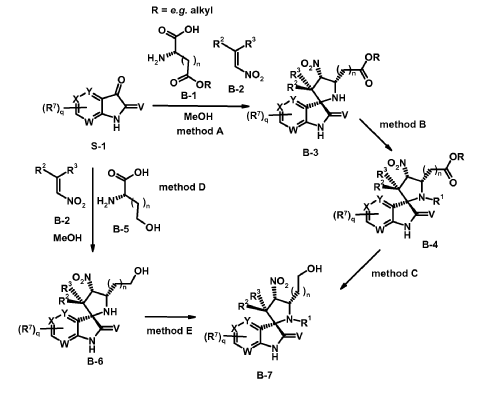
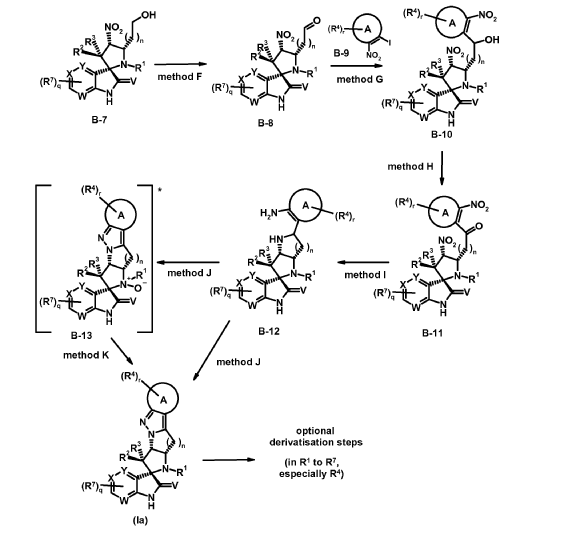
intermediates B-7
Experimental procedure for the synthesis of B-7 a (method E)
To a solution of cyclopropanecarbaldehyde (1.7 mL, 22.7 mmol) in AcOH (19.5 mL) is added intermediate B-6a (1.60 g, 3.8 mmol) and the reaction mixture is stirred for 15 min. Sodium triacetoxyborohydride (1.34 g, 6.3 mmol) is added and the reaction mixture is stirred overnight. Water is added to the reaction mixture and it is extracted with EtOAc. The combined organic layer is dried (MgSO4), filtered, concentrated in vacuo and the crude product B-7a is purified by chromatography if necessary.
Experimental procedure for the synthesis of B-3a (method A)
6-Chloroisatin S-1a (5 g, 27,0 mmol), 1-(3-chloro-2-fluoro-phenyl)-2-nitroethene B-2a (5.5 g, 27.0 mmol) and amino acid B-1a (4.4 g, 27.0 mmol) are refluxed in MeOH for 4 h. The reaction mixture is concentrated in vacuo and purified by crystallization or chromatography if necessary.
Synthesis of compounds (la) according to the invention
Experimental procedure for the synthesis of la-1 (method J)
To a solution of intermediate B-12a (329 mg, 0.65 mmol) in DCM (7 mL) is added a solution of Oxone® (793 mg, 1.29 mmol) in H2O (7 mL) at 0 °C dropwise. The biphasic reaction mixture is stirred vigorously for 20 min at 0 °C and for additional 2 h at rt. The reaction mixture is diluted with H2O and is extracted with DCM. The combined organic layer is dried (MgSO4), filtered, concentrated in vacuo and the crude product is purified by chromatography which gives compound la-1.
Experimental procedure for the synthesis of la-20 (method J + method K)
* The location of overoxidation/N-oxid formation is not entirely clear. B-13a as depicted seems to be probable.
To a solution of intermediate B-12j (417 mg, 0.68 mmol) in DCM (10 mL) is added a solution of Oxone® (841 mg, 1.37 mmol) in H2O (7 mL) at 0 °C dropwise. The biphasic reaction mixture is stirred vigorously for 20 min at 0 °C and for additional 6 h at rt. The reaction mixture is diluted with H2O and extracted with DCM. The combined organic layer is dried (MgSO4), filtered, concentrated in vacuo which gives a crude mixture of la-20 and an oxidized form B-13a (M+H = 621). This mixture is dissolved in MeCN (4.2 mL) and bis(pinacolato)diborone (326 mg, 1.28 mmol) is added. The reaction mixture is heated under microwave irradiation to 100 °C for 30 min. The reaction mixture is diluted with H2O and extracted with DCM. The combined organic layer is dried (MgSO4), filtered, concentrated in vacuo and the crude product is purified by chromatography which gives compound la-20.
References
^ “Brigimadlin”. pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- ^ Rinnenthal, Joerg; Rudolph, Dorothea; Blake, Sophia; Gollner, Andreas; Wernitznig, Andreas; Weyer-Czernilofsky, Ulrike; Haslinger, Christian; Garin-Chesa, Pilar; Moll, Jürgen; Kraut, Norbert; McConnell, Darryl; Quant, Jens (1 July 2018). “Abstract 4865: BI 907828: A highly potent MDM2 inhibitor with low human dose estimation, designed for high-dose intermittent schedules in the clinic”. Cancer Research. 78 (13_Supplement): 4865. doi:10.1158/1538-7445.AM2018-4865. S2CID 56768874.
- ^ Rudolph, Dorothea; Reschke, Markus; Blake, Sophia; Rinnenthal, Jörg; Wernitznig, Andreas; Weyer-Czernilofsky, Ulrike; Gollner, Andreas; Haslinger, Christian; Garin-Chesa, Pilar; Quant, Jens; McConnell, Darryl B.; Norbert, Kraut; Moll, Jürgen (1 July 2018). “Abstract 4866: BI 907828: A novel, potent MDM2 inhibitor that induces antitumor immunologic memory and acts synergistically with an anti-PD-1 antibody in syngeneic mouse models of cancer”. Cancer Research. 78 (13_Supplement): 4866. doi:10.1158/1538-7445.AM2018-4866. S2CID 80770832.
- ^ Cornillie, J.; Wozniak, A.; Li, H.; Gebreyohannes, Y. K.; Wellens, J.; Hompes, D.; Debiec-Rychter, M.; Sciot, R.; Schöffski, P. (April 2020). “Anti-tumor activity of the MDM2-TP53 inhibitor BI-907828 in dedifferentiated liposarcoma patient-derived xenograft models harboring MDM2 amplification”. Clinical and Translational Oncology. 22 (4): 546–554. doi:10.1007/s12094-019-02158-z. PMID 31201607. S2CID 189862528.
- ^ Schöffski, Patrick; Lahmar, Mehdi; Lucarelli, Anthony; Maki, Robert G (March 2023). “Brightline-1: phase II/III trial of the MDM2–p53 antagonist BI 907828 versus doxorubicin in patients with advanced DDLPS”. Future Oncology. 19 (9): 621–629. doi:10.2217/fon-2022-1291. PMID 36987836. S2CID 257802972.
- ^ Schoeffski, P.; Lorusso, P.; Yamamoto, N.; Lugowska, I.; Moreno Garcia, V.; Lauer, U.; Hu, C.; Jayadeva, G.; Lahmar, M.; Gounder, M. (October 2023). “673P A phase I dose-escalation and expansion study evaluating the safety and efficacy of the MDM2–p53 antagonist brigimadlin (BI 907828) in patients (pts) with solid tumours”. Annals of Oncology. 34: S472 – S473. doi:10.1016/j.annonc.2023.09.1859. S2CID 264392338.
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name(3S,10’S,11’S,14’S)-6-chloro-11′-(3-chloro-2-fluorophenyl)-13′-(cyclopropylmethyl)-6′-methyl-2-oxospiro[1H-indole-3,12′-8,9,13-triazatetracyclo[7.6.0.02,7.010,14]pentadeca-1,3,5,7-tetraene]-5′-carboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 2095116-40-6 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 128922236 |
| DrugBank | DB18578 |
| EC Number | 826-645-5 |
| KEGG | D12842 |
| PubChem CID | 129264140 |
| UNII | 9A934ZAN94 |
| showInChI | |
| showSMILES | |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C31H25Cl2FN4O3 |
| Molar mass | 591.46 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[1] | |
| Pictograms | |
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H300, H360Df, H372, H413 |
| Precautionary statements | P203, P260, P264, P270, P273, P280, P301+P316, P318, P319, P321, P330, P405, P501 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
/////////////BRIGIMADLIN, BI-907828, BI 907828, 9A934ZAN94














