Ibrilatazar
CAS 57818-44-7
MF C18H32O3 MW 296.4 g/mol
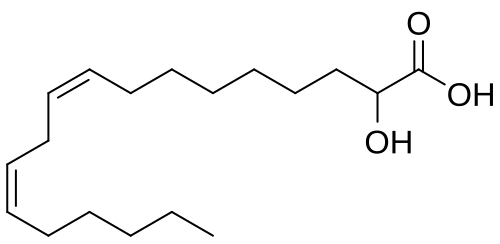
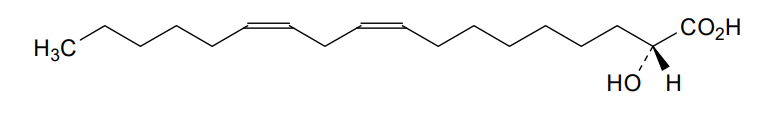
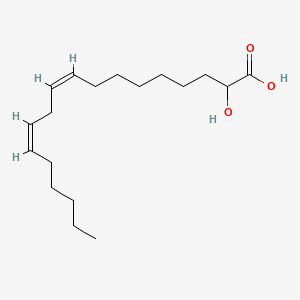
rac-(2R)-(9Z,12Z)-2-hydroxyoctadeca-9,12-dienoic acid
(9Z,12Z)-2-hydroxyoctadeca-9,12-dienoic acid
peroxisome proliferator activated receptor (PPAR) alpha and gamma agonist, antineoplastic, ABILITY PHARMA, ABTL 0812, alpha-Hydroxylinoleic acid, ABTL0812
- alpha-Hydroxylinoleic acid
- ABTL0812
- 2-hydroxylinoleic acid
| Ingredient | UNII | CAS | InChI Key |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABTL-0812 Sodium | X1840C8161 | Not Available | VFXKYDDSDQXKLC-NBTZWHCOSA-M |
Ibrilatazar also known as α-hydroxylinoleic acid is a small-molecule, experimental cancer drug being developed by Ability Pharmaceuticals.[1]
Ibrilatazar is an orally bioavailable, lipid analogue and inhibitor of raptor-mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) (mTOR complex 1; mTORC1), rictor-mTOR (mTOR complex 2; mTORC2) and dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) with potential antineoplastic activity. Upon oral administration, ibrilatazar binds to and inhibits both mTORC1 and mTORC2, which may result in apoptosis and a decrease in proliferation in mTORC1/2-expressing tumor cells. mTOR is a serine/threonine kinase that is upregulated in some tumors; it plays an important role in the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway which is often deregulated in cancer cells. In addition, ibrilatazar inhibits DHFR, an enzyme that reduces dihydrofolic acid to tetrahydrofolic acid, thereby blocking tetrahydrofolate synthesis, and resulting in both the depletion of nucleotide precursors and the inhibition of DNA, RNA and protein synthesis. This induces autophagy-induced cell death and further inhibition of cell proliferation.
- A Study of ABTL0812 in Pancreatic CancerCTID: NCT03417921Phase: Phase 1/Phase 2Status: SuspendedDate: 2024-07-31
- ABTL0812 in Combination With FOLFIRINOX for First-line Treatment of Metastatic Pancreatic StudyCTID: NCT04431258Phase: Phase 1/Phase 2Status: CompletedDate: 2024-03-18
- Phase I/Ib Clinical Trial of ABTL0812 in Advanced Cancer PatientsCTID: NCT02201823Phase: Phase 1Status: CompletedDate: 2015-07-02
- Microbiological production method of γ- and δ-lactonesPublication Number: JP-H03187387-APriority Date: 1989-08-04
- Process for the microbiological production of gamma- and delta-lactonesPublication Number: US-5168054-APriority Date: 1989-08-04Grant Date: 1992-12-01
- Degradation control of environmentally degradable disposable materialsPublication Number: US-2002123546-A1Priority Date: 1988-08-08
- Degradation control of environmentally degradable disposable materialsPublication Number: US-6323307-B1Priority Date: 1988-08-08Grant Date: 2001-11-27
- Degradation control of environmentally degradable disposable materialsPublication Number: US-6740731-B2Priority Date: 1988-08-08Grant Date: 2004-05-25
PAT
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=US38087288&_cid=P12-MH8IQK-97634-1



AS ON JUNE2025 4.45 LAKHS VIEWS ON BLOG WORLDREACH AVAILABLEFOR YOUR ADVERTISEMENT

join me on Linkedin
Anthony Melvin Crasto Ph.D – India | LinkedIn
join me on Researchgate
RESEARCHGATE

join me on Facebook
Anthony Melvin Crasto Dr. | Facebook
join me on twitter
Anthony Melvin Crasto Dr. | twitter
+919321316780 call whatsaapp
EMAIL. amcrasto@gmail.com

……
History
In 2015, Ability announced that it had received orphan drug designation (ODD) for pediatric cancer neuroblastoma from the European Medical Agency (EMA) and the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA).[1] Also in 2016 a preclinical study confirmed that ABTL0812 was well tolerated.[2] In December 2016 the company announced Ibrilatazar has received an Orphan Drug Designation for the treatment of pancreatic cancer.[1]
Mechanism of action
One mechanism of action is the activation of the PPAR-alpha and PPAR-gamma receptors which in turn up-regulate the expression of the TRIB3 gene, leading to inhibition of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. This pathway is excessively activated in most human cancers, supporting tumor growth. It is a principal target of various new anti-tumour drugs. Tumor cells are killed via autophagic cell death, rather than apoptosis.[3][4]
ABTL0812 activates the PPAR receptors, inducing TRIB3 over-expression. TRIB3 binds to the Akt oncogene and inhibits the Akt/mTOR axis.[3]
Clinical trials
ABTL0812 showed efficacy in Phase I clinical trials in patients with advanced cancer, with low toxicity and high tolerability.[3]
References
- “Ability Pharmaceuticals Announces Orphan Drug Designation in the US for ABTL0812 in Pancreatic Cancer”. Ability Pharmaceuticals SL.
- “Ability Pharmaceuticals Announces Positive Phase 1 1b Study Results Of ABTL0812 In Cancer Patients With Advanced Solid Tumors”. www.biospace.com.
- “New mechanism of antitumor action identified”. Medical Xpress. 25 January 2016.
- Erazo T, Lorente M, López-Plana A, Muñoz-Guardiola P, Fernández-Nogueira P, García-Martínez JA, et al. (May 2016). “The New Antitumor Drug ABTL0812 Inhibits the Akt/mTORC1 Axis by Upregulating Tribbles-3 Pseudokinase”. Clinical Cancer Research. 22 (10): 2508–19. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-15-1808. hdl:2445/207600. PMID 26671995.
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | α-Hydroxylinoleic acid; 2-Hydroxylinoleic acid; ABTL-0812 |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | Investigational |
| Identifiers | |
| IUPAC name | |
| CAS Number | 57818-44-7 |
| PubChem CID | 21158511 |
| ChemSpider | 20118100 |
| UNII | 0DE74TJ7EZ |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:136927 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DTXSID301258077 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H32O3 |
| Molar mass | 296.451 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | Interactive image |
| SMILES | |
| InChI | |
/////////Ibrilatazar, peroxisome proliferator activated receptor (PPAR) alpha and gamma agonist, antineoplastic, ABILITY PHARMA, ABTL 0812, alpha-Hydroxylinoleic acid, ABTL0812














