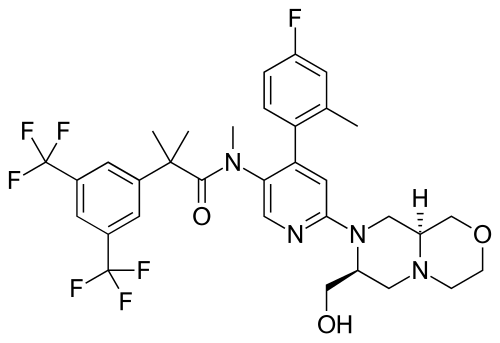
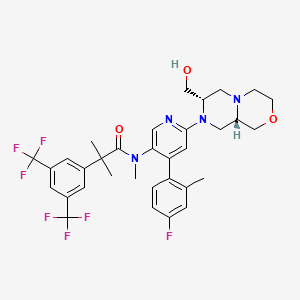
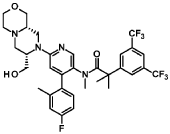
Elinzanetant
CAS 929046-33-3
MW 668.6 g/mol MF C33H35F7N4O3
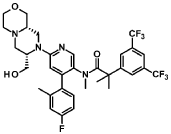
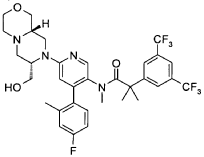
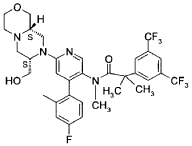
N-[6-[(7S,9aS)-7-(hydroxymethyl)-3,4,6,7,9,9a-hexahydro-1H-pyrazino[2,1-c][1,4]oxazin-8-yl]-4-(4-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-3-pyridinyl]-2-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-N,2-dimethylpropanamide
FDA 10/24/2025, Lynkuet, To treat moderate-to-severe vasomotor symptoms due to menopause
BAY-3427080; GSK-1144814; NT-814, UNII-NZW2BOW35N
Elinzanetant, sold under the brand name Lynkuet, is a medication used for the treatment of moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms due to menopause.[4] It is an neurokinin 1 and neurokinin 3 receptor antagonist.[4] It was developed by Bayer Healthcare.[4] It is taken by mouth.[4]
Elinzanetant is a non-hormonal, selective, neurokinin 1 (NK-1) and neurokinin 3 (NK-3) receptor antagonist.[5] By blocking NK-1 and NK-3 receptors signaling, elinzanetant is postulated to normalize neuronal activity involved in thermo- and sleep regulation in the hypothalamus.[5]
Elinzanetant is an orally bioavailable neurokinin/tachykinin 1 receptor (NK1-receptor; NK1R; NK-1R) and NK3 receptor (NK-3R; NK3R) antagonist, that may be used to treat vasomotor symptoms in menopausal woman. Upon oral administration, elinzanetant targets, competitively binds to and blocks the activity of the NK1R and NK3R in the central nervous system (CNS), thereby inhibiting the binding of the endogenous ligands and neuropeptides substance P (SP; neurokinin-1; NK1) and neurokinin B (NKB). This inhibits NK1R/NK3R-mediated signal transduction and may prevent certain menopausal symptoms such as hot flashes. Neurokinin-mediated signaling may increase during hormone deficiency and may cause hot flashes.
SYN
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=WO2021094247&_cid=P20-MHLSZY-53200-1
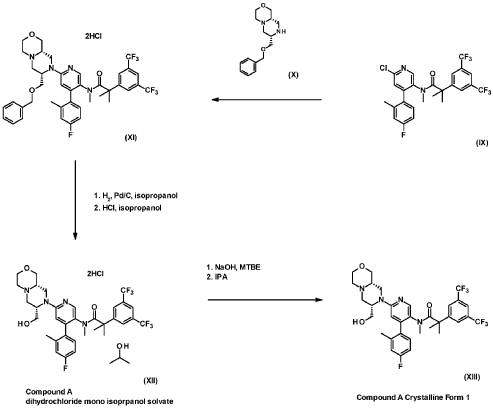
“Compound A” refers to 2-[3,5-Bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-N-{4-(4-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-6-[(7S,9aS)-7-(hydroxymethyl)hexahydropyrazino[2,l-c][l,4]oxazin-8(lH)-yl]-3-pyridi-nyl}-N,2-dimethylpropanamide, and has the chemical structure depicted below.
(Compound A).
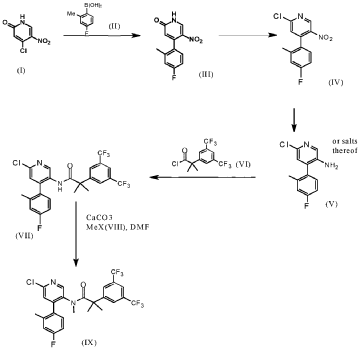
Example 8
2-[3.5-Bis(trifluoromethyl¾phenyl1-N-{4-(4-fluoro-2-methylphenyl¾-6-[(7S.9aS¾-7-(hvdroxymethyl¾hexa-hvdropyrazino[2,l-c1[l,41oxazin-8(lH)-yl1-3-pyridinyl}-N, 2-dimethyl propanamide as anhydrous crys talline form (Compound A)
Example 7 (2-[3,5-Bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-N-{4-(4-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-6-[(7S,9aS)-7-(hy-droxymethyl)hexahydropyrazino[2,l-c][l,4]oxazin-8(lH)-yl]-3-pyridinyl}-N,2-dimethylpropanamide dihydrochloride salt mono-isopropanol solvate (Compound XII)) (3.4 kg), methyl-f-butyl ether (from now on, MTBE) (15.0 L/kg of Example 7) and NaOH 2.5N (4.9 L/kg of Example 7) were loaded, heated to 40QC and stirred for 10 to 30 min. The layers were settled for not less than 30 min at 40QC and the bottom aqueous layer discarded.
An aqueous solution of L-cysteine 9 wt% (5.0 L water per kg of Example 7+ 0.5 w/w L-cysteine per Ex ample 7) was added over the organic layer and stirred at 40QC for not less than 60 min. The layers were settled for not less than 30 min at 40QC and the bottom aqueous layer discarded.
Water (5.0 L/kg of Example 7) was added over the organic layer and stirred at 40QC for not less than 15 min. The layers were settled for not less than 60 min at 40QC and the bottom aqueous layer dis carded.
Water (5.0 L/kg of Example 7) was added over the organic layer and stirred at 40QC for not less than 15 min. The layers were settled for not less than 60 min at 40QC and the bottom aqueous layer dis carded.
The organic layer was concentrated at atmospheric pressure to 2.5 L/kg of Example 7. Iso-octane (8.3 L/kg of Example 7) was added at 50/55QC in not less than lh and the solution distilled under light vac uum to 4.0 L/kg of Example 7. A sample was taken for controlling the water and MTBE removal.
Isopropanol (0.8 L/kg of Example 7) was added and stirred at 65/75QC until total dissolution. The solu tion was cooled down to 45/55QC and filtered to remove any foreign matters. Iso-octane (4.5 L/kg of Example 7) was added and the batch heated to 70QC for not less than 30 min. The solution was cooled down to 50QC and seeded with a slurry of 2-[3,5-Bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-N-{4-(4-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-6-[(7S,9aS)-7-(hydroxymethyl)hexahydropyrazino[2,l-c][l,4]oxazin-8(lH)-yl]-3-pyridi-nyl}-N,2-dimethylpropanamide(0.008% w/w of Example 7) in iso-octane (0.07 L/kg of Example 7) and isopropanol (0.01 L/kg of Example 7). The seeds were aged at 50QC for not less than 3h and additional iso-octane (4.2 L/kg of Example 7) was added in not less than 3h keeping the temperature at 50/55QC. The slurry was held at 50QC for not less than 8h, cooled down to 0QC in not less than 5h and aged for not less than 3h before proceeding with the centrifugation step.
The slurry was centrifuged and the cake washed with iso-octane (2 x 3.3 L/kg of Example 7).
The wet product was dried under vacuum at 50QC to obtain 2.34 kg of the title compound (yield = 82.7%). This product was sieved for delumping to obtain 2.26kg of the title compound with a 99.8% purity as a white powder.
NMR spectrometer: Varian Agilent Mercury Vx 400 (16 scans, sw 6400 Hz, 25 °C).
*H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-ds): d 8.02 (s, 1 H), 7.85 (s, 1 H), 7.74 (bd, 2 H), 7.22-6.92 (m, 3 H), 6.61 (s, 1 H), 4.70 (m, 1 H), 4.21 (bd, 1 H), 4.09 (bd, 1 H), 3.75 (m, 3 H), 3.55 (td, 11.3 Hz, 2.2 Hz, 1 H), 3.40 (bd, 1 H), 3.15 (t, 10.5 Hz, 1 H), 3.02 (d, 11.3 Hz, 1 H), 2.63 (d, 11.3 Hz, 1 H), ca. 2.5 (bd, 2 H), 2.31-2.00 (m, 7 H), 1.58-1.10 (m, 6 H).
SYN
- WO2007028654
- https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=WO2007028654&_cid=P20-MHLT4M-58180-1
Example 34
2-[3,5-Bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-yV-{4-(4-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-6-[(7S,9aS)-7-(hydroxymethyl)hexahydropyrazino[2,1 -c][1 ,4]oxazin-8(1 H)-yl]-3-pyridinyl}-A/,2-dimethylpropanamide (E34)
2-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-Λ/-[6-[(7S,9aS)-7-({[(1 , 1 -dimethylethyl)(dimethyl)silyl]oxy}methyl)hexahydropyrazino[2,1-c][1 ,4]oxazin-8(1H)-yl]-4-(4-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-3-pyridinyl]-Λ/,2-dimethylpropanamide (D24) (390 mg, 0.498 mmol) was dissolved 17 ml. of methanol. To this solution was added concentrated HCI (0.9 mL) at 00C, and stirring was continued at room temperature for 3h (complete conversion). The reaction mixture was loaded on a SCX cartridge and washed with MeOH. The product was eluted with 0.5 M methanolic ammonia. The product-containing fractions were evaporated, leaving the target compound as a white solid: 310 mg, 0.464 mmol, 93%.
UPLC/MS: m/z= 669 (M+1 ).
1H-NMR (DMSO-d6): δ (ppm) 8.07-7.97 (s, 1 H), 7.88-7.81 (s, 1 H), 7.79-7.69 (br. s, 2H), 7.19-7.11 (d, 1 H), 7.14-7.06 (br. s, 2H) 6.64-6.56 (s, 1 H), 4.75-4.65 (m, 1 H), 4.31-4.13 (br. S, 1 H), 4.15-4.01 (br. s, 1 H), 3.80-3.68 (m, 3H), 3.58-3.49 (t, 1 H); 3.43-3.34 (m, 1 H); 3.18-3.09 (t, 1 H); 3.04-2.98 (d, 1 H); 2.68-2.58 (d, 1 H); 2.51-2.45 (s, 3H); 2.20-2.13 (s, 3H); 2.29-2.00 (m, 4H); 1.54-1.39 (s, 3H); 1.39-1.28 (s, 3H).
SYN
Crystalline forms of a pyridine derivative
Publication Number: WO-2010015626-A1
Priority Date: 2008-08-05
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=WO2010015626&_cid=P20-MHLT79-60873-1
ntermediate 7
2-r3.5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenvn-Λ/-f4-(4-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-6-r(7S,9aS)-7-(hvdroxymethyl)hexahvdro-pyrazinoF2,1-c1f1 ,41oxazin-8(1/-/)-vn-3-pyridinyl}-Λ/.2-dimethylpropanamide
16.90 g of bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-Λ/-[6-chloro-4-(4-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-3-pyridinyl]- Λ/,2-dimethylpropanamide (WO 2005/002577) 4.58 g sodium tert-butoxide and 2.1O g Bis-(tri-terf-butylphposphine-palladium(O) catalyst was loaded into the vessel under nitrogen.
10.00 g intermediate 6 dissolved in 338 mL toluene was charged to afford a dark brown solution. The solution was heated to 800C and stirred for at least 16 h (thin suspension obtained).
The reaction mixture was cooled down to 20-25°C and 16.90 g celite was added to give a brown suspension. The suspension was filtered over 16.90 g celite and washed with 33.8 mL toluene. 338 mL sat. sodium bicarbonate solution was added and the biphasic system was stirred for 5 min. at 20-250C. After phase separation, the aqueous layer was extracted twice with 118 mL toluene. The combined organic layers were treated with 90 mL of a 10% aqueous cysteine solution and stirred for 1 h at 25°C. After phase separation the organic layer was treated again with 90 mL of a 10% cysteine-solution and stirred for a further 1 h at 25°C. After phase separation , the organic layer was washed with 85 mL half saturated sodium bicarbonate solution then solvent exchanged to dioxane. The dioxane solution was cooled down to 10-150C. 63.5 mL of 4M hydrogen chloride in dioxane was added at 10-150C over at least 10 min. The solution was warmed to 20-25°C and stirred for 2 h.
Dioxane was concentrated down to 85 mL at 45°C under reduced pressure. 85 mL water and 254 mL dichloromethane were added to the residue to give a thin suspension. The biphasic system was stirred for 5 min. at 20-250C. The layers were separated and the organic phase was washed with 33.8 mL saturated sodium bicarbonate solution at 20-25°C (pH adjusted to 7-8). The biphasic system was stirred for 5 min. at 20-250C and the organic layer separated and concentrated under reduced pressure at 500C to afford crude title compound as a pale brown solid. 8.00 g of the title compound (78.8% a/a HPLC) was dissolved in 16 mL ethyl acetate. The filter was loaded with 80 to 104 g silica gel and conditioned with ethyl acetate. The product solution was loaded on top of the column and chromatography was started using ethyl acetate as solvent. The product fractions were combined and partially concentrated at 45-50°C under reduced pressure. To the mixture was added 2.64 g to 4.00 g silicycle (Si-Thiol, 1.2 mmol/g) at rt and stirred for 2 h. Filtration over 8.00 g celite and washing with 32 mL ethyl acetate gave the filtrate which was concentrated to dryness at 45°C afford the title compound as a light brown solid. ( Weight yield 72%) 1H-NMR [ppm, CDCI3]: 8.04-7.91 , (m, 1 H); 7.77, (s, 1 H); 7.72-7.60, (m, 2H); 7.59-7.16, (m, 1H); 7.06-6.74, (m, 2H); 6.44, (s, 1 H); 4.64-4.43, (m, 1 H); 4.38-4.18, (m, 1 H); 4.07-3.96, (m, 2H); 3.95-3.76, (m, 3H); 3.76-3.61 , (m, 1 H); 3.37-3.27, (m, 1 H); 3.16-2.98, (m, 2H); 2.84-2.70, (m, 1 H); 2.67-2.51 , (m, 2H); 2.49-2.22, (m, 5H); 2.19-2.06, (m, 2H); 1.64-1.31 , (m, 5H), OH broad and not observed
LIT
- Elinzanetant: a phase III therapy for postmenopausal patients with vasomotor symptomsPublication Name: Expert Opinion on Investigational DrugsPublication Date: 2024-01-02PMID: 38224099DOI: 10.1080/13543784.2024.2305122
- Elinzanetant (NT-814), a Neurokinin 1,3 Receptor Antagonist, Reduces Estradiol and Progesterone in Healthy WomenPublication Name: The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolismPublication Date: 2021-02-24PMCID: PMC8277204PMID: 33624806DOI: 10.1210/clinem/dgab108
- Pleiotypic responses of regenerating liverPublication Name: Advances in Enzyme RegulationPublication Date: 1976PMID: 9791DOI: 10.1016/0065-2571(76)90023-6
PAT
Pyridine Derivatives and Their Use in the Treatment of Psychotic Disorders
Publication Number: US-2008269208-A1
Priority Date: 2005-06-06
- Pyridine Derivatives And Their Use In The Treatment Of Psychotic DisordersPublication Number: US-2011190276-A1Priority Date: 2005-09-09
- Pyridine derivatives and their use in the treatment of psychotic disordersPublication Number: US-7683056-B2Priority Date: 2005-09-09Grant Date: 2010-03-23
- Pyridine derivatives and their use in the treatment of psychotic disordersPublication Number: US-7919491-B2Priority Date: 2005-09-09Grant Date: 2011-04-05
- Pyridine derivatives and their use in the treatment of psychotic disordersPublication Number: US-8097618-B2Priority Date: 2005-09-09Grant Date: 2012-01-17
- Pyridine derivatives and their use in the treatment of psychotic disordersPublication Number: WO-2007028654-A1Priority Date: 2005-09-09



AS ON OCT2025 4.511 LAKHS VIEWS ON BLOG WORLDREACH AVAILABLEFOR YOUR ADVERTISEMENT

join me on Linkedin
Anthony Melvin Crasto Ph.D – India | LinkedIn
join me on Researchgate
RESEARCHGATE

join me on Facebook
Anthony Melvin Crasto Dr. | Facebook
join me on twitter
Anthony Melvin Crasto Dr. | twitter
+919321316780 call whatsaapp
EMAIL. amcrasto@gmail.com

……
Medical uses
Elinzanetant is indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause.[4]
Society and culture
Legal status
In September 2025, the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use of the European Medicines Agency adopted a positive opinion, recommending the granting of a marketing authorization for the medicinal product Lynkuet, intended for the treatment of moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms (hot flushes).[5] The applicant for this medicinal product is Bayer AG.[5]
Lynkuet was approved for medical use in the United States in October 2025.[6]
Names
Elinzanetant is the international nonproprietary name.[7]
Elinzanetant is sold under the brand name Lynkuet.[8]
References
- “Details for: Lynkuet”. Drug and Health Products Portal. 23 July 2025. Retrieved 28 September 2025.
- “Lynkuet product information”. Lynkuet. 23 July 2025. Retrieved 28 September 2025.
- “MHRA approves elinzanetant to treat moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms (hot flushes) caused by menopause”. Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (Press release). 8 July 2025. Retrieved 28 September 2025.
- https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2025/219469s000lbl.pdf
- “Lynkuet EPAR”. European Medicines Agency (EMA). 19 September 2025. Retrieved 27 September 2025. Text was copied from this source which is copyright European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.
- “Novel Drug Approvals for 2025”. U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 24 October 2025. Retrieved 29 October 2025.
- World Health Organization (2020). “International nonproprietary names for pharmaceutical substances (INN): recommended INN: list 84”. WHO Drug Information. 34 (3). hdl:10665/340680.
- “Bayer’s Lynkuet (elinzanetant), the First and Only Neurokinin 1 and Neurokinin 3 Receptor Antagonist, Receives FDA Approval for Moderate to Severe Hot Flashes Due to Menopause” (Press release). Bayer. 24 October 2025. Retrieved 29 October 2025 – via Business Wire.
External links
- Clinical trial number NCT05042362 for “A Study to Learn More About How Well Elinzanetant Works and How Safe it is for the Treatment of Vasomotor Symptoms (Hot Flashes) That Are Caused by Hormonal Changes Over 26 Weeks in Women Who Have Been Through the Menopause (OASIS-1)” at ClinicalTrials.gov
- Clinical trial number NCT05099159 for “A Study to Learn More About How Well Elinzanetant Works and How Safe it is for the Treatment of Vasomotor Symptoms (Hot Flashes) That Are Caused by Hormonal Changes Over 26 Weeks in Women Who Have Been Through the Menopause (OASIS-2)” at ClinicalTrials.gov
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Lynkuet |
| Other names | BAY-3427080; GSK-1144814; NT-814 |
| License data | US DailyMed: Elinzanetant |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | None |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | CA: ℞-only[1][2]UK: POM (Prescription only)[3]US: ℞-only[4] |
| Identifiers | |
| IUPAC name | |
| CAS Number | 929046-33-3 |
| PubChem CID | 16063568 |
| ChemSpider | 17223178 |
| UNII | NZW2BOW35N |
| KEGG | D12123 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DTXSID101337049 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C33H35F7N4O3 |
| Molar mass | 668.657 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | Interactive image |
| SMILES | |
| InChI | |
///////elinzanetant, Lynkuet, FDA 2025, APPROVALS 2025, BAY 3427080, GSK 1144814, NT 814














