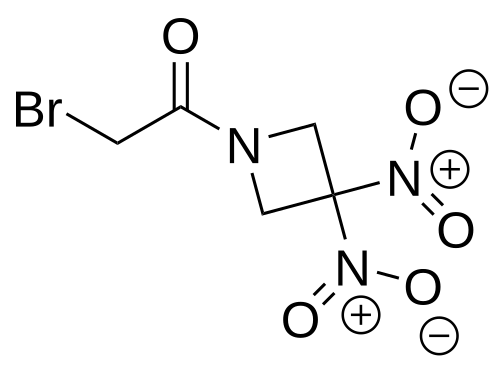
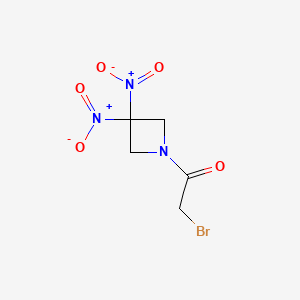
Nibrozetone
CAS 925206-65-1
MF C5H6BrN3O5 MW268.02 g/mol
2-bromo-1-(3,3-dinitroazetidin-1-yl)ethan-1-one
2-Bromo-1-(3,3-dinitroazetidin-1-yl)ethanone
2-BROMO-1-(3,3-DINITROAZETIDIN-1-YL)ETHAN-1-ONE
anti-inflammatory, RRx-001, RRx 001, ABDNAZ
Nibrozetone is an investigational new drug that is being evaluated by EpicentRx for the treatment of oral mucositis in head and neck cancer patients. It is a small molecule that combines direct inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome, induction of NRF2, and release of nitric oxide under hypoxic conditions.[1][2] It has received Fast Track designation from the FDA for severe oral mucositis in head and neck cancer patients.[3]
Nibrozetone (RRx-001) is an investigational, multi-action small molecule drug that is being developed by EpicentRx for a range of conditions, including head and neck cancers, small cell lung cancer, and neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson’s and ALS. Its mechanism involves inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome, activating the Nrf2 pathway, and releasing nitric oxide in hypoxic tumor environments, while also protecting healthy tissues. It is being evaluated for its potential to reduce the side effects of cancer treatments and as a disease-modifying therapy itself.
How it works
- Anti-inflammatory: Nibrozetone inhibits the NLRP3 inflammasome, which is a key driver of inflammation in several diseases.
- Antioxidant: It activates the Nrf2 pathway, a cellular defense mechanism that protects against oxidative stress.
- Tumor-specific delivery: It acts as a “hypoxia-activated” drug, releasing a nitric oxide-releasing radical only in the low-oxygen environment of tumors, which can be toxic to cancer cells.
- Protective to normal tissue: The drug’s protective mechanisms are thought to keep it from causing harm to healthy tissues outside of the tumor environment.
Current and potential uses
- Oral mucositis: It is being studied to prevent and treat severe mouth sores that can be a side effect of head and neck cancer radiation therapy.
- Small cell lung cancer (SCLC): It is being investigated in a Phase 3 trial for the treatment of SCLC.
- Neurodegenerative diseases: Animal studies have shown promising neuroprotective effects in models of Parkinson’s and ALS.
- Other potential applications: Research is ongoing for its use as a treatment for other conditions, including endometriosis, toxic exposures, and various types of cancers.
- RRx-001 in Lung Cancer, Ovarian Cancer and Neuroendocrine Tumors Prior to Re-administration of Platinum Based Doublet Regimens (QUADRUPLE THREAT)CTID: NCT02489903Phase: Phase 2Status: CompletedDate: 2025-03-17
- RRx-001 for Reducing Oral Mucositis in Patients Receiving Chemotherapy and Radiation for Head and Neck CancerCTID: NCT05966194Phase: Phase 2Status: RecruitingDate: 2024-11-15
- Safety and Efficacy of RRx-001 in the Attenuation of Oral Mucositis in Patients Receiving Chemoradiation for the Treatment of Oral CancersCTID: NCT03515538Phase: Phase 2Status: CompletedDate: 2024-11-04
- Safety and Pharmacokinetic Study of RRx-001 in Cancer SubjectsCTID: NCT01359982Phase: Phase 1Status: CompletedDate: 2024-11-01
- RRx-001 Given With Irinotecan and Temozolomide for Pediatric Patients With Recurrent or Progressive Malignant Solid and Central Nervous System TumorsCTID: NCT04525014Phase: Phase 1Status: TerminatedDate: 2024-10-31
REF
- Dinitroazetidines Are a Novel Class of Anticancer Agents and Hypoxia-Activated Radiation Sensitizers Developed from Highly Energetic MaterialsPublication Name: Cancer ResearchPublication Date: 2012-05-14PMID: 22589277DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.can-11-2303
- Properties of delta5-3beta-hydroxysteroid oxidoreductase isolated from Streptomyces griseocarneusPublication Name: Acta microbiologica Academiae Scientiarum HungaricaePublication Date: 1975PMID: 5856
PAT
- Dinitroazetidines Are a Novel Class of Anticancer Agents and Hypoxia-Activated Radiation Sensitizers Developed from Highly Energetic MaterialsPublication Name: Cancer ResearchPublication Date: 2012-05-14PMID: 22589277DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.can-11-2303
- Properties of delta5-3beta-hydroxysteroid oxidoreductase isolated from Streptomyces griseocarneusPublication Name: Acta microbiologica Academiae Scientiarum HungaricaePublication Date: 1975PMID: 5856
- Cyclic nitro compounds, pharmaceutical compositions thereof and uses thereofPublication Number: US-8927527-B2Priority Date: 2005-08-12Grant Date: 2015-01-06
- Cyclic nitro compounds, pharmaceutical compositions thereof and uses thereofPublication Number: US-9226915-B2Priority Date: 2005-08-12Grant Date: 2016-01-05
- Cyclic nitro compounds, pharmaceutical compositions thereof and uses thereofPublication Number: WO-2007022225-A2Priority Date: 2005-08-12
- Cyclic nitro compounds, pharmaceutical compositions thereof and uses thereofPublication Number: US-2022016077-A1Priority Date: 2005-08-12
- Cyclic nitro compounds, pharmaceutical compositions thereof and uses thereofPublication Number: US-11925617-B2Priority Date: 2005-08-12Grant Date: 2024-03-12
- Methods of synthesizing and isolating N-(bromoacetyl)-3,3-dinitroazetidine and a composition including the samePublication Number: US-8471041-B2Priority Date: 2010-02-09Grant Date: 2013-06-25
- Methods of synthesizing and isolating n-(bromoacetyl)-3,3-dinitroazetidine and a composition including the samePublication Number: WO-2011100090-A1Priority Date: 2010-02-09
- Methods of synthesizing and isolating n-(bromoacetyl)-3,3-dinitroazetidine and a composition including the samePublication Number: IL-221141-A0Priority Date: 2010-02-09
- Cyclic nitro compounds, pharmaceutical compositions thereof and uses thereofPublication Number: EP-1924253-A2Priority Date: 2005-08-12
- Cyclic nitro compounds, pharmaceutical compositions thereof and uses thereofPublication Number: EP-1924253-B1Priority Date: 2005-08-12Grant Date: 2014-12-10
SYN
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=WO2011100090&_cid=P11-MHTYGA-61308-1
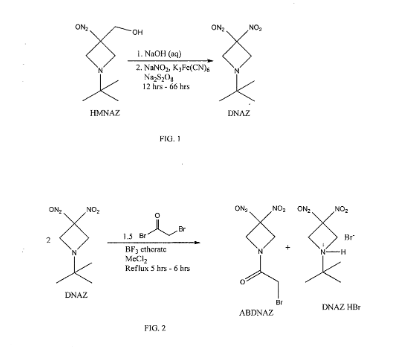
Cyclic nitro compounds, such as ABDNAZ, are being investigated for their potential use in treating cancer. Methods of synthesizing ABDNAZ have been described, such as in United States Patent No. 7,507,842 to Bednarski et al.
(“Bednarski”). In Bednarski, ABDNAZ is synthesized by reacting
l-½rt-butyl-3,3-dinitroazetidine (DNAZ) with bromoacetyl bromide and boron trifluoride etherate. For every mole of ABDNAZ produced, a mole of a hydrogen bromide salt of DNAZ (DNAZ HBr) is also produced as a coproduct. The ABDNAZ is isolated from the DNAZ HBr by cooling the reaction mixture, adding
dichloromethane, and filtering the DNAZ HBr. Solid DNAZ HBr is sensitive to impact, friction, and other external stimuli and, therefore, must be handled carefully. The dichloromethane filtrate is washed with water, dried, and then the dichloromethane is evaporated, producing a crude ABDNAZ mixture. The product is washed sequentially with diethyl ether and dried under vacuum, yielding ABDNAZ that is approximately 98% pure and at a yield of approximately 75% (based on bromoacetyl bromide). The 2% of impurities remaining in the ABDNAZ are believed to include
bromoacetic acid, unreacted DNAZ, and DNAZ HBr. This method of producing ABDNAZ is referred to herein as the Bednarski process. While the Bednarski process provides ABDNAZ at a reasonable purity and yield, the purity is not sufficient for pharmaceutical uses. In addition, solid DNAZ HBr produced during the Bednarski process is an explosive compound, which adds to the complexity of producing
Example 2
Synthesis of ABDNAZ from DNAZ
A three neck round bottom flask (3 L) equipped with a magnetic stir bar and a water jacketed reflux condenser was charged with the dichloromethane solution of DNAZ (produced as described in Example 1). A nitrogen gas purge of the apparatus was initiated and, after ten minutes, boron trifluoride diethyletherate (6.37 mL, 52 mmol) was added, followed by bromoacetyl bromide (33.77 mL, 388 mmol). The flask was sealed, except for a small vent at the top of the condenser, and the solution was heated to a mild reflux. After six hours (± 0.5 hour), heating was stopped and dichloromethane (1000 mL) and distilled water (800 mL) were added, in that order, to the heterogeneous mixture. The two-phase system was stirred vigorously for sixteen hours, until all solids (DNAZ HBr) were dissolved. The two-phase system was then transferred to a separatory funnel. The aqueous phase was removed and the organic phase was washed with additional distilled water (4 x 500 mL). The organic phase was dried with sodium sulfate (100 g – 150 g) and then transferred to a single neck, round bottom flask. The solution was concentrated on a rotary evaporator to approximately half of its initial volume and then ethanol (250 mL) was added. The remaining dichloromethane was removed by a rotary evaporator, causing precipitation of clear, colorless crystals. The flask was chilled in an ice bath for thirty minutes. The precipitate was isolated by vacuum filtration, rinsed with additional cold ethanol (5 x 150 mL), and dried to afford pure ABDNAZ (56.04 g, 81% yield): Ή NMR
(d6-acetone) δ 4.02 (s, 2H, -CH2Br ), 4.96 (br s, 2H, ring -CH2), 5.36 (br s, 2H, ring -CH2); 13C NMR (d6-acetone) δ 25.58, 58.58, 60.53, 107.69, 167.48.
SYN
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=WO2007022225&_cid=P11-MHTYDP-59218-1
Example 5: Synthesis of ABDNAZ
[00139] A 25 ml, three-neck, round bottom flask was charged with 7 ml of methylene chloride and 2.50 g (12.3 mmol) of t-BuDNAZ prepared as described in Archibald et at, Journal of Organic Chemistry, 1990, 2920. Under nitrogen, 0.16 ml (1.23 mmol) of boron trifluoride etherate was added. After stirring 5 min. at ambient temperature, 0.54 ml (6.15 mol) of bromoacetyl bromide was added. The solution was heated between 50-600C for 2 h. The darkened reaction mixture was cooled to ambient temperature, diluted with 50 ml methylene chloride, and filtered. The solid was identified as the HBr salt of t-BuDNAZ. The methylene chloride filtrate was washed with two 20 ml portions of water, dried over sodium sulfate, filtered, and evaporated under reduced pressure. The resultant solid was washed with three 20 ml portions of ethyl ether and dried under vacuum to yield 1.24 g (75.2% based on bromoacetyl bromide) of BrADNAZ as a white solid (mp = 124-1250C). 1H NMR (CDCl3): δ 3.76 (s, 2H), 4.88 (br s, 2H), 5.14 (br s, 2H); 13C NMR (CDCl3): δ 165.2, 105.0, 59.72, 57.79, 23.90. CaIc. for C5H6BrN3O5: %C 22.41, %H 2.26, %N 15.68; Found: %C 22.61, %H 2.36, %N 15.58.
HPLC/MS C-8 reverse phase column with acetonitrile/water mobile phase – m/e 266.95 (100%), 268.95 (98.3%). FT-IR 3014.24 (weak), 1677.66, 1586.30, 1567.65, 1445.55 (NO2), 1367.80, 1338.00, 1251.27 cm‘1.



AS ON OCT2025 4.511 LAKHS VIEWS ON BLOG WORLDREACH AVAILABLEFOR YOUR ADVERTISEMENT

join me on Linkedin
Anthony Melvin Crasto Ph.D – India | LinkedIn
join me on Researchgate
RESEARCHGATE

join me on Facebook
Anthony Melvin Crasto Dr. | Facebook
join me on twitter
Anthony Melvin Crasto Dr. | twitter
+919321316780 call whatsaapp
EMAIL. amcrasto@gmail.com

……
References
- Oronsky B, Takahashi L, Gordon R, Cabrales P, Caroen S, Reid T (2023). “RRx-001: a chimeric triple action NLRP3 inhibitor, Nrf2 inducer, and nitric oxide superagonist”. Frontiers in Oncology. 13 1204143. doi:10.3389/fonc.2023.1204143. PMC 10258348. PMID 37313460.
- Jayabalan N, Oronsky B, Cabrales P, Reid T, Caroen S, Johnson AM, et al. (April 2023). “A Review of RRx-001: A Late-Stage Multi-Indication Inhibitor of NLRP3 Activation and Chronic Inflammation”. Drugs. 83 (5): 389–402. doi:10.1007/s40265-023-01838-z. PMC 10015535. PMID 36920652.
- Ryan C (30 March 2023). “FDA Grants Fast Track Designation to RRx-001 for Severe Oral Mucositis in Head and Neck Cancer”. OncLive.
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Rrx-001 |
| Identifiers | |
| IUPAC name | |
| CAS Number | 925206-65-1 |
| PubChem CID | 15950826 |
| DrugBank | DB12060 |
| ChemSpider | 13092644 |
| UNII | 7RPW6SU9SC |
| KEGG | D12720 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL3526802 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C5H6BrN3O5 |
| Molar mass | 268.023 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | Interactive image |
| SMILES | |
| InChI | |
/////////Nibrozetone, anti-inflammatory, RRx-001, RRx 001, ABDNAZ














