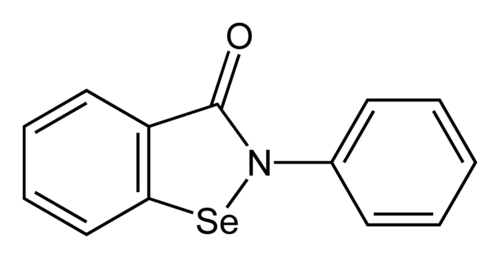
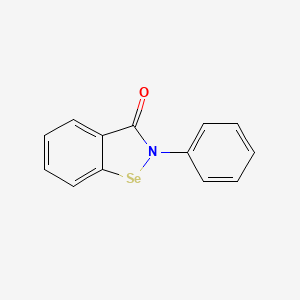
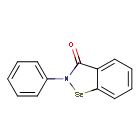
Ebselen
274.19 g/mol,
C13H9NOSe
2-phenyl-1,2-benzoselenazol-3-one
- CAS 60940-34-3
- 2-phenyl-1,2-benzoselenazol-3-one
- 2-Phenyl-1,2-benzisoselenazol-3(2H)-one
- Ebselene
- PZ 51, DR3305, and SPI-1005
- 40X2P7DPGH
Ebselen is a benzoselenazole that is 1,2-benzoselenazol-3-one carrying an additional phenyl substituent at position 2. Acts as a mimic of glutathione peroxidase. It has a role as a neuroprotective agent, an apoptosis inducer, an anti-inflammatory drug, an antioxidant, a hepatoprotective agent, a genotoxin, a radical scavenger, an enzyme mimic, an EC 1.3.1.8 [acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (NADP(+))] inhibitor, an EC 1.8.1.12 (trypanothione-disulfide reductase) inhibitor, an EC 1.13.11.33 (arachidonate 15-lipoxygenase) inhibitor, an EC 1.13.11.34 (arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase) inhibitor, an EC 2.5.1.7 (UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 1-carboxyvinyltransferase) inhibitor, an EC 2.7.10.1 (receptor protein-tyrosine kinase) inhibitor, an EC 3.5.4.1 (cytosine deaminase) inhibitor, an EC 5.1.3.2 (UDP-glucose 4-epimerase) inhibitor, a ferroptosis inhibitor, an antifungal agent, an EC 3.4.22.69 (SARS coronavirus main proteinase) inhibitor, an anticoronaviral agent, an antibacterial agent, an antineoplastic agent and an EC 3.1.3.25 (inositol–phosphate phosphatase) inhibitor.
Ebselen (also called PZ 51, DR3305, and SPI-1005), is a synthetic organoselenium molecule under preliminary investigation as a drug candidate.[1] It belongs to the class of compounds related to benzene and its derivatives.[1] It is being developed by the Seattle biotechnology company, Sound Pharmaceuticals, Inc.[1] It has also been reported to target tubulin, blocking its polymerization.[2]
Ebselen has been investigated for the treatment and basic science of Meniere’s Disease, Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, and Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus.
Ebselen has been entered into clinical trials as a lead compound intended for the potential treatment of various diseases.[3] Its most advanced clinical trial is a Phase III study in people with Meniere’s disease, completed in July 2024.[4]
In vitro, ebselen is a mimic of glutathione peroxidase and reacts with peroxynitrite.[5] It is purported to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.[1][5]
Synthesis
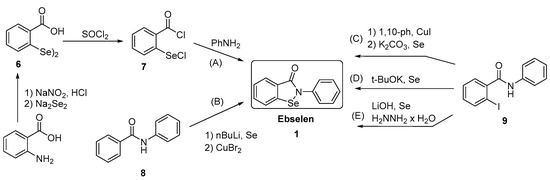
Generally, synthesis of the characteristic scaffold of ebselen, the benzoisoselenazolone ring system, can be achieved either through reaction of primary amines (RNH2) with 2-(chloroseleno)benzoyl chloride (Route I),[6] by ortho-lithiation of benzanilides followed by oxidative cyclization (Route II) mediated by cupric bromide (CuBr2),[7] or through the efficient Cu-catalyzed selenation / heterocyclization of o-halobenzamides, a methodology developed by Kumar et al.[8] (Route III).

SYN
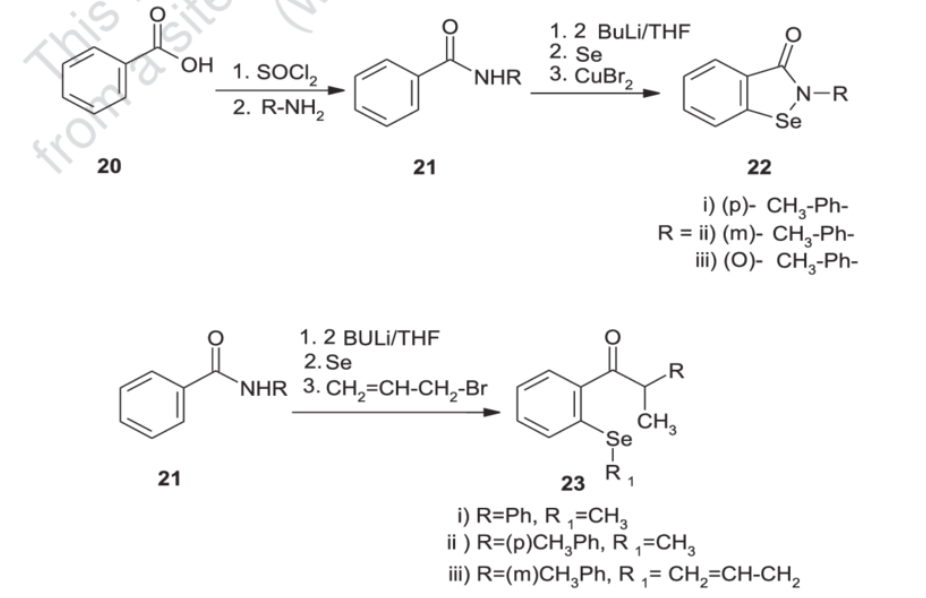
Synthesis of ebselen from benzoic acid by ortholithiation of benzanilide SOCl 2 =Thionyl chloride, R-NH 2 =Substituted aryl mine, BuLi/THF=n-butyllithium/ tetrahydrofuran, CuBr 2 =Cupper bromide, CH 2 =CH- CH 2 -Br = Allyl bromide.
SYN
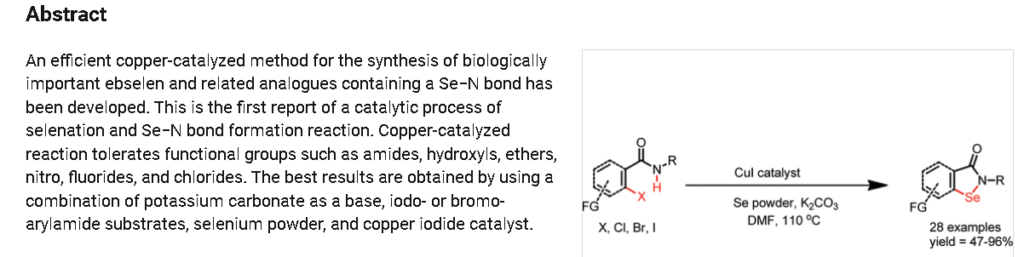
New Chiral Ebselen Analogues with Antioxidant and Cytotoxic Potential
Molecules, March 2017, 22(3):492
SYN
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/ol102027j
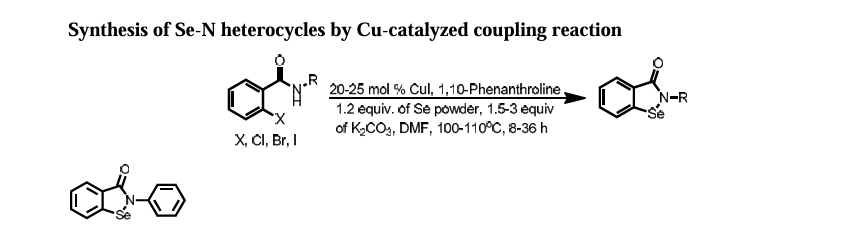
2-Phenylbenzo[d][1,2]selenazol-3(2H)-one (1) from 2-Iodo-N-phenylbenzamide (Typical
Procedure): Copper iodide (114 mg, 0.6 mmol) and 1,10-phenanthroline (108 mg, 0.6 mmol)
were added into DMF (3 mL) in a single neck flask. Resulted brownish solution was stirred for
15 min and then 2-iodo-N-phenylbenzamide1 (0.97 g, 3.0 mmol), selenium powder (0.29 g, 3.6
mmol), and potassium carbonate powder (0.65 g, 4.7 mmol) were added sequentially to same reaction flask. Brown colored reaction mixture was refluxed at 110oC using refluxing condenser
under nitrogen atmosphere. Progress of reaction was monitored by TLC. Reaction mixture was
refluxed for 8h. After this, reaction mixture poured over brine solution (60 mL) and stirred for 3
h. Product was precipitated as white solid which was collected by filtration over Buchner funnel,
product was washed with water (15 mL x 2), dried in air, dissolved in ethyl acetate, concentrated
over rotary evaporator, resulted brown solid which was purified by column chromatography
using hexane/ ethyl acetate (8:2) over silica gel. Yield 0.69 g (84%), mp 182-183 °C (180-181
°C).14,15 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) 8.09 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 7.91 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H),
7.71-7.62 (m, 3H), 7.51-7.43 (m, 3H), 7.28 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3)
8.12 (d, 7.6 Hz, 1H), 7.68-7.62 (m, 4H), 7.52-7.41 (m, 3H), 7.29 (m, 1H). IR (plate): 3057, 2921,
1598, 1443, 1346, 1263, 1028 cm-1; ESMS m/z: 276 (M+H+).
2-Phenylbenzo[d][1,2]selenazol-3(2H)-one (1) from 2-Iodo-N-phenylbenzamide at 74 mmol
scale: Reaction was carried out at 74 mmol scale using 2-iodo-N-phenylbenzamide (24.00 g,
74.3 mmol), selenium powder (7.04 g, 89.1 mmol), CuI (2.83 g, 14.9 mmol), 1,10
phenanthroline (2.69 g, 14.9 mmol), and anhydrous potassium carbonate powder (15.40 g, 111.4
mmol) in DMF (50 mL) and procedure and workup followed are similar to 3.6 mmol scale
reaction. Yield 16.28 g (80%), Figure S1.
2-Phenylbenzo[d][1,2]selenazol-3(2H)-one (1) from 2-Bromo-N-phenylbenzamide: Ebselen 1
was prepared from 2-bromo-N-phenylbenzamide2 (1.00 g, 3.6 mmol), selenium powder (0.34 g,
4.3 mmol), K2CO3 powder (0.74 g, 5.4 mmol), CuI (137 mg, 0.7 mmol), and 1,10-phenanthroline
(130 mg, 0.7 mmol) in DMF (3 mL). Reaction mixture was refluxed for 16 h at 110oC. Progress of reaction was monitored by TLC. After completion of reaction, mixture was poured into brine
solution (60 mL) and the resulted white precipitate was washed with water (20 mL x 2), and
dried in air. Purification by column chromatography on silica gel using CH2Cl2 provided white
crystalline solid (0.77 g, 78%).
2-Phenylbenzo[d][1,2]selenazol-3(2H)-one (1) from 2-Chloro-N-phenylbenzamide: Reaction
was carried out at 4 mmol scale using 2-chloro-N-phenylbenzamide3 (1.00 g, 4.3 mmol), CuI
(172 mg, 0.9 mmol), 1,10-phenanthroline (162 mg, 0.9 mmol), selenium powder (0.41 g, 5.2
mmol), K2CO3 (0.89 g, 6.4 mmol) in DMF (4 mL). Reaction mixture was refluxed for 24 h at
110oC. Workup procedure is similar as followed for bromo substrate. Yield 0.55 g (47%).
History
The first patent for 2-phenyl-1,2-benzoselenazol-3(2H)-one was filed in 1980 and granted in 1982.[9]
Research
Ebselen is in preliminary clinical development for the potential treatment of hearing loss and depression, among other medical indications.[3][10]



AS ON JUNE2025 4.45 LAKHS VIEWS ON BLOG WORLDREACH AVAILABLEFOR YOUR ADVERTISEMENT

join me on Linkedin
Anthony Melvin Crasto Ph.D – India | LinkedIn
join me on Researchgate
RESEARCHGATE

join me on Facebook
Anthony Melvin Crasto Dr. | Facebook
join me on twitter
Anthony Melvin Crasto Dr. | twitter
+919321316780 call whatsaapp
EMAIL. amcrasto@gmail.com

……
References
- “Ebselen”. DrugBank. 29 January 2025. Retrieved 4 February 2025.
- Baksheeva VE, La Rocca R, Allegro D, Derviaux C, Pasquier E, Roche P, Morelli X, Devred F, Golovin AV, Tsvetkov PO (2025). “NanoDSF Screening for Anti-tubulin Agents Uncovers New Structure–Activity Insights”. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5c01008.
- “Ebselen pipeline”. Sound Pharmaceuticals, Inc. 2025. Retrieved 4 February 2025.
- “SPI-1005 for the Treatment of Meniere’s Disease (STOPMD-3)”. ClinicalTrials.gov, US National Library of Medicine. 1 August 2024. Retrieved 4 February 2025.
- Schewe T (October 1995). “Molecular actions of ebselen – an antiinflammatory antioxidant”. General Pharmacology. 26 (6): 1153–69. doi:10.1016/0306-3623(95)00003-J. PMID 7590103.
- Kamigata N, Iizuka H, Izuoka A, Kobayashi M (July 1986). “Photochemical Reaction of 2-Aryl-1, 2-benzisoselenazol-3 (2 H)-ones”. Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan. 59 (7): 2179–83. doi:10.1246/bcsj.59.2179.
- Engman L, Hallberg A (1989-06-01). “Expedient synthesis of ebselen and related compounds”. The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 54 (12): 2964–2966. doi:10.1021/jo00273a035. ISSN 0022-3263.
- Balkrishna SJ, Bhakuni BS, Chopra D, Kumar S (December 2010). “Cu-catalyzed efficient synthetic methodology for ebselen and related Se-N heterocycles”. Organic Letters. 12 (23): 5394–7. doi:10.1021/ol102027j. PMID 21053969.
- DE3027073A1, Etschenberg, Eugen Dr; Renson, Marcel Prof Dipl-Chem Jupille & Winkelmann, Johannes Dr 5000 Köln, “2-phenyl-1,2-benzisoselenazol-3(2h)-on enthaltende pharmazeutische praeparate und ihre verwendung”, issued 1982-02-18
- “Ebselen search: list of clinical trials sponsored by Sound Pharmaceuticals”. ClinicalTrials.gov, US National Library of Medicine. 2025. Retrieved 4 February 2025.
External links
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name2-Phenyl-1,2-benzoselenazol-3(2H)-one | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 60940-34-3 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | Interactive imageInteractive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:77543 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL51085 |
| ChemSpider | 3082 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.132.190 |
| PubChem CID | 3194 |
| UNII | 40X2P7DPGH |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DTXSID7045150 |
| InChI | |
| SMILES | |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C13H9NOSe |
| Molar mass | 274.17666 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
References
- Zhou Y, Zhang Y, Zhao D, Yu X, Shen X, Zhou Y, Wang S, Qiu Y, Chen Y, Zhu F: TTD: Therapeutic Target Database describing target druggability information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Jan 5;52(D1):D1465-D1477. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad751. [Article]
////////Ebselen, Ebselene, PZ 51, DR 3305, SPI 1005, PHASE 3, 40X2P7DPGH, Meniere’s Disease, Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus














