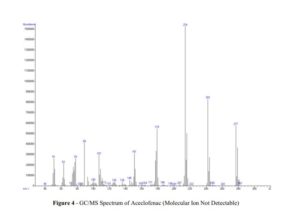
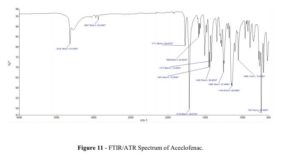
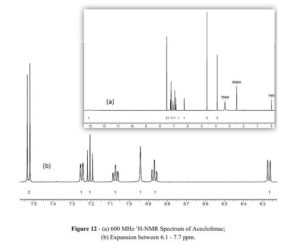
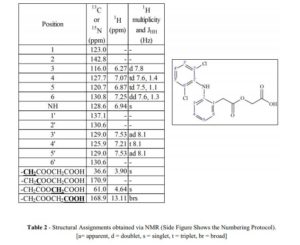
Aceclofenac
アセクロフェナク
- Molecular FormulaC16H13Cl2NO4
- Average mass354.185 Da
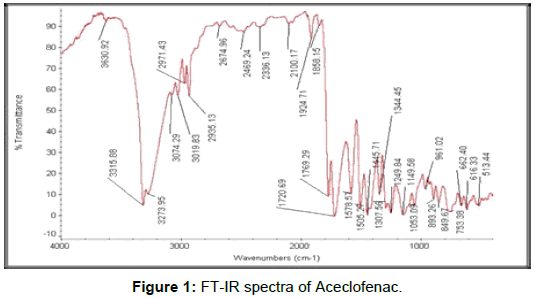


Characterization of Aceclofenac by 1H NMR spectroscopy
1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 3.896 (s, 2H, Aliphatic –CH2), 4.634 (s, 2H, Aliphatic –CH2), 6.279 (d J= 8.00HZ, 1H, Aromatic), 6.887 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 6.936 (s, 1H, NH), 7.039(t, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H, Aromatic), 7.225 (t J= 8.00 HZ, 1H, Aromatic), 7.260 (d J= 8.00 HZ, 1H, Aromatic), 7.537 (d J= 8.4HZ, 2H, Aromatic), 13.076 (s, 1H, Carboxylic acid) …https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2214180417301290
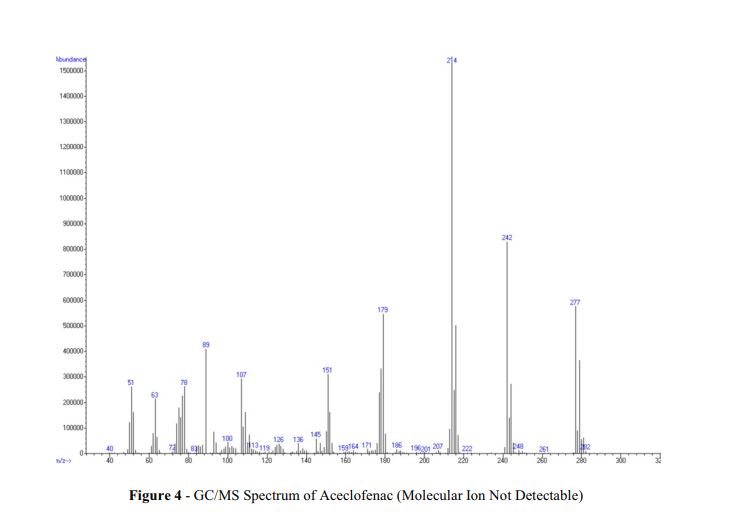
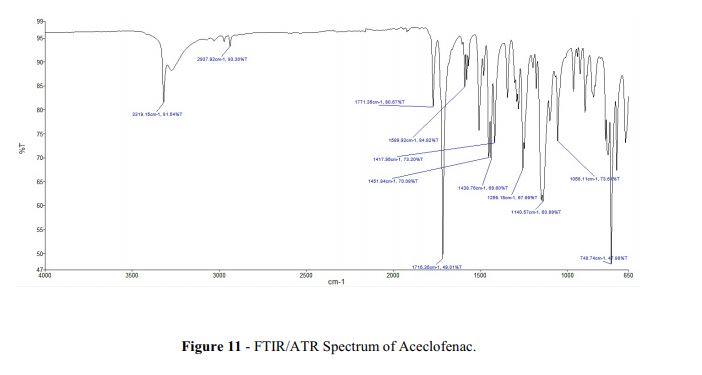
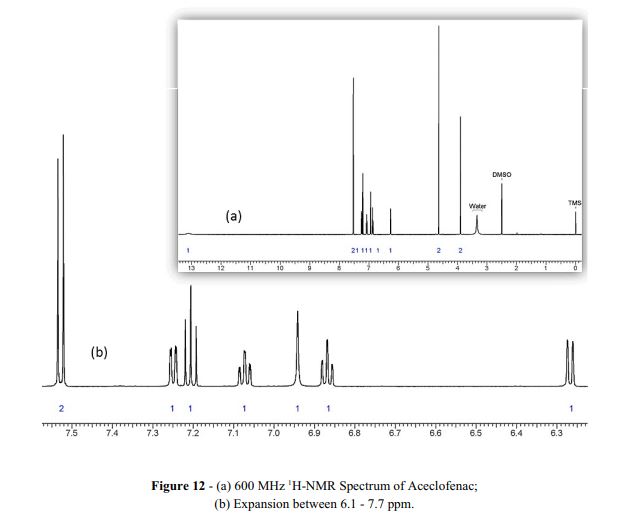
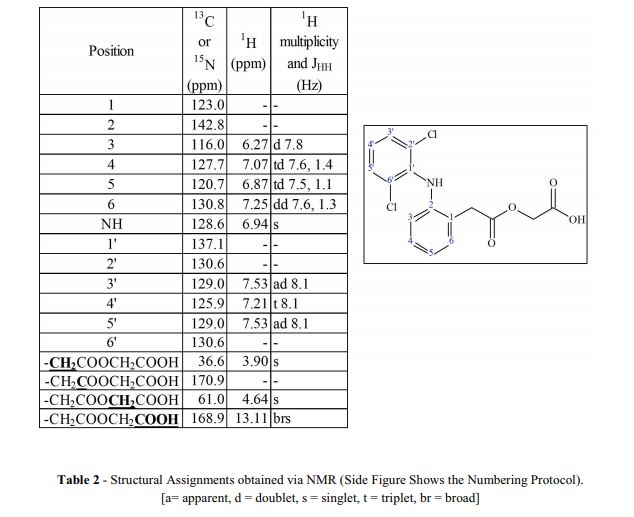
https://www.dea.gov/sites/default/files/pr/microgram-journals/2014/mj11-1_29-41.pdf
Aceclofenac is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) analog of diclofenac. It is used for the relief of pain and inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis and ankylosing spondylitis.
Aceclofenac (C16H13Cl2NO4), chemically [(2-{2, 6-dichlorophenyl) amino} phenylacetooxyacetic acid], is a crystalline powder with a molecular weight of 354.19. It is practically insoluble in water with good permeability. It is metabolized in human hepatocytes and human microsomes to form [2-(2′,6′-dichloro-4′-hydroxy- phenylamino) phenyl] acetoxyacetic acid as the major metabolite, which is then further conjugated. According to the Biopharmaceutical Classification System (BCS) drug substances are classified to four classes upon their solubility and permeability. Aceclofenac falls under the BCS Class II, poorly soluble and highly permeable drug.[1]
Aceclofenac works by inhibiting the action of cyclooxygenase (COX) that is involved in the production of prostaglandins (PG) which is accountable for pain, swelling, inflammation and fever. The incidence of gastric ulcerogenicity of aceclofenac has been reported to be significantly lower than that of the other frequently prescribed NSAIDs, for instance, 2-folds lesser than naproxen, 4-folds lesser than diclofenac, and 7-folds lesser than indomethacin.
Aceclofenac should not be given to people with porphyria or breast-feeding mothers, and is not recommended for children. It should be avoided near term in a pregnant woman because of the risk of having a patent ductus arteriosus in the neonate.

SYN
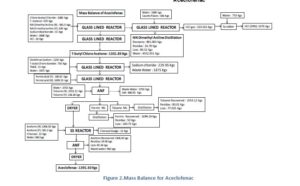
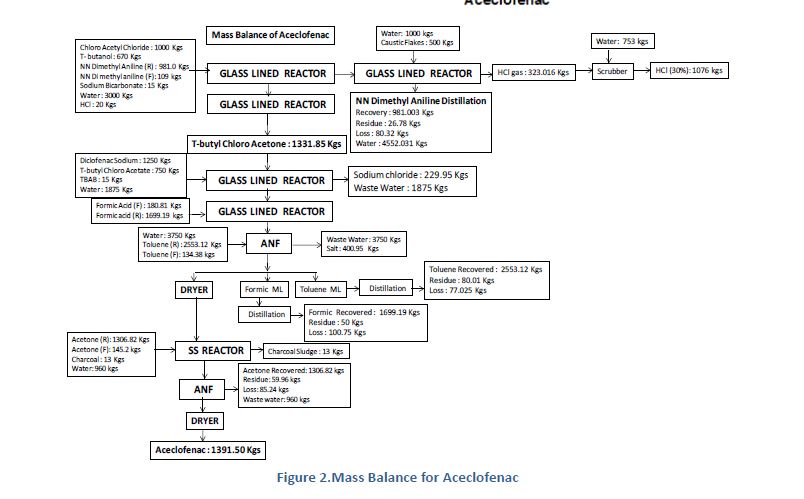
Manufacturing Process for Aceclofenac
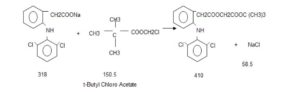
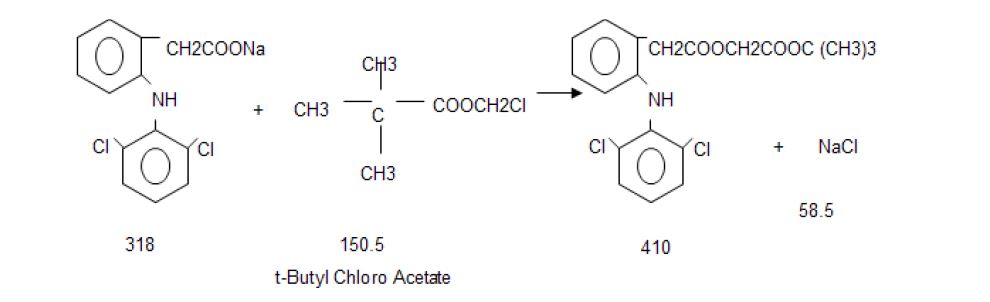
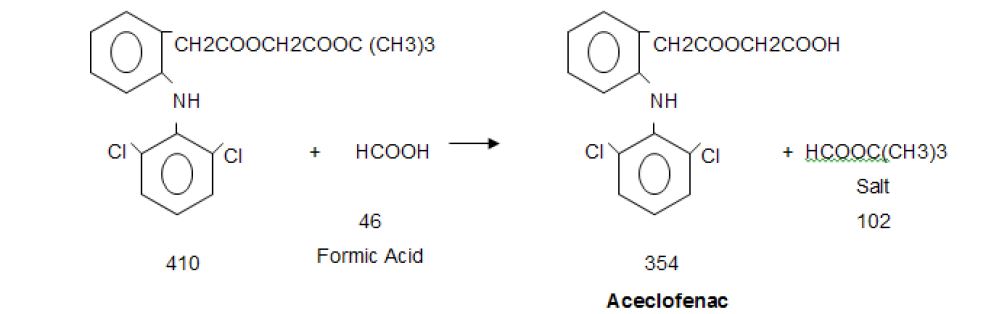
Stage-1
T Butanol and Chloro Acetyl Chloride react in presence of NN Dimethyl Aniline at low temperature. After reaction
organics mass wash with water and sodium bicarbonate solution to get stage-1
Stage-2
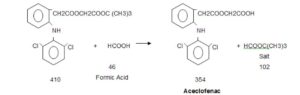
Stage-I react with Diclofenac Sodium in presence of TBAB in Toluene media, further react with formic acid and
reaction mass quenching in water and product is isolated by filtration. Finally Crude Aceclofenac purified in ethyl
acetate and charcoal. Pure product isolated by filtration.
SYN’
EP 0119932; US 4548952
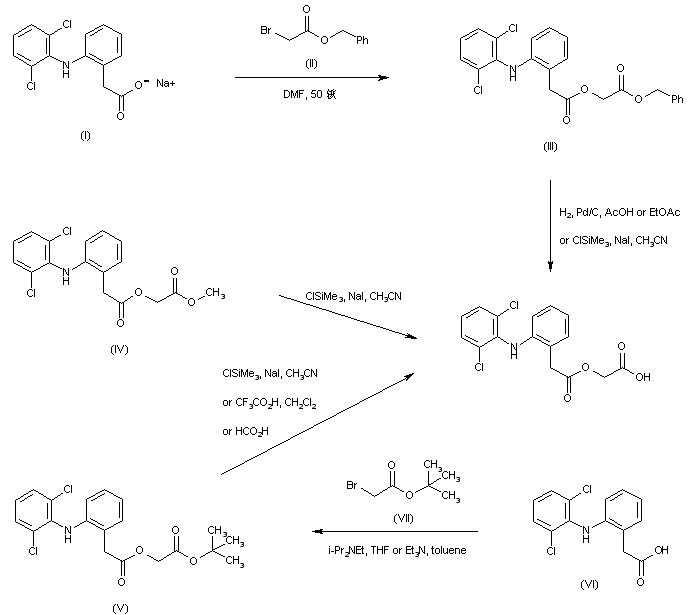
Alkylation of the sodium salt of diclofenac (I) with benzyl bromoacetate (II) in hot DMF yielded the (arylacetoxy)acetate (III). Subsequent hydrogenolysis of the benzyl ester of (III) in the presence of Pd/C gave the title carboxylic acid. Alternatively, the benzyl ester group of (III) was cleaved by means of the combination of chlorotrimethylsilane and sodium iodide. This method of selective ester hydrolysis with in situ generated iodotrimethylsilane was also applied to the corresponding methyl (IV) and tert-butyl (V) esters. In a related procedure, tert-butyl ester (V) was prepared by alkylation of diclofenac (VI) with tert-butyl bromoacetate (VII) in the presence of tertiary amines. Selective cleavage of the tert-butyl ester group of (V) was then performed by treatment with either trifluoroacetic or formic acid.
SYN
| ES 2046141 |
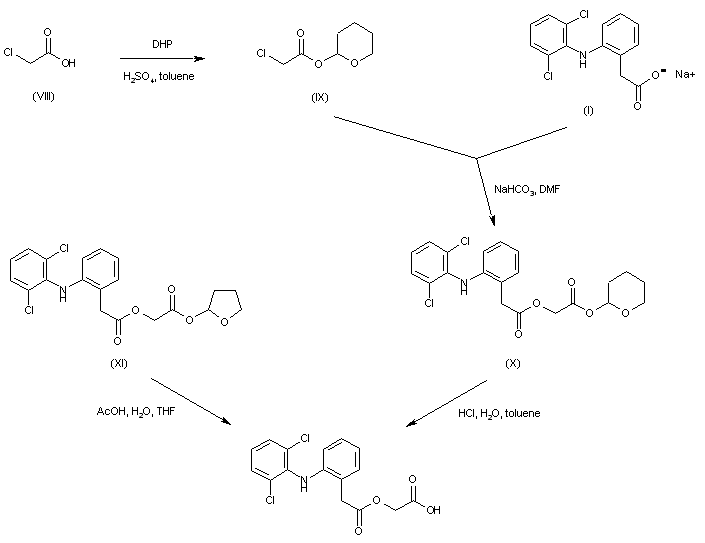
Aceclofenac was prepared by selective hydrolysis of other labile ester precursors. Alkylation of diclofenac sodium (I) with tetrahydropyranyl chloroacetate (IX), prepared by protection of chloroacetic acid (VIII) with dihydropyran, furnished the tetrahydropyranyl ester of aceclofenac (X), which was then deprotected by treatment with HCl. Similarly, the preparation of aceclofenac was reported by acidic hydrolysis of the analogous tetrahydrofuranyl ester (XI).
References
- ^ Karmoker, J.R.; Sarkar, S.; Joydhar, P.; Chowdhury, S.F. (2016). “Comparative in vitro equivalence evaluation of some Aceclofenac generic tablets marketed in Bangladesh” (PDF). The Pharma Innovation Journal. 5: 3–7. Retrieved 2016-09-01.
- Sources
- British National Formulary 55, March 2008; ISBN 978-0-85369-776-3 p. 537
References
-
- EP 119 932 (Prodes; appl. 19.3.1984; E-prior. 21.3.1983).
- US 4 548 952 (Prodes; 22.10.1985; appl. 15.3.1984; E-prior. 21.3.1983).
-
Alternative synthesis:
- ES 2 020 146 (Prodesfarma; appl. 29.5.1990).
- ATC:M01AB16
- Use:non-steroidal anti-inflammatory, analgesic, non-selective cyclooxigenase inhibitor
- Chemical name:2-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino]benzeneacetic acid carboxymethyl ester
- Formula:C16H13Cl2NO4
- MW:354.19 g/mol
- CAS-RN:89796-99-6
- InChI Key:MNIPYSSQXLZQLJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
- InChI:InChI=1S/C16H13Cl2NO4/c17-11-5-3-6-12(18)16(11)19-13-7-2-1-4-10(13)8-15(22)23-9-14(20)21/h1-7,19H,8-9H2,(H,20,21)
- LD50:121 mg/kg (M, p.o.)
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Hifenac, Cincofen, Zerodol, Nacsiv, Acenac, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration |
oral, topical |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.169.686 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C16H13Cl2NO4 |
| Molar mass | 353.02161 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
//////////Aceclofenac, ацеклофенак , أسيكلوفيناك , 醋氯芬酸 , アセクロフェナク