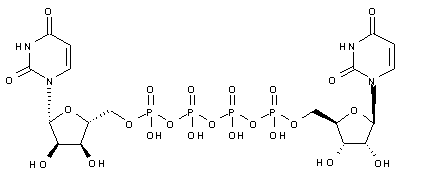
Diquafosol
- Molecular FormulaC18H26N4O23P4
- Average mass790.307 Da
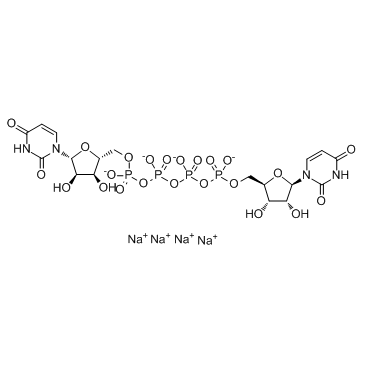
Diquafosol tetrasodium
- Molecular FormulaC18H22N4Na4O23P4
- Average mass878.234 Da
- Company:
- Santen (Originator)
- Sales:
- $80 Million (Y2015);

$71.7 Million (Y2014);
$79.3 Million (Y2013);
$67.1 Million (Y2012);
$36 Million (Y2011); - ATC Code:
- S01
Diquafosol tetrasodium was approved by Pharmaceuticals Medical Devices Agency of Japan (PMDA) on April 16, 2010. It was developed and marketed as Diquas® by Santen Pharmaceutical Corporation in Japan.
Diquafosol tetrasodium is a P2Y2 purinoceptor receptor agonist. It is indicated for improve dry eye symptoms by promoting secretion of mucin and water, thereby bringing the tear film closer to a normal state. No serious ocular or systemic adverse drug reactions were found during the clinical trials. Dry eye begins with symptoms of ocular discomfort such as burning, stinging or a foreign body sensation.
Diquas® is available as solution for ophthalmic use, containing 3% of Diquafosol tetrasodium. The recommended dose is 1 drop at a time, 6 times a day.
Index:
Diquafosol (tradename Diquas) is a pharmaceutical drug for the treatment of dry eye disease. It was approved for use in Japan in 2010.[1] It is formulated as a 3% ophthalmic solution of the tetrasodium salt.
Its mechanism of action involves agonism of the P2Y2 purinogenic receptor.[2]
SYN
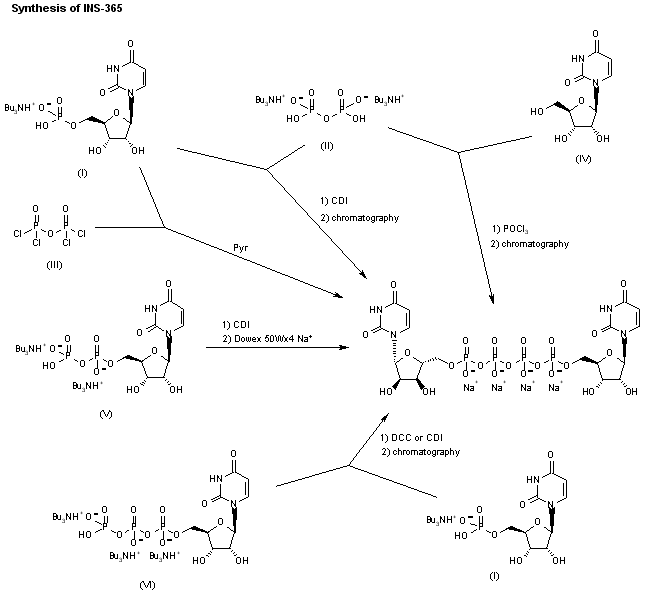
INS-365 can also been obtained by the following ways: 4) Dimerization of uridine-5′-monophosphate tributyl-ammonium salt (I) with bis(tributylammonium) pyrophosphate (II) by means of CDI, followed by purification by semipreparative ion璭xchange chromatography. 5) Dimerization of uridine-5′-monophosphate tributyl-ammonium salt (I) with pyrophosphoryl chloride (III) in pyridine, followed by chromatographic purification as before. 6) Condensation of uridine (IV) with POCl3 and bis(tributylammonium) pyrophosphate (II) by means of tributylamine in trimethyl phosphate, followed by chromatographic purification as before. 7) Dimerization of uridine-5′-diphosphate tributylammonium salt (V) by means of CDI in DMF, followed by purification over Dowex 50Wx4 Na+. 8) Condensation of uridine-5′-triphosphate tributylammonium salt (VI) with uridine-5′-monophosphate tributyl-ammonium salt (I) by means of DCC in DMF, followed by chromatographic purification as before. 9) Reaction of uridine-5′-monophosphate tributylammonium salt (I) with CDI in DMF, followed by condensation with uridine-5′-triphosphate (VI) and chromatographic purification as before.
CLIP
1. WO1999005155.
1. WO2014103704.
SYN
Practical and Efficient Approach to the Preparation of Diquafosol Tetrasodium
- Pengfei Xu
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/suppl/10.1021/acs.oprd.0c00209/suppl_file/op0c00209_si_001.pdf
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.oprd.0c00209
A scalable and practical route to synthesize the P2Y2 receptor agonist diquafosol tetrasodium has been described. Diquafosol tetrasodium was obtained via a four-step process starting from commercially available 5′-uridylic acid disodium salt. The whole procedure gives the target product in a 45% overall yield with high purity (>99%). Key steps in this process including isolation of impurities and the target product by using anion-exchange resin are discussed in detail. The optimized process has been successfully demonstrated on a large scale to support the development of diquafosol tetrasodium in China.



References
- ^ “Santen and Inspire Announce Approval of DIQUAS for Dry Eye Treatment in Japan”. April 16, 2010.
- ^ Pendergast, W; Yerxa, BR; Douglass Jg, 3rd; Shaver, SR; Dougherty, RW; Redick, CC; Sims, IF; Rideout, JL (2001). “Synthesis and P2Y receptor activity of a series of uridine dinucleoside 5′-polyphosphates”. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 11 (2): 157–60. doi:10.1016/S0960-894X(00)00612-0. PMID 11206448.
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
[[[[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(2,4-Dioxopyrimidin-1-yl)-3,4-dihydroxy-tetrahydrofuran-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxy-phosphoryl]oxy-hydroxy-phosphoryl]oxy-hydroxy-phosphoryl] [(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(2,4-dioxopyrimidin-1-yl)-3,4-dihydroxy-tetrahydrofuran-2-yl]methyl hydrogen phosphate
|
|
| Other names
P1,P4-Bis(5′-uridyl) tetraphosphate; INS-365; Diquafosol tetrasodium
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
|
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| Properties | |
| C18H26N4O23P4 | |
| Molar mass | 790.306 g·mol−1 |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
| Infobox references | |
///////////// INS 365, Diquafosol, INS-365, DE 089, KPY 998, JAPAN 16
| 59985-21-6 (Diquafosol ); 211427-08-6 (Diquafosol Tetrasodium); |



















