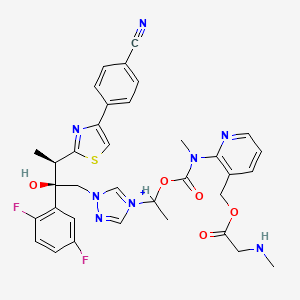

| MOLECULAR FORMULA: | C35H36F2N8O9S2 |
|---|---|
| MOLECULAR WEIGHT: | 814.837 g/mol |


Syn……https://newdrugapprovals.org/2013/10/02/isavuconazole-basilea-reports-positive-results-from-study/
PRODUCT PATENT
https://patents.google.com/patent/US6300353
InventorTadakatsu HayaseShigeyasu IchiharaYoshiaki IsshikiPingli LiuJun OhwadaToshiya SakaiNobuo ShimmaMasao TsukazakiIsao UmedaToshikazu Yamazaki
Current Assignee Basilea Pharmaceutica International Ltd Original
AssigneeBasilea Pharmaceutica AG Priority date 1998-03-06
https://patents.google.com/patent/WO1999045008A1/en
POLYMORPHS OF BASE
WO 2016055918
https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2016055918A1/en
PATENT
IN 2014MU03189
WOCKHARDT
Isavuconazole, isavuconazonium, Voriconazole, and Ravuconazole are azole derivatives and known as antifungal drugs for treatment of systemic mycoses as reported in US 5,648,372, US 5,792,781, US 6,300,353 and US 6,812,238. The US patent No. 6,300,353 discloses Isavuconazole and its process. It has chemical name [(2R,3R)-3-[4-(4-cyanophenyl)thiazol-2-yl)]-1-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-2-(2,5- difluorophenyl)-butan-2-ol;
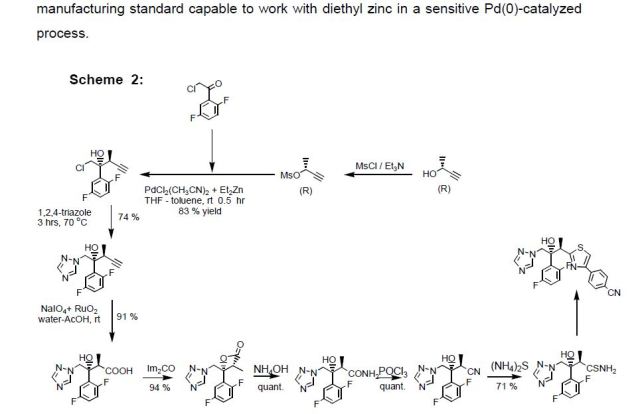
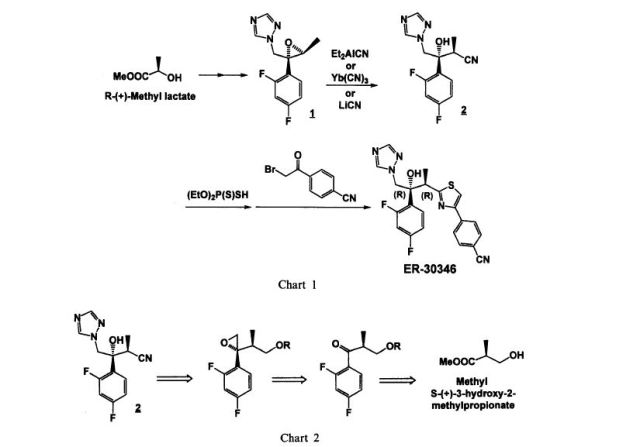
The Isavuconazonium iodide hydrochloride and Isavuconazonium sulfate can be prepared according to known methods, e.g. pending Indian Patent Applications IN 2424/MUM/2014 and IN 2588/MUM/2014.
Example-1: Preparation of Amorphous Isavuconazole
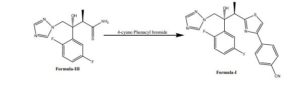
4-cyano Phenacyl bromide F F N N N OH N S CN Formula-I Formula-III In a round bottomed flask charged ethanol (250 ml), thioamide compound of formula-II (25.0 gm) and 4-cyano phenacyl bromide (18.4 gm) under stirring. The reaction mixture were heated to 70 0C. After completion of reaction the solvent was removed under vacuum distillation and water (250 ml) and Ethyl acetate (350 ml) were added to reaction mass. The reaction mixture was stirred and its pH was adjusted between 7 to 7.5 by 10 % solution of sodium bicarbonate. The layer aqueous layer was discarded and organic layer was washed with saturated sodium chloride solution (100 ml) and concentrated under vacuum to get residue. The residue was suspended in methyl tert-butyl ether (250 ml) and the reaction mixture was heated to at 40°C to make crystals uniform and finally reaction mass is cooled to room temperature filtered and washed with the methyl tert-butyl ether. The product was isolated dried to get pale yellowish solid product. Yield: 26.5 gm HPLC purity: 92.7%
CLIP
March 6, 2015
Release
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration today approved Cresemba (isavuconazonium sulfate), a new antifungal drug product used to treat adults with invasive aspergillosis and invasive mucormycosis, rare but serious infections.
Aspergillosis is a fungal infection caused by Aspergillus species, and mucormycosis is caused by the Mucorales fungi. These infections occur most often in people with weakened immune systems.
Cresemba belongs to a class of drugs called azole antifungal agents, which target the cell wall of a fungus. Cresemba is available in oral and intravenous formulations.
“Today’s approval provides a new treatment option for patients with serious fungal infections and underscores the importance of having available safe and effective antifungal drugs,” said Edward Cox, M.D., M.P.H, director of the Office of Antimicrobial Products in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research.
Cresemba is the sixth approved antibacterial or antifungal drug product designated as a Qualified Infectious Disease Product (QIDP). This designation is given to antibacterial or antifungal drug products that treat serious or life-threatening infections under the Generating Antibiotic Incentives Now (GAIN) title of the FDA Safety and Innovation Act.
As part of its QIDP designation, Cresemba was given priority review, which provides an expedited review of the drug’s application. The QIDP designation also qualifies Cresemba for an additional five years of marketing exclusivity to be added to certain exclusivity periods already provided by the Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. As these types of fungal infections are rare, the FDA also granted Cresemba orphan drug designations for invasive aspergillosis and invasive mucormycosis.
The approval of Cresemba to treat invasive aspergillosis was based on a clinical trial involving 516 participants randomly assigned to receive either Cresemba or voriconazole, another drug approved to treat invasive aspergillosis. Cresemba’s approval to treat invasive mucormycosis was based on a single-arm clinical trial involving 37 participants treated with Cresemba and compared with the natural disease progression associated with untreated mucormycosis. Both studies showed Cresemba was safe and effective in treating these serious fungal infections.
The most common side effects associated with Cresemba include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headache, abnormal liver blood tests, low potassium levels in the blood (hypokalemia), constipation, shortness of breath (dyspnea), coughing and tissue swelling (peripheral edema). Cresemba may also cause serious side effects including liver problems, infusion reactions and severe allergic and skin reactions.
Cresemba is marketed by Astellas Pharma US, Inc., based in Northbrook, Illinois.

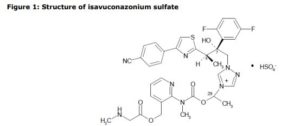
The active substance is isavuconazonium sulfate, a highly water soluble pro-drug of the active triazole isavuconazole. The chemical name of the active substance isavuconazonium sulfate is 1-{(2R,3R)-3-[4-(4-cyanophenyl)-1,3- thiazol-2-yl]-2-(2,5-difluoro-phenyl)-2-hydroxybutyl}-4-[(1RS)-1-({methyl[3-({[(methylamino)acetyl] oxy}methyl) pyridin-2-yl]carbamoyl}oxy)ethyl]-1H-1,2,4-triazol-4-ium monosulfate (IUPAC), corresponding to the molecular formula C35H35F2N8O5S·HSO4 and has a relative molecular mass of 814.84 g/mol. The relative molecular mass of isavuconazole is 437.47. The active substance has the following structure:

The structure of the active substance has been confirmed by elemental analysis, mass spectrometry, UV, IR, 1H-, 13C- and 19F-NMR spectrometry, and single crystal X-ray analysis, all of which support the chemical structure. It appears as a white, amorphous, hygroscopic powder. It is very soluble in water and over the pH range 1-7. It is also very soluble in methanol and sparingly soluble in ethanol. Two pKa values have been found and calculated to be 2.0 and 7.3. Its logPoct/wat calculated by software is 1.31.
Isavuconazonium sulfate has three chiral centres. The stereochemistry of the active substance is introduced by one of the starting materials which is controlled by appropriate specification. The two centres, C7 and C8 in the isavuconazole moiety and in an intermediate of the active substance, have R configuration. The third chiral centre, C29, is not located on isavuconazole moiety and has both the R and S configurations. The nondefined stereo centre at C29 has been found in all batches produced so far to be racemic. Erosion of stereochemical purity has not been observed in the current process. The active substance is a mixture of two epimers of C29.
An enantiomer of drug substance was identified as C7 (S), C8 (S) and C29 (R/S) structure. The control of the stereochemistry of isavuconazonium sulfate is performed by chiral HPLC on the active substance and its two precursors. Subsequent intermediates are also controlled by relevant specification in the corresponding steps. Two crystal forms have been observed by recrystallisation studies. However the manufacturing process as described yields amorphous form only.
Two different salt forms of isavuconazonuium (chloride and sulfate) were identified during development. The sulfate salt was selected for further development. A polymorph screening study was also performed. None of the investigated salts could be obtained in crystalline Form………http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Public_assessment_report/human/002734/WC500196130.pdf



Clip
Isavuconazonium (Cresemba ) is a water-soluble prodrug of the triazole antifungal isavuconazole (BAL4815), a 14-a-demethylase inhibitor, under development byBasilea Pharmaceutica International Ltd and Astellas Pharma Inc. Isavuconazonium, in both its intravenous and oral formulations, was approved for the treatment of invasive aspergillosis and invasive mucormycosis (formerly termed zygomycosis) in the US in March 2015. Isavuconazonium is under regulatory review in the EU for invasive aspergillosis and mucormycosis. It is also under phase III development worldwide for the treatment of invasive candidiasis and candidaemia. This article summarizes the milestones in the development of isavuconazonium leading to the first approval for invasive spergillosis and mucormycosis.
Introduction
The availability of both an intravenous (IV) and an oral formulation of isavuconazonium (Cresemba ), as a result of its water solubility, rapid hydrolysis to the active entity isavuconazole and very high oral bioavailability, provides maximum flexibility to clinicians for treating seriously ill patients with invasive fungal infections [1]. Both the IV and oral formulations have been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat adults with invasive aspergillosis and invasive mucormycosis [2]. The recommended dosages of each formulation are identical, consisting of loading doses of 372 mg (equivalent to 200 mg of isavuconazole) every eight hours for six doses, followed by maintenance therapy with 372 mg administered once daily [3]. The Qualified Infectious Disease Product (QIDP) designation of the drug with priority review status by the FDA isavuconazonium in the US provided and a five year extension of market exclusivity from launch. Owing to the rarity of the approved infections,
isavuconazonium was also granted orphan drug designation by the FDA for these indications [2]. It has also been granted orphan drug and QIDP designation in the US for the treatment of invasive candidiasis [4]. In July 2014, Basilea Pharmaceutica International Ltd submitted a Marketing Authorization Application to the European Medicines Agency (EMA) for isavuconazonium in the treatment of invasive aspergillosis and invasive mucormycosis, indications for which the EMA has granted isavuconazonium orphan designation [5, 6]. Isavuconazonium is under phase III development in many countries worldwide for the treatment of invasive candidiasis and candidaemia.
1.1 Company agreements
In 2010, Basilea Pharmaceutica International Ltd (a spinoff from Roche, founded in 2000) entered into a licence agreement with Astellas Pharma Inc in which the latter would co-develop and co-promote isavuconazonium worldwide, including an option for Japan. In return for milestone payments, Astellas Pharma was granted an exclusive right to commercialize isavuconazonium, while Basilea Pharmaceutica retained an option to co-promote the drug in the US, Canada, major European countries and China [7]. The companies amended their agreement in 2014, making Astellas Pharma responsible for all regulatory filings, commercialization and manufacturing of isavuconazonium in the US and Canada. Basilea Pharmaceutica waived its right to co-promote the product in the US and Canada, in order to assume all rights in the rest of the world [8]. However, Astellas Pharma remains as sponsor of the multinational, phase III ACTIVE trial in patients with invasive candidiasis.
2 Scientific Summary
Isavuconazonium (as the sulphate; BAL 8557) is a prodrug that is rapidly hydrolyzed by esterases (mainly butylcholinesterase) in plasma into the active moiety isavuconazole
(BAL 4815) and an inactive cleavage product (BAL 8728).
References
1. Falci DR, Pasqualotto AC. Profile of isavuconazole and its potential in the treatment of severe invasive fungal infections. Infect Drug Resist. 2013;6:163–74.
2. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves new antifungal drug Cresemba. 2015. http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm437106.htm. Accessed 12 Mar 2015.
3. US Food and Drug Administration. Cresemba (isavuconazonium sulfate): US prescribing information. 2015. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2015/207500Orig1s000lbl.pdf. Accessed 18 Mar 2015.
4. Astellas Pharma US Inc. FDA grants Astellas Qualified Infectious Disease Product designation for isavuconazole for the treatment of invasive candidiasis (media release). 2014. http://newsroom astellas.us/2014-07-16-FDA-Grants-Astellas-Qualified-Infectious-Disease-Product-Designation-for-Isavuconazole-for-the-Treatmentof-Invasive-Candidiasis.
5. European Medicines Agency. Public summary of opinion on orphan designation: isavuconazonium sulfate for the treatment of invasive aspergillosis. 2014. http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Orphan_designation/2014/07/WC500169890.pdf. Accessed 18 Mar 2015.
European Medicines Agency. Public summary of opinion on orphan designation: isavuconazonium sulfate for the treatment of mucormycosis. 2014. http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Orphan_designation/2014/07/WC500169714.pdf. Accessed 18 Mar 2015.
7. Basilea Pharmaceutica. Basilea announces global partnership with Astellas for its antifungal isavuconazole (media release).2010. http://www.basilea.com/News-and-Media/Basilea-announcesglobal-partnership-with-Astellas-for-its-antifungal-isavuconazole/343.
8. Basilea Pharmaceutica. Basilea swaps its isavuconazole North American co-promote rights for full isavuconazole rights outside of North America (media release). 2014. http://www.basilea.com/News-and-Media/Basilea-swaps-its-isavuconazole-North-Americanco-promote-rights-for-full-isavuconazole-rights-outside-
CLIP

http://www.jpharmsci.org/article/S0022-3549(15)00035-0/pdf
A CLIP
http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2015/207500Orig1207501Orig1s000ChemR.pdf
EMA
On 4 July 2014 orphan designation (EU/3/14/1284) was granted by the European Commission to Basilea Medical Ltd, United Kingdom, for isavuconazonium sulfate for the treatment of invasive aspergillosis.
Update: isavuconazonium sulfate (Cresemba) has been authorised in the EU since 15 October 2015. Cresemba is indicated in adults for the treatment of invasive aspergillosis.
Consideration should be given to official guidance on the appropriate use of antifungal agents.
The active substance is isavuconazonium sulfate, a highly water soluble pro-drug of the active triazole isavuconazole. The chemical name of the active substance isavuconazonium sulfate is 1-{(2R,3R)-3-[4-(4-cyanophenyl)-1,3- thiazol-2-yl]-2-(2,5-difluoro-phenyl)-2-hydroxybutyl}-4-[(1RS)-1-({methyl[3-({[(methylamino)acetyl] oxy}methyl) pyridin-2-yl]carbamoyl}oxy)ethyl]-1H-1,2,4-triazol-4-ium monosulfate (IUPAC), corresponding to the molecular formula C35H35F2N8O5S·HSO4 and has a relative molecular mass of 814.84 g/mol. The relative molecular mass of isavuconazole is 437.47. The active substance has the following structure
It appears as a white, amorphous, hygroscopic powder. It is very soluble in water and over the pH range 1-7. It is also very soluble in methanol and sparingly soluble in ethanol. Two pKa values have been found and calculated to be 2.0 and 7.3. Its logPoct/wat calculated by software is 1.31.
Isavuconazonium sulfate has three chiral centres. The stereochemistry of the active substance is introduced by one of the starting materials which is controlled by appropriate specification. The two centres, C7 and C8 in the isavuconazole moiety and in an intermediate of the active substance, have R configuration. The third chiral centre, C29, is not located on isavuconazole moiety and has both the R and S configurations. The nondefined stereo centre at C29 has been found in all batches produced so far to be racemic. Erosion of stereochemical purity has not been observed in the current process. The active substance is a mixture of two epimers of C29. An enantiomer of drug substance was identified as C7 (S), C8 (S) and C29 (R/S) structure. The control of the stereochemistry of isavuconazonium sulfate is performed by chiral HPLC on the active substance and its two precursors.
FDA Orange Book Patents
US 6812238
US 7459561
| FDA ORANGE BOOK PATENTS: 1 OF 2 | |
|---|---|
| Patent | 7459561 |
| Expiration | Oct 31, 2020 |
| Applicant | ASTELLAS |
| Drug Application | N207500 (Prescription Drug: CRESEMBA. Ingredients: ISAVUCONAZONIUM SULFATE) |
FREE FORM
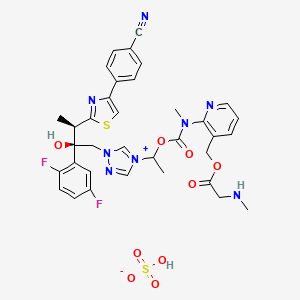
Isavuconazonium; Isavuconazonium ion; Cresemba; BAL-8557; 742049-41-8;
[2-[1-[1-[(2R,3R)-3-[4-(4-cyanophenyl)-1,3-thiazol-2-yl]-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-2-hydroxybutyl]-1,2,4-triazol-4-ium-4-yl]ethoxycarbonyl-methylamino]pyridin-3-yl]methyl 2-(methylamino)acetate
| MOLECULAR FORMULA: | C35H35F2N8O5S+ |
|---|---|
| MOLECULAR WEIGHT: | 717.773 g/mol |
Patent IDDatePatent Title
US20102494262010-09-30STABILIZED PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOSITION
US74595612008-12-02N-substituted carbamoyloxyalkyl-azolium derivativesUS71898582007-03-13N-phenyl substituted carbamoyloxyalkyl-azolium derivatives
US71511822006-12-19Intermediates for N-substituted carbamoyloxyalkyl-azolium derivatives
US68122382004-11-02N-substituted carbamoyloxyalkyl-azolium derivatives
REF
http://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB06636
////////// BAL 8557, BAL-8557-002, CRESEMBA, ISAVUCONAZONIUM SULFATE, QIDP designation, Cresemba , priority review, FDA 2015, EU 2015, BAL8557-002, BCS CLASS I, orphan designation, invasive aspergillosis, invasive mucormycosis, RO-0098557 , AK-1820, fast track designation, QIDP, 946075-13-4
CC(C1=NC(=CS1)C2=CC=C(C=C2)C#N)C(CN3C=[N+](C=N3)C(C)OC(=O)N(C)C4=C(C=CC=N4)COC(=O)CNC)(C5=C(C=CC(=C5)F)F)O
CC(C1=NC(=CS1)C2=CC=C(C=C2)C#N)C(CN3C=[N+](C=N3)C(C)OC(=O)N(C)C4=C(C=CC=N4)COC(=O)CNC)(C5=C(C=CC(=C5)F)F)O.OS(=O)(=O)[O-]
UPDATE NEW PATENT
WOCKHARDT, WO 2016016766, ISAVUCONAZONIUM SULPHATE, NEW PATENT


(WO2016016766) A PROCESS FOR THE PREPARATION OF ISAVUCONAZONIUM OR ITS SALT THEREOF
WOCKHARDT LIMITED [IN/IN]; D-4, MIDC Area, Chikalthana, Aurangabad 431006 (IN)
KHUNT, Rupesh Chhaganbhai; (IN).
RAFEEQ, Mohammad; (IN).
MERWADE, Arvind Yekanathsa; (IN).
DEO, Keshav; (IN)
The present invention relates to a process for the preparation of stable Isavuconazonium or its salt thereof. In particular of the present invention relates to process for the preparing of isavuconazonium sulfate, Isavuconazonium iodide hydrochloride and Boc-protected isavuconazonium iodide has purity more than 90%. The process is directed to preparation of solid amorphous form of isavuconazonium sulfate, isavuconazonium iodide hydrochloride and Boc-protected isavuconazonium iodide. The present invention process of Isavuconazonium or its salt thereof is industrially feasible, simple and cost effective to manufacture of isavuconazonium sulfate with the higher purity and better yield.
Isavuconazonium sulfate is chemically known l-[[N-methyl-N-3-[(methylamino) acetoxymethyl]pyridin-2-yl] carbamoyloxy]ethyl-l-[(2R,3R)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-2-hydroxy-3-[4-(4-cyanophenyl)thiazol-2-yl]butyl]-lH-[l,2,4]-triazo-4-ium Sulfate and is structurally represented by formula (I):


Formula I
Isavuconazonium sulfate (BAL8557) is indicated for the treatment of antifungal infection. Isavuconazonium sulfate is a prodrug of Isavuconazole (BAL4815), which is chemically known 4-{2-[(lR,2R)-(2,5-Difluorophenyl)-2-hydroxy-l-methyl-3-(lH-l ,2,4-triazol-l-yl)propyl]-l ,3-thiazol-4-yl}benzonitrile compound of Formula II


Formula II
US Ppatent No. 6,812,238 (referred to herein as ‘238); 7,189,858 (referred to herein as ‘858); 7,459,561 (referred to herein as ‘561) describe Isavuconazonium and its process for the preparation thereof.
The US Pat. ‘238 patent describes the process of preparation of Isavuconazonium chloride hydrochloride.
The US Pat. ‘238 described the process for the Isavuconazonium chloride hydrochloride, involves the condensation of Isavuconazole and [N-methyl-N-3((tert-butoxycarbonyl methylamino) acetoxymethyl) pyridine-2-yl]carbamic acid 1 -chloro-ethyl ester. The prior art reported process require almost 15-16 hours, whereas the present invention process requires only 8-10 hours. Inter alia prior art reported process requires too many step to prepare isavuconazonium sulfate, whereas the present invention process requires fewer steps.
Moreover, the US Pat. ‘238 describes the process for the preparation Isavuconazonium hydrochloride, which may be used as the key intermediate for the synthesis of isavuconazonium sulfate, compound of formula I. There are several drawbacks in the said process, which includes the use of anionic resin to prepare Isavuconazonium chloride hydrochloride, consequently it requires multiple time lyophilization, which makes the said prior art process industrially, not feasible.
The inventors of the present invention surprisingly found that Isavuconazonium or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof in yield and purity could be prepared by using substantially pure intermediates in suitable solvent.
Thus, an object of the present invention is to provide simple, cost effective and industrially feasible processes for manufacture of isavuconazonium sulfate. Inventors of the present invention surprisingly found that isavuconazonium sulfate prepared from isavuconazonium iodide hydrochloride, provides enhanced yield as well as purity.
The process of the present invention is depicted in the following scheme:


Formula I
Formula-IA
The present invention is further illustrated by the following example, which does not limit the scope of the invention. Certain modifications and equivalents will be apparent to those skilled in the art and are intended to be included within the scope of the present application.
Examples
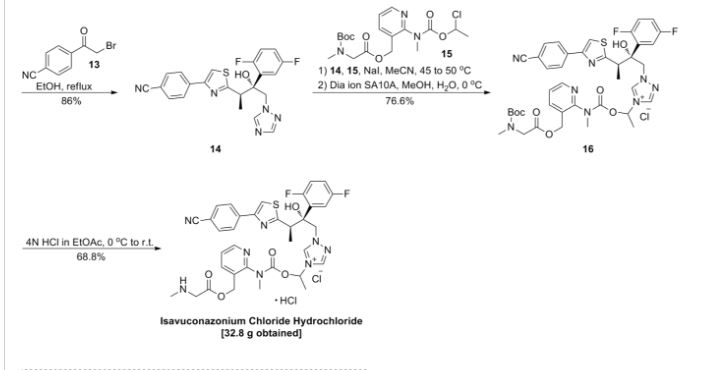
Example-1: Synthesis of l-[[N-methyl-N-3-[(t-butoxycarbonylmethylamino) acetoxymethyl]pyridin-2-yl]carbamoyloxy]ethyl-l-[(2R,3R)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-2-hydroxy-3 – [4-(4-cyanophenyl)thiazol-2-yl]butyl] – 1 H-[ 1 ,2,4] -triazo-4-ium iodide
Isavuconazole (20 g) and [N-methyl-N-3((tert-butoxycarbonylmethylamino)acetoxy methyl)pyridine-2-yl]carbamic acid 1 -chloro-ethyl ester (24.7 g) were dissolved in acetonitrile (200ml). The reaction mixture was stirred to add potassium iodide (9.9 g). The reaction mixture was stirred at 47-50°C for 10-13 hour. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature. The reaction mass was filtered through celite bed and washed acetonitrile. Residue was concentrated under reduced pressure to give the crude solid product (47.7 g). The crude product was purified by column chromatography to get its pure iodide form (36.5 g).
Yield: 84.5 %
HPLC Purity: 87%
Mass: m/z 817.4 (M- 1)+
Example-2: Synthesis of l-[[N-methyl-N-3-[(methylamino)acetoxymethyl]pyridin-2-yl] carbamoyloxy]ethyl-l-[(2R,3R)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-2-hydroxy-3-[4-(4-cyanophenyl) thiazol-2-yl]butyl]-lH-[l ,2,4]-triazo-4-ium iodide hydrochloride
l-[[N-methyl-N-3-[(t-butoxycarbonylmethylamino)acetoxymethyl]pyridin-2-yl] carbamoyloxy]ethyl-l-[(2R,3R)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-2-hydroxy-3-[4-(4-cyanophenyl) thiazol-2-yl]butyl]-lH-[l ,2,4]-triazo-4-ium iodide (36.5 g) was dissolved in ethyl acetate (600 ml). The reaction mixture was cooled to -5 to 0 °C. The ethyl acetate hydrochloride (150 ml) solution was added to reaction mixture. The reaction mixture was stirred for 4-5 hours at room temperature. The reaction mixture was filtered and obtained solid residue washed with ethyl acetate. The solid dried under vacuum at room temperature for 20-24 hrs to give 32.0 gm solid.
Yield: 93 %
HPLC Purity: 86%
Mass: m/z 717.3 (M-HC1- 1)
Example-3: Preparation of Strong anion exchange resin (Sulfate).
Indion GS-300 was treated with aqueous sulfate anion solution and then washed with DM water. It is directly used for sulfate salt.
Example-4: Synthesis of l-[[N-methyl-N-3-[(methylamino)acetoxymethyl]pyridin-2-yl] carbamoyloxy]ethyl-l-[(2R,3R)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-2-hydroxy-3-[4-(4-cyanophenyl) thiazol-2-yl]butyl]-lH-[l ,2,4]-triazo-4-ium Sulfate
Dissolved 10.0 g l-[[N-methyl-N-3-[(methylamino)acetoxymethyl]pyridin-2-yl] carbamoyloxy]ethyl-l-[(2R,3R)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-2-hydroxy-3-[4-(4-cyanophenyl) thiazol-2-yl]butyl]-lH-[l ,2,4]-triazo-4-ium iodide hydrochloride in 200 ml deminerahzed water and 30 ml methanol. The solution was cooled to about 0 to 5°C. The strong anion exchange resin (sulfate) was added to the cooled solution. The reaction mixture was stirred to about 60-80 minutes. The reaction was filtered and washed with 50ml of demineralized water and methylene chloride. The aqueous layer was lyophilized to obtain
(8.0 g) white solid.
Yield: 93 %
HPLC Purity: > 90%
Mass: m/z 717.4 (M- HS04) +
PATENT
CN 105288648
PATENT
CN 106883226
https://patents.google.com/patent/CN106883226A/en
PATENT
CN 107982221
PAPER
| Introduction of New Drugs Approved by the U.S. FDA in 2015 |
| Ma Shuai; Wenying Ling; Zhou Weicheng; |
| China Pharmaceutical Industry |
| Tongfangzhiwang Beijing Technology Co., Ltd. |
| 10.16522/j.cnki.cjph.2016.01.022 |
| 2016-02-19 02:04:15 |
///////////////