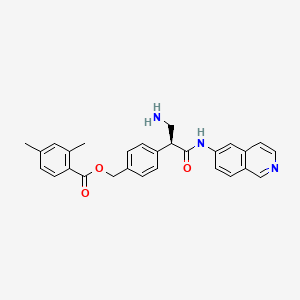
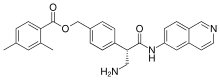
Netarsudil
| Molecular Formula: | C28H27N3O3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight: | 453.542 g/mol |
Netarsudil; UNII-W6I5QDT7QI; W6I5QDT7QI; 1254032-66-0; Netarsudil [USAN]; AR-11324 free base
1422144-42-0 (mesylate) 1254032-66-0 (free base) 1253952-02-1 (HCl)
[4-[(2S)-3-amino-1-(isoquinolin-6-ylamino)-1-oxopropan-2-yl]phenyl]methyl 2,4-dimethylbenzoate
Approved by US-FDA in December-2017 for dimesylate salt
- AR 13324
- Rhopressa
nmr http://file.selleckchem.com/downloads/nmr/s822601-netarsudil-ar-13324-hnmr-selleck.pdf

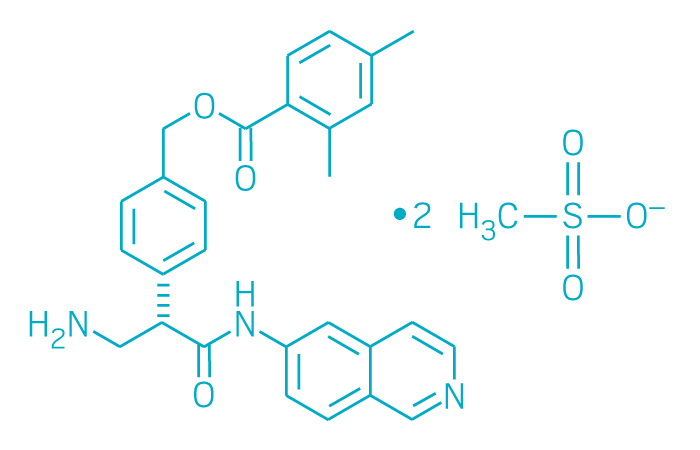
Netarsudil Mesylate
CAS: 1422144-42-0 (mesylate)
Chemical Formula: C30H35N3O9S2
Molecular Weight: 645.742
Netarsudil dimesylate is a light yellow-to-white powder that is freely soluble in water, soluble in methanol, sparingly soluble in dimethyl formamide, and practically insoluble in dichloromethane and heptane.
Netarsudil ophthalmic solution 0.02% is supplied as a sterile, isotonic, buffered aqueous solution of netarsudil dimesylate with a pH of approximately 5 and an osmolality of approximately 295 mOsmol/kg. It is intended for topical application in the eye. Each mL of netarsudil contains 0.2 mg of netarsudil (equivalent to 0.28 mg of netarsudil dimesylate). Benzalkonium chloride, 0.015%, is added as a preservative. The inactive ingredients are: boric acid, mannitol, sodium hydroxide to adjust pH, and water for injection
Netarsudil, also known as AR-11324, is a Rho-associated protein kinase inhibitor. Netarsudil is potential useful for treating glaucoma and/or reducing intraocular pressure. Netarsudil Increases Outflow Facility in Human Eyes Through Multiple Mechanisms. Netarsudil inhibited kinases ROCK1 and ROCK2 with a Ki of 1 nM each, disrupted actin stress fibers and focal adhesions in TM cells with IC50s of 79 and 16 nM, respectively, and blocked the profibrotic effects of TGF-β2 in HTM cells. Netarsudil produced large reductions in IOP in rabbits and monkeys that were sustained for at least 24 h after once daily dosing, with transient, mild hyperemia observed as the only adverse effect.
Netarsudil (trade name Rhopressa) is a drug for the treatment of glaucoma. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administrationhas approved a 0.02% ophthalmic solution for the lowering of elevated intraocular pressure in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension.[1]
Rho-associated protein kinase (ROCK) is a kinase belonging to the AGC (PKA/ PKG/PKC) family of serine-threonine kinases. It is involved mainly in regulating the shape and movement of cells by acting on the cytoskeleton. ROCK signaling plays an important role in many diseases including diabetes, neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson´s disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, pulmonary hypertension and cancer. It has been shown to be involved in causing tissue thickening and stiffening around tumours in a mouse model of skin cancer, principally by increasing the amount of collagen in the tissue around the tumour.
WO 2014144781
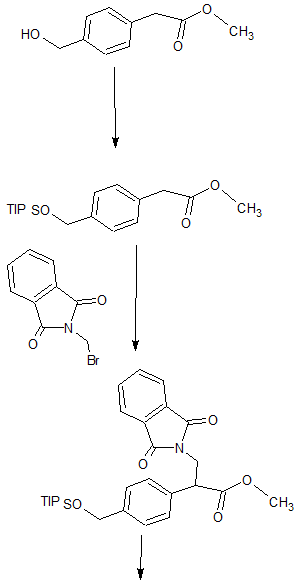
SYNTHESIS
WO2010127329
CONTINUED………..
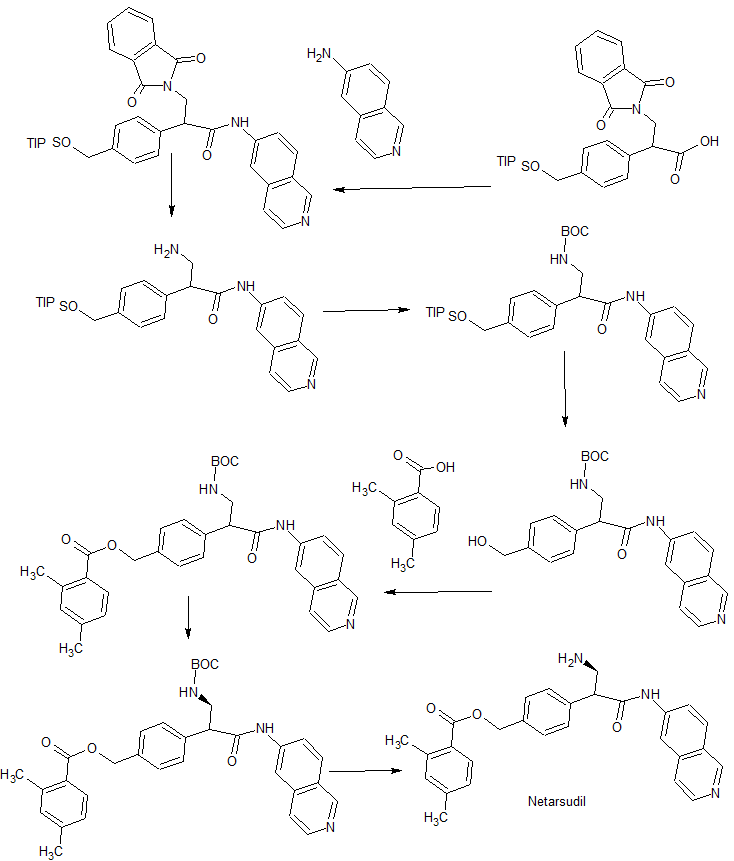
PATENT
WO 2014144781
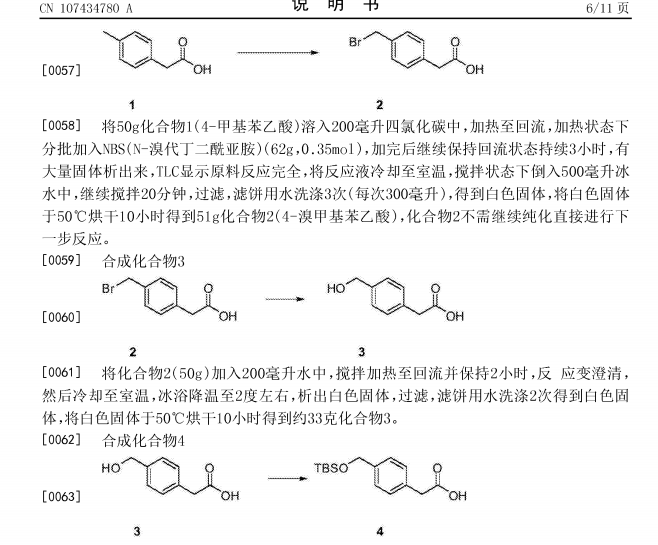
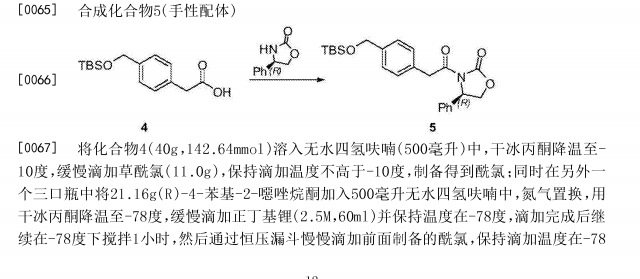
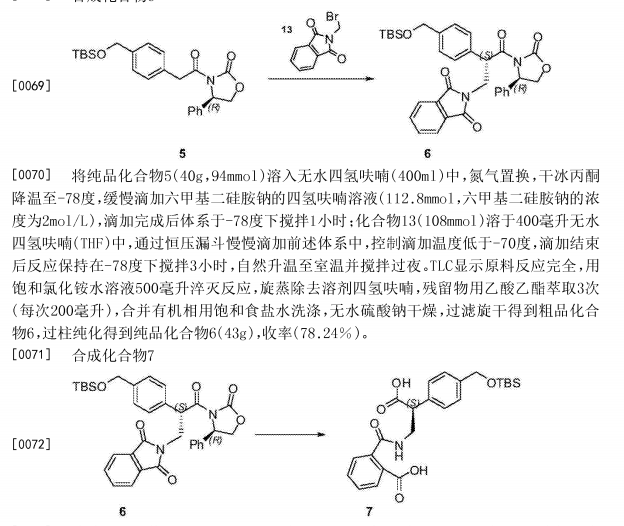
CN 107434780
https://www.google.com/patents/CN107434780A?cl=en

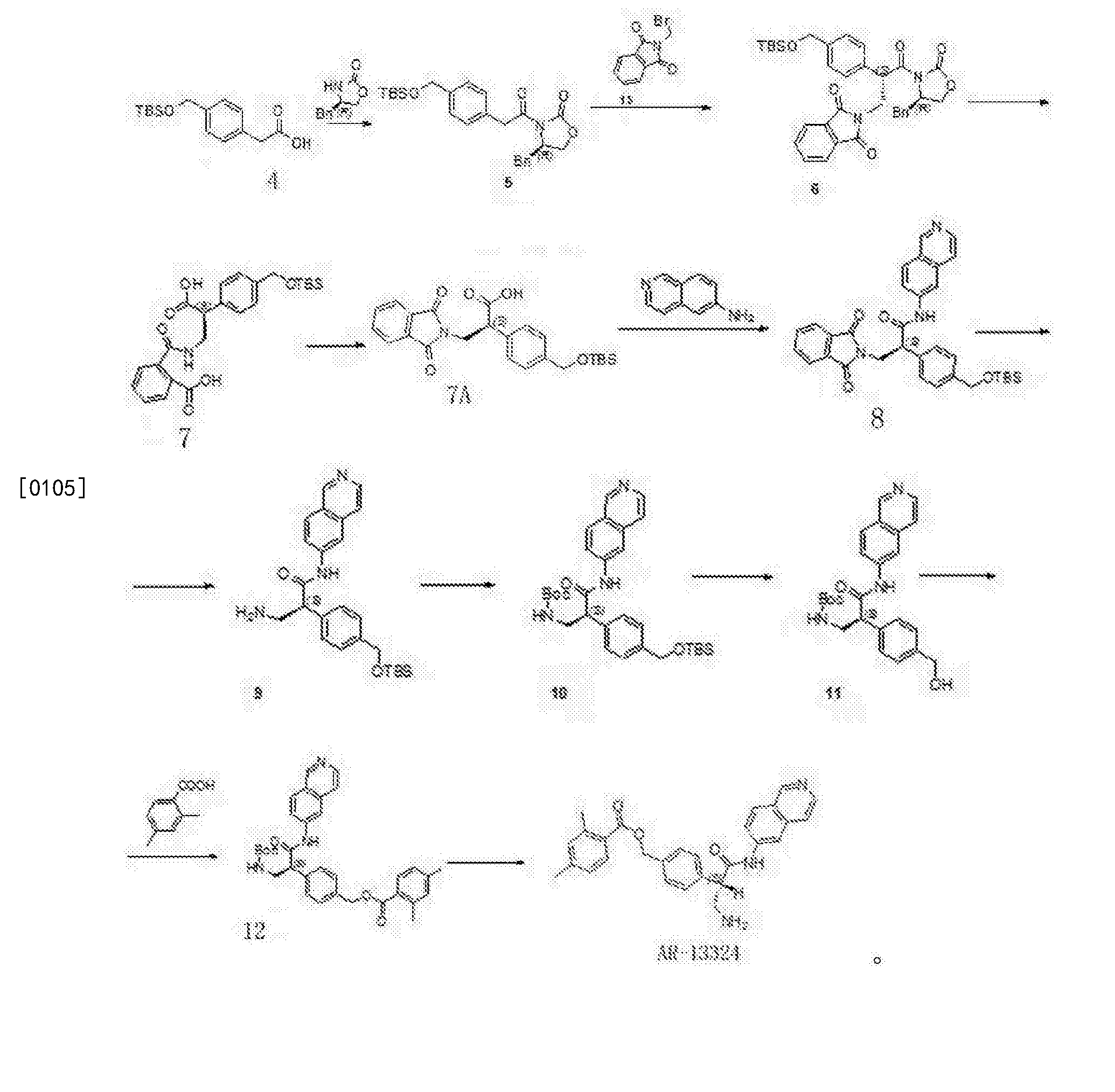
Synthesis of Compound 12
[0091] The 2,4-dimethyl benzoic acid (1.5g, IOmmol) and a catalytic amount of DMF was added to the toluene and cooled to 2-5 ° C, was added dropwise oxalyl chloride (I.64g, 13_〇1 ), warmed to room temperature after dropwise, stirred overnight, during which a solid gradually dissolved to give a clear solution, evaporated to dryness under reduced pressure to give a yellow oil with dichloromethane (IOml) was dissolved in dichloromethane to give the acid chloride ;
[0092] Compound 11 (3.2g, 7.7mmo 1) and triethylamine (2ml) were added 20ml of dichloromethane, nitrogen, the above prepared acid chloride solution in dichloromethane dropwise at 0-5 ° C the increases after mixing, overnight; TLC (dichloromethane: methanol = 20: 1) to monitor the reaction, completion of the reaction, evaporated to dryness under reduced pressure, and then stirred with saturated sodium carbonate solution, filtered, the filter cake was washed with water 3 times, dried to give 3.9g white solid, i.e. compound 12; purity: 991%, optical purity: 100% (CHIRALPAK AS-H, 0.46cm IDX15cm L, Me0H + 0.1DEA) / C02 = 20/80 (V / V, 2.0ml / min), R-type, Rt = 3 · 253min; S type Rt = 4.3min).
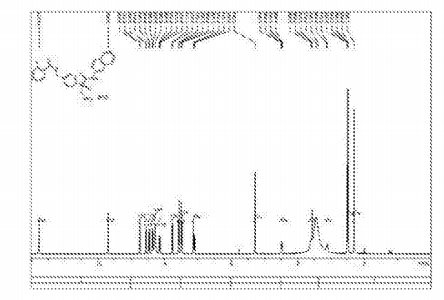
Compound 12 (3.9g) in DCM was added, with stirring to obtain clear solution, was then added dropwise I, a solution of hydrogen chloride in dioxane 15ml 4_ (concentration 4mol / L, 4mol HCl gas dissolved in two IL oxygen six ring), and then stirred for 4 hours at room temperature, rotary evaporated under reduced pressure, and filtered to give 3.65g product as a white solid, was obtained HNMR detectable substance is the AR-13324 hydrochloride, which IHNMR spectrum Referring to FIG. 1 , MS, purity, 99.4%, lHNMR (400MHz, DMS0,300) S (Ppm) c3Il .773 (s, 1H), 9.702 (s, lH), 8.740 (d, lH), 8.560 (d, 1H), 8.469 (d, 1H), 8.360 (d, 1H), 8.280 (s, 3H), 8.158 (dd, lH), 7.777 (d, lH), 7.577 (d, 2H), 7.496 (d, 2H), 7.134 (s, lH), 7.111 (d, lH), 5.281 (s, 2H), 4.504 (q, lH), 3.609 (q, lH), 3.139 (q, lH), 2.483 (s, 3H), 2.302 ( s, 3H).
Example 2
[0097] In this embodiment, the same processing steps except that Compound 12, the other the same as in Example 1.
[0098] Compound 12 processing steps are as follows: The compound is dissolved in 12 (3.9g) 40ml of dichloromethane, followed by dropwise addition of methanesulfonic acid (2g, 21.6mmol), stirred at room temperature overnight, rotary evaporated under reduced pressure, IOOml diethyl ether was added thereto, followed by stirring, a large amount of white solid was filtered, dried to give a white solid (4.54 g of), yield 97.8%, purity 98.2%, the resulting substance was detected IHNMR AR-13324 is the mesylate salt.
References
- Jump up^ “Aerie (AERI) Gets Early FDA Approval for Lead Drug Rhopressa”. December 19, 2017.
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Rhopressa |
| Synonyms | AR-11324 |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C28H27N3O3 |
| Molar mass | 453.54 g·mol−1 |
REFERENCES
1: Sturdivant JM, Royalty SM, Lin CW, Moore LA, Yingling JD, Laethem CL, Sherman B, Heintzelman GR, Kopczynski CC, deLong MA. Discovery of the ROCK inhibitor netarsudil for the treatment of open-angle glaucoma. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2016 May 15;26(10):2475-80. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2016.03.104. Epub 2016 Apr 1. PubMed PMID: 27072905.
2: Ren R, Li G, Le TD, Kopczynski C, Stamer WD, Gong H. Netarsudil Increases Outflow Facility in Human Eyes Through Multiple Mechanisms. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016 Nov 1;57(14):6197-6209. doi: 10.1167/iovs.16-20189. PubMed PMID: 27842161; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC5114035.
3: Li G, Mukherjee D, Navarro I, Ashpole NE, Sherwood JM, Chang J, Overby DR, Yuan F, Gonzalez P, Kopczynski CC, Farsiu S, Stamer WD. Visualization of conventional outflow tissue responses to netarsudil in living mouse eyes. Eur J Pharmacol. 2016 Sep 15;787:20-31. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.04.002. Epub 2016 Apr 13. PubMed PMID: 27085895; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC5014700.
4: Lin CW, Sherman B, Moore LA, Laethem CL, Lu DW, Pattabiraman PP, Rao PV, deLong MA, Kopczynski CC. Discovery and Preclinical Development of Netarsudil, a Novel Ocular Hypotensive Agent for the Treatment of Glaucoma. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2017 Jun 13. doi: 10.1089/jop.2017.0023. [Epub ahead of print] PubMed PMID: 28609185.
5: Lu LJ, Tsai JC, Liu J. Novel Pharmacologic Candidates for Treatment of Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma. Yale J Biol Med. 2017 Mar 29;90(1):111-118. eCollection 2017 Mar. Review. PubMed PMID: 28356898; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC5369028.
/////////////Netarsudil, fda 2017, Rhopressa, AR-11324, AR 11324
CC1=CC(=C(C=C1)C(=O)OCC2=CC=C(C=C2)C(CN)C(=O)NC3=CC4=C(C=C3)C=NC=C4)C