Tamibarotene
тамибаротен , تاميباروتان , 他米巴罗汀 ,
94497-51-5 CAS
- Molecular FormulaC22H25NO3
- Average mass351.439 Da
4-(((5,6,7,8-Tetrahydro-5,5,8,8-tetramethyl-2-naphthalenyl)amino)carbonyl)benzoic Acid, Tamibarotene
- Am 80
- Am 80 (pharmaceutical)
- Amnolake
- NSC 608000
- RR 110
Hisao Ekimoto, “TAMIBAROTENE CAPSULE PREPARATION.” U.S. Patent US20100048708, issued February 25, 2010.

Tamibarotene , a small molecule retinoic acid receptor alpha (RARα) agonists developed by Nippon Shinyaku, was approved in Japan for the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) in 2005. Recently, the drug was in clinical development for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML), myelodysplasia, pediatric solid tumor, and steroid-refractory
Tamibarotene (brand name: Amnolake), also called retinobenzoic acid, is orally active, synthetic retinoid, developed to overcome all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) resistance, with potential antineoplastic activity against acute promyelocytic leukaemia (APL) .[1] It is currently marketed only in Japan and early trials have demonstrated that it tends to be better tolerated than ATRA.[2] It has also been investigated as a possible treatment for Alzheimer’s disease, multiple myeloma and Crohn’s disease.[2][3]
Synthesis
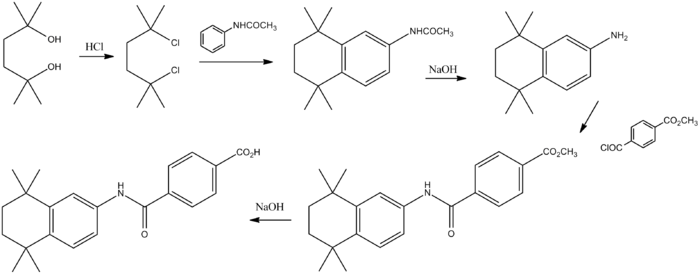
The tetralin-based compound tamibarotene (7) has been tested as an agent for treating leukaemias.
Reaction of the diol (1) with hydrogen chloride affords the corresponding dichloro derivative (2). Aluminum chloride mediated Friedel–Crafts alkylation of acetanilide with the dichloride affords the tetralin (3). Basic hydrolysis leads to the primary amine (4). Acylation of the primary amino group with the half acid chloride half ester from terephthalic acid (5) leads to the amide (6). Basic hydrolysis of the ester grouping then affords (7).[4]
PAPER
Synthesis of Tamibarotene via Ullmann-Type Coupling
An effective process was developed for the preparation of tamibarotene via an Ullmann-type coupling in a nonpressurized l-proline/DMSO system. Notable features were the telescoping of reactions, avoiding environmentally hazardous materials, and an acceptable overall yield. The safe scalable process was validated on a 1 kg scale.
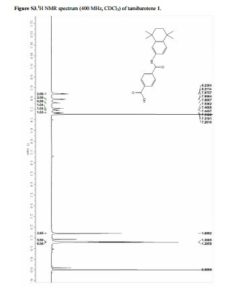
Mp 223–225 °C (lit. SEE BELOW mp 231–232 °C); 1H NMR (400 MHz, chloroform-d) δ 8.22 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 2H), 7.97 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 2H), 7.80 (s, 1H), 7.54 (s, 1H), 7.46 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.33 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 1.70 (s, 4H), 1.31 (s, 6H), 1.29 (s, 6H); MS (ESI) m/z: 350.0 [M – H]−
…Journal of Medicinal Chemistry (1988), 31 (11), 2182-92

PAPER
Journal of Medicinal Chemistry (1988), 31 (11), 2182-92
PAPER
Chem. Pharm. Bull. 61(8) 846–852 (2013)
https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/cpb/61/8/61_c13-00356/_pdf
References
- Jump up^ “Tamibarotene: AM 80, retinobenzoic acid, Tamibaro”. Drugs in R&D. 5 (6): 359–62. 2004. doi:10.2165/00126839-200405060-00010. PMID 15563242.
- ^ Jump up to:a b Miwako, I; Kagechika, H (August 2007). “Tamibarotene”. Drugs Today (Barc). 43 (8): 563–568. doi:10.1358/dot.2007.43.8.1072615. PMID 17925887.
- Jump up^ Fukasawa, H; Nakagomi, M; Yamagata, N; Katsuki, H; Kawahara, K; Kitaoka, K; Miki, T; Shudo, K (2012). “Tamibarotene: a candidate retinoid drug for Alzheimer’s disease” (PDF). Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin. 35 (8): 1206–1212. doi:10.1248/bpb.b12-00314. PMID 22863914.
- Jump up^ Y. Hamada, I. Yamada, M. Uenaka, T. Sakata, U.S. Patent 5,214,202 (1993).
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
4-[(1,1,4,4-tetramethyltetralin-6-yl)carbamoyl]benzoic acid
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| 3564473 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| Properties | |
| C22H25NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 351.45 g·mol−1 |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
////////////Tamibarotene, тамибаротен , تاميباروتان , 他米巴罗汀 ,
CC1(C)CCC(C)(C)C2=C1C=CC(NC(=O)C1=CC=C(C=C1)C(O)=O)=C2