-cas-1446321-46-5.png)
VOXELOTOR
GBT 440; GTx-011, Treatment of Sickle Cell Disease
RN: 1446321-46-5
UNII: 3ZO554A4Q8
Molecular Formula, C19-H19-N3-O3, Molecular Weight, 337.3771
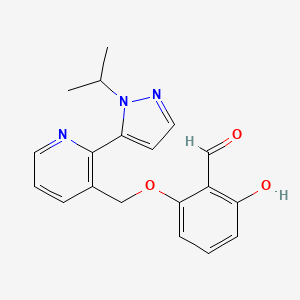
Benzaldehyde, 2-hydroxy-6-((2-(1-(1-methylethyl)-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)-3-pyridinyl)methoxy)-
2-hydroxy-6-((2-(1-(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)pyridin-3-yl)methoxy)benzaldehyde
NMR http://file.selleckchem.com/downloads/nmr/S854001-GBT440-CDCl3-hnmr-selleck.pdf
- Originator Global Blood Therapeutics
- Class Antianaemics; Small molecules
- Mechanism of Action Abnormal haemoglobin modulators; Sickle haemoglobin modulators
- Orphan Drug Status Yes – Sickle cell anaemia
- New Molecular Entity Yes
Highest Development Phases
- Phase III Sickle cell anaemia
- Phase I Hypoxia; Liver disorders
- Discontinued Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Most Recent Events
- 01 Nov 2017 Chemical structure information added
- 28 Oct 2017 Efficacy and adverse event data from a case study under the compassionate use programme in Sickle cell anaemia released by Global Blood Therapeutics
- 27 Oct 2017 Discontinued – Phase-II for Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in USA (PO)
Voxelotor, also known as GBT-440, is a hemoglobin S allosteric modulator. GBT440 Inhibits Sickling of Sickle Cell Trait Blood Under In Vitro Conditions Mimicking Strenuous Exercise. GBT440 increases haemoglobin oxygen affinity, reduces sickling and prolongs RBC half-life in a murine model of sickle cell disease. GBT440 increases haemoglobin oxygen affinity, reduces sickling and prolongs RBC half-life in a murine model of sickle cell disease.
Treatment Of Sickle Cell Disease In Adults And Adolescents With Episodes Of Vaso-Occlusive Crisis
FDA gave breakthrough therapy designation to this product
Innovator – Global Blood Therapeutics

PATENT
WO 2013102142
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=WO2013102142
Hemoglobin (Hb) is a tetrameric protein in red blood cells that transports up to four oxygen molecules from the lungs to various tissues and organs throughout the body.
Hemoglobin binds and releases oxygen through conformational changes, and is in the tense (T) state when it is unbound to oxygen and in the relaxed (R) state when it is bound to oxygen. The equilibrium between the two conformational states is under allosteric regulation. Natural compounds such as 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate (2,3-BPG), protons, and carbon dioxide stabilize hemoglobin in its de-oxygenated T state, while oxygen stabilizes hemoglobin in its oxygenated R state. Other relaxed R states have also been found, however their role in allosteric regulation has not been fully elucidated.
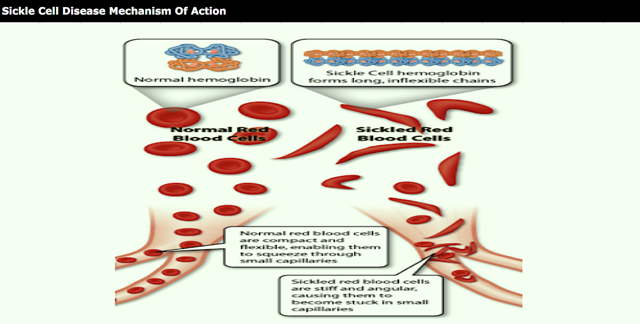
Sickle cell disease is a prevalent disease particularly among those of African and Mediterranean descent. Sickle hemoglobin (HbS) contains a point mutation where glutamic acid is replaced with valine, allowing the T state to become susceptible to polymerization to give the HbS containing red blood cells their characteristic sickle shape. The sickled cells are also more rigid than normal red blood cells, and their lack of flexibility can lead to blockage of blood vessels. Certain synthetic aldehydes have been found to shift the equilibrium from the polymer forming T state to the non-polymer forming R state (Nnamani et al. Chemistry & Biodiversity Vol. 5, 2008 pp. 1762-1769) by acting as allosteric modulators to stabilize the R state through formation of a Schiff base with an amino group on hemoglobin.
US 7, 160,910 discloses 2-furfuraldehydes and related compounds that are also allosteric modulators of hemoglobin. One particular compound 5-hydroxymethyl-2-furfuraldehyde (5HMF) was found to be a potent hemoglobin modulator both in vitro and in vivo. Transgenic mice producing human HbS that were treated with 5HMF were found to have significantly improved survival times when exposed to extreme hypoxia (5% oxygen). Under these hypoxic conditions, the 5HMF treated mice were also found to have reduced amounts of hypoxia-induced sickled red blood cells as compared to the non-treated mice.
A need exists for therapeutics that can shift the equilibrium between the deoxygenated and oxygenated states of Hb to treat disorders that are mediated by Hb or by abnormal Hb such as HbS. A need also exists for therapeutics to treat disorders that would benefit from having Hb in the R state with an increased affinity for oxygen. Such therapeutics would have applications ranging, for example, from sensitizing hypoxic tumor cells that are resistant to standard radiotherapy or chemotherapy due to the low levels of oxygen in the cell, to treating pulmonary and hypertensive disorders, and to promoting wound healing
Example 18. Preparation of 2-hydroxy-6-((2-(1-isopropyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)pyridin-3-yl)methoxy)benzaldehyde (Compound 43).

A mixture of 2,6-dihydroxybenzaldehyde (1.58 g, 11.47 mmol, 2 eq.) and K2CO3 (2.4 g, 17.22 mmol, 3 eq.) in DMF (150 mL) was stirred at rt for 10 min. To this mixture was added 3-(chloromethyl)-2-(1-isopropyI-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)pyridine hydrochloride (1.56 g, 5.74 mmol, leq.) at rt. The mixture was heated at 50 °C for 2 h, filtered, concentrated and purified on silica gel using a mixture of EtOAc and hexanes as eluent to give 2-hydroxy-6-((2-(1-isopropyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)pyridin-3-yl)methoxy)benzaldehyde (1.71 g, 88%) as a pale yellow solid.
PAPER
ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters (2017), 8(3), 321-326.
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acsmedchemlett.6b00491
Discovery of GBT440, an Orally Bioavailable R-State Stabilizer of Sickle Cell Hemoglobin
ACS Editors’ Choice – This is an open access article published under an ACS AuthorChoice License, which permits copying and redistribution of the article or any adaptations for non-commercial purposes.

We report the discovery of a new potent allosteric effector of sickle cell hemoglobin, GBT440 (36), that increases the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen and consequently inhibits its polymerization when subjected to hypoxic conditions. Unlike earlier allosteric activators that bind covalently to hemoglobin in a 2:1 stoichiometry, 36 binds with a 1:1 stoichiometry. Compound 36 is orally bioavailable and partitions highly and favorably into the red blood cell with a RBC/plasma ratio of ∼150. This partitioning onto the target protein is anticipated to allow therapeutic concentrations to be achieved in the red blood cell at low plasma concentrations. GBT440 (36) is in Phase 3 clinical trials for the treatment of sickle cell disease (NCT03036813).

aReagents and conditions: (a) MOMCl, DIEPA, DCM, 0 °C to rt 2 h, 90%; (b) nBuLi, DMF, THF, −78 to 0 °C, 94%; (c) 12 N HCl, THF, rt, 1.5 h, 81%; (d) Pd(dppf)Cl2, NaHCO3, H2O/dioxane, 100 °C, 12 h, 40%; (e) SOCl2, DCM, rt, 100%; (f) Na2CO3, DMF, 65 °C, 1.5 h, 81%; (g) 12 N HCl, THF, rt, 3 h, 96%.
GBT440 (36) (15.3 g).
HRMS calcd for C19H20N3O3 (M+H + ) 338.1499, found 338.1497; MS (ESI) m/z 338.4 [M+H]+ ;
1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 11.94 (s, 1H), 10.37 (d, J = 0.6 Hz, 1H), 8.75 (dd, J = 4.8, 1.7 Hz, 1H), 7.97 (dd, J = 7.8, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.63 – 7.57 (m, 1H), 7.46 – 7.33 (m, 2H), 6.57 (dt, J = 8.6, 0.7 Hz, 1H), 6.34 (d, J = 1.9 Hz, 1H), 6.27 (dt, J = 8.3, 1.0 Hz, 1H), 5.07 (s, 2H), 4.65 (hept, J = 6.6 Hz, 1H), 1.47 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, 7H);
13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 194.0, 162.9, 161.1, 149.6, 149.1, 139.1, 138.2, 138.2, 138.0, 131.6, 124.0, 111.1, 110.2, 107.4, 103.5, 67.8, 50.5, 23.1.
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/suppl/10.1021/acsmedchemlett.6b00491/suppl_file/ml6b00491_si_001.pdf
PATENT
WO 2015031285
https://www.google.co.in/patents/WO2015031285A1?cl=en
2-Hydroxy-6-((2-(l-isopropyl-lH-pyrazol-5-yl)pyridin-3-yl)methoxy)benzaldehyde is a compound having the formula:

Sickle cell disease is a disorder of the red blood cells, found particularly among those of African and Mediterranean descent. The basis for sickle cell disease is found in sickle hemoglobin (HbS), which contains a point mutation relative to the prevalent peptide sequence of hemoglobin (Hb).
[ Hemoglobin (Hb) transports oxygen molecules from the lungs to various tissues and organs throughout the body. Hemoglobin binds and releases oxygen through
conformational changes. Sickle hemoglobin (HbS) contains a point mutation where glutamic acid is replaced with valine, allowing HbS to become susceptible to polymerization to give the HbS containing red blood cells their characteristic sickle shape. The sickled cells are also more rigid than normal red blood cells, and their lack of flexibility can lead to blockage of blood vessels. A need exists for therapeutics that can treat disorders that are mediated by Hb or by abnormal Hb such as HbS, such as 2-hydroxy-6-((2-(l-isopropyl-lH-pyrazol-5-yl)pyridin-3-yl)methoxy)benzaldehyde hydrochloride.
When used for treating humans, it is important that a crystalline form of a therapeutic agent, like 2-hydroxy-6-((2-(l-isopropyl-lH-pyrazol-5-yl)pyridin-3-yl)methoxy)benzaldehyde, or a salt thereof, retains its polymorphic and chemical stability, solubility, and other physicochemical properties over time and among various manufactured batches of the agent. If the physicochemical properties vary with time and among batches, the administration of a therapeutically effective dose becomes problematic and may lead to toxic side effects or to ineffective therapy, particularly if a given polymorph decomposes prior to use, to a less active, inactive, or toxic compound. Therefore, it is important to choose a form of the crystalline agent that is stable, is manufactured reproducibly, and has physicochemical properties favorable for its use as a therapeutic agent.

Example ί : Synthesis of Compound 15
OH DIPEA OMOM

(8063J To s solution of 2 >ronao enzsae-i -diol (5 g, 26.45 m ol) m. DCM (50 ml) at 0 *C was added DIPEA (11.54 mL, 66.13 aan l) and MOMCi (4.42 mL. 58.19 ratnoi). The mixture was stirred at 0 °C for 1.5 h, and then warmed to room temperature. The so ntioa was dilated with DCM, washed with sat. NaH€<¾, brum dried and concentrated to give crude product, which was purified by coinran ihexane&/EtOAc~4;l) to give desired product 15.58 g (90%).
14C
Example 2: Synthesis of Compound 13 from 15

[0064] To a solution of 2-bromo-l ,3-bis(methoxymethoxy)benzene (15) (19.9g, 71.8 mmol) in THF (150 mL) at -78 °C was added BuLi (2.5 M, 31.6 mL, 79.0 mmol) dropwise. The solution was stirred at -78 °C for 25 min (resulting white cloudy mixture), then it was warmed to 0 °C and stirred for 25 min. The reaction mixture slowly turns homogenous. To the solution was added DMF at 0 °C. After 25 min, HPLC showed reaction completed. The mixture was quenched with sat. NH4C1 (150 mL), diluted with ether (300 mL). The organic layer was separated, aq layer was further extracted with ether (2X200 mL), and organic layer was combined, washed with brine, dried and concentrated to give crude product, which was triturated to give 14.6 g desired product. The filtrate was then concentrated and purified by column to give additional 0.7 g, total mass is 15.3 g.
Example 3: Synthesis of Compound 13 from resorcinol 11
1.1 R:TMEDA R:BuLi S:THF 2 h -10°C

Journal of Organic Chemistry, 74(1 1), 431 1-4317; 2009
[0065] A three-necked round-bottom flask equipped with mechanical stirrer was charged with 0.22 mol of NaH (50 % suspension in mineral oil) under nitrogen atmosphere. NaH was washed with 2 portions (100 mL) of n-hexane and then with 300 mL of dry diethyl ether; then 80 mL of anhydrous DMF was added. Then 0.09 mol of resorcinol 11, dissolved in 100 mL of diethyl ether was added dropwise and the mixture was left under stirring at rt for 30 min. Then 0.18 mol of MOMCI was slowly added. After 1 h under stirring at rt, 250 mL of water was added and the organic layer was extracted with diethyl ether. The extracts were
15A
washed with brine, dried (Na2S04), then concentrated to give the crude product that was purified by silica gel chromatography to give compound 12 (93 % yield).
15B
[0066] A three-necked round-bottom flask was charged with 110 mL of n-hexane, 0.79 mol of BuLi and 9.4 mL of tetramethylethylendiamine (TMEDA) under nitrogen atmosphere. The mixture was cooled at -10 °C and 0.079 mol of bis-phenyl ether 12 was slowly added. The resulting mixture was left under magnetic stirring at -10 °C for 2 h. Then the temperature was raised to 0 °C and 0.067 mol of DMF was added dropwise. After 1 h, aqueous HC1 was added until the pH was acidic; the mixture was then extracted with ethyl ether. The combined extracts were washed with brine, dried (Na2S04), and concentrated to give aldehyde 13
(84%).
[0067] 2,6-bis(methoxymethoxy)benzaldehyde (13): mp 58-59 °C (n-hexane) ; IR (KBr) n: 1685 (C=0) cm“1; 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDC13) δ 3.51 (s, 6H, 2 OCH3), 5.28 (s, 4H, 2 OCH20), 6.84 (d, 2H, J = 8.40 Hz, H-3, H-5), 7.41 (t, 1H, J = 8.40 Hz, H-4), 10.55 (s, 1H, CHO); MS, m/e (relative intensity) 226 (M+, 3), 180 (4), 164 (14), 122 (2), 92 (2), 45 (100); Anal. Calc’d. for CnHi405: C,58.40; H, 6.24. Found: C, 57.98; H, 6.20.
Example 4: The Synthesis of Compound 16

13 16
81 %
[0068] To a solution of 2,6-bis(methoxymethoxy)benzaldehyde (13) (15.3 g, 67.6 mmol) in THF (105 mL) (solvent was purged with N2) was added cone. HC1 (12N, 7 mL) under N2, then it was further stirred under N2 for 1.5 h. To the solution was added brine (100 mL) and ether (150 ml). The organic layer was separated and the aqueous layer was further extracted with ether (2×200 mL). The organic layer was combined, washed with brine, dried and concentrated to give crude product, which was purified by column (300g,
hexanes/EtOAc=85: 15) to give desired product 16 (9.9 g) as yellow liquid.
Example 5: Synthesis of Compound 17

16
[0069] To a solution of 2-hydroxy-6-(methoxymethoxy)benzaldehyde (16) (10.88 g, 59.72 mmol) in DMF (120 mL) (DMF solution was purged with N2 for 10 min) was added K2C03 (32.05 g, 231.92 mmol) and 3-(chloromethyl)-2-(l-isopropyl-lH-pyrazol-5-yl)pyridine hydrochloride (10) (15.78 g, 57.98 mmol). The mixture was heated at 65 °C for 1.5 h, cooled to rt, poured into ice water (800 mL). The precipitated solids were isolated by filtration, dried and concentrated to give desired product (17, 18 g).
Example 6: Synthesis of Compound (I)

[0070] To a solution of 2-((2-(l-isopropyl-lH-pyrazol-5-yl)pyridin-3-yl)methoxy)-6-(methoxymethoxy)benzaldehyde (17) (18 g, 47.19 mmol) in THF (135 mL, solution was purged with N2) was added cone. HCI (12N, 20 mL). The solution was stirred at rt for 3 h when HPLC showed the reaction complete. The mixture was added to a solution of NaHC03 (15 g) in water (1.2 L), and the resulting precipitate was collected by filtration, dried to give crude solid, which was further purified by column (DCM/EtOAc=60:40) to give pure product
(15.3 g).
Example 7: Synthesis of Compound I (free base) and its HCI salt form
[0071] Compound (I) free base (40g) was obtained from the coupling of the alcohol intermediate 7 and 2,6-dihydroxybenzaldedhye 9 under Mitsunobu conditions. A procedure is also provided below:

17
Example 8: Synthesis of Compound (I) by Mitsunobu coupling
[0072] Into a 2000-mL three neck round-bottom flask, which was purged and maintained with an inert atmosphere of nitrogen, was placed a solution of [2-[l-(propan-2-yl)-lH-pyrazol-5-yl]pyridin-3-yl]methanol (7) (70 g, 322.18 mmol, 1.00 equiv) in tetrahydrofuran (1000 mL). 2,6-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde (9) (49.2 g, 356.21 mmol, 1.10 equiv) and PPh3 (101 g, 385.07 mmol, 1.20 equiv) were added to the reaction mixture. This was followed by the addition of a solution of DIAD (78.1 g, 386.23 mmol, 1.20 equiv) in tetrahydrofuran (200 ml) dropwise with stirring. The resulting solution was stirred overnight at room temperature. The resulting solution was diluted with 500 ml of H20. The resulting solution was extracted with 3×500 ml of dichloromethane and the combined organic layers were dried over sodium sulfate and concentrated under vacuum. The residue was applied onto a silica gel column with EA:PE (1 :50-l :3) as eluent to yield the crude product. The crude product was re-crystallized from i-propanol/H20 in the ratio of 1/1.5. This resulted in 40 g (37%) of 2-hydroxy-6-([2-[l-(propan-2-yl)-lH-pyrazol-5-yl]pyridin-3-yl]methoxy)benzaldehyde as a light yellow solid. The compound exhibited a melting point of 80-82 °C. MS (ES, m/z): 338.1 [M+l]. 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.72(s, 1H), 10.21(s, 1H), 8.76(d, J=3.6Hz, 1H), 8.24(d, J=2.7Hz, lH),7.55(m, 3H), 6.55(m,3H) ,5.21 (s, 2H), 4.65 (m, 1H), 1.37 (d, J=5.1Hz, 6H). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDC13) δ 11.96 (s, 1H), 10.40 (s, 1H), 8.77 (dd, J= 4.8, 1.5 Hz, 1H), 8.00 (d, J= 7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.63 (d, J= 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.49 – 7.34 (m, 2H), 6.59 (d, J= 8.5 Hz, 1H), 6.37 (d, J= 1.8 Hz, 1H), 6.29 (d, J= 8.2 Hz, 1H), 5.10 (s, 2H), 4.67 (sep, J= 6.7 Hz, 1H), 1.50 (d, J= 6.6 Hz, 6H).
[0073] In another approach, multiple batches of Compound (I) free base are prepared in multi gram quantities (20g). The advantage of this route is the use of mono-protected 2,6-dihydroxybenzaldehyde (16), which effectively eliminates the possibility of bis-alkylation side product. The mono-MOM ether of 2,6-dihydroxybenzaldehyde (16) can be obtained from two starting points, bromoresorcinol (14) or resorcinol (11) [procedures described in the Journal of Organic Chemistry, 74(11), 4311-4317; 2009 ]. All steps and procedures are provided below. Due to the presence of phenolic aldehyde group, precautions (i.e., carry out all reactions under inert gas such as nitrogen) should be taken to avoid oxidation of the phenol and/or aldehyde group.
18
Preparation of compound I HC1 salt: A solution of compound I (55.79 g, 165.55 mmol) in acetonitrile (275 mL) was flushed with nitrogen for 10 min, then to this solution was added 3N aqueous HC1 (62 mL) at room temperature. The mixture was stirred for additional 10 min after the addition, most of the acetonitrile (about 200 mL) was then removed by evaporation on a rota
PATENT
WO2017096230
PATENT
WO-2017197083
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=WO2017197083
Processes for the preparation of 2-hydroxy-6-((2-(1-isopropyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)-pyridin-3-yl)methoxy)benzaldehyde (also referred to as voxelotor or Compound (I)) and its intermediates is claimed. Compound (I) binds to hemoglobin and increases it oxygen affinity and hence can be useful for the treatment of diseases such as sickle cell disease.
Disclosed herein are processes for synthesizing 2-hydroxy-6-((2-(l-isopropyl-lH-pyrazol-5-yl)-pyridin-3-yl)methoxy)benzaldehyde (Compound (I)) and intermediates used in such processes. Compound (I) binds to hemoglobin and increases it oxygen affinity and hence can be useful for the treatment of diseases such as sickle cell disease.
BACKGROUND
Compound (I) is disclosed in Example 17 of the International Publication No.
WO2013/102142. Compound (I) binds to hemoglobin and increases it oxygen affinity and hence can be useful for the treatment of diseases such as sickle cell disease.
In general, for a compound to be suitable as a therapeutic agent or part of a therapeutic agent, the compound synthesis must be amendable to large scale manufacturing and isolation. The large scale manufacturing and isolation should not impact the physical properties and purity of the compound nor should it negatively impact cost or efficacy of a formulated active ingredient. Accordingly, scale up of manufacturing and isolation may require significant efforts to meet these goals.
ompound (I) has been synthesized by certain methods starting with 2,6-dihydroxbenzaldehyde (compound 1) where each hydroxyl moiety is protected with an unbranched, straight-chain alkyl or alkoxyalkyl such as, for example, methyl or methoxymethyl. Following installation of the aldehyde group, various methods of deprotection of the hydroxyl group were employed to synthesize compound (1) used in the synthesis and production of Compound (I). However, the deprotection processes used lead to unwanted polymerization and decomposition reactions of compound (1) – attributed, in part, to the conditions used for
deprotection of the hydroxy groups. The undesired byproducts yield complex mixtures, lower yields of Compound (I), and require significant effort to purify Compound (I) to a degree acceptable for use as a part of a therapeutic agent, thus rendering the above processes impractical for commercial scale synthesis of Compound (I).
Provided herein are processes for the synthesis of Compound (I):

Examples
Example 1
Synthesis of 2,6-dihydroxybenzaldehyde (Compound (1))

Step 1:
Tetrahydrofuran (700 mL) was added to resorcinol (170g, 1.54 mol, leq.) under inert gas protection, followed by addition of pyridinium tosylate (3.9 g, 15.4 mmol, O.Oleq.), THF 65 mL) and the reaction mixture was cooled down to 0 – 5 °C. Within 1 – 1.5 h ethylvinyl ether (444 mL, 4.63 mol, 3.0 eq.) was added while maintaining a temperature <5°C. After the addition was complete the reaction mixture was allowed to reach room temperature within 1.5 h. The reaction was stirred overnight, cooled down to 10-15 °C, and 510 mL of ½ sat. NaHC03 was added while maintaining the reaction solution below 20 °C. The phases were separated. The organic phase was washed once with 425 mL of water and once with 425 mL 12.5% NaCl solution and evaporated and azeotroped with THF to give bis-EOE-protected resorcinol (401.2 g, 1.55 mol, 102% uncorrected) as a clear colorless to yellowish oil.
Step 2:
Bis-EOE-protected resorcinol (390 g of, actual: 398.6g = 1.53 mol, 1 eq., corrected to 100%) conversion) was added under inert gas protection to a 6 L glass vessel and THF (1170 mL) was added. The reaction mixture was cooled down to -10°C to -5°C and n-BuLi (625 mL, 2.7 M in heptane, 1.687 mol, 1.1 eq.) was added. The reaction mixture was agitated at -5°C- 0°C for 30-40 min and then DMF (153.4 mL, 1.99 mmol, 1.3 eq.) was added starting at -10°C to -5°C. The reaction mixture was stirred until complete and then quenched with lNHCl/EtOAc. It was also discovered, inter alia, that protection with the EOE groups not only resulted in less byproducts but appeared to increase the speed of the formylation reaction to provide 2,6-bis(l-ethoxyethoxy)benzaldehyde (compound (2)).
The mixture was worked up, phase separated and the aqueous washed with MTBE. After aqueous wash to remove salts the organic phase was concentrated to the neat oil to obtain the compound (2) as yellow oil (almost quantitative).
A batch preparation was performed using solvent swap and was completed faster than other known methods for synthesizing Compound (I) with better purity and yield. The deprotection sequence allowed in-situ use of compound (2).
Step 3:
To the reaction solution of Step 2 was added IN HC1 (1755 mL) while maintaining the temperature < 20°C. The pH was of the solution was adjusted to pH = 0.7 – 0.8 with 6 M HC1.
The reaction mixture was stirred for 16 h. After the reaction was complete the organic phase was separated and 1560 mL of methyl tert butyl ether was added. The organic phase was washed once with 1170 mL of IN HC1, once with 780 mL of ½ sat. NaCl solution and once with 780 mL of water and then concentrated to a volume of – 280mL. To the solution was added 780 mL of methyl tert butyl ether and concentrate again to 280 mL [temperature <45°C, vacuo]. To the slurry was added 780 mL of acetonitrile and the solution was concentrated in vacuo at T < 45°C to a final volume of – 280 mL. The slurry was heated to re-dissolve the solids. The solution was cooled slowly to RT and seeded at 60-65 °C to initiate crystallization of the product. The slurry was cooled down to -20°C to -15°C and agitated at this temperature for 1-2 h. The product was isolated by filtration and washed with DCM (pre-cooled to -20°C to -15°C) and dried under a stream of nitrogen to give 2,6-dihydroxybenzaldehyde as a yellow solid. Yield: 138.9 g (1.00 mol, 65.6%).
Example 1A
Alternate Synthesis of 2,6-dihydroxybenzaldehyde compound (1)

Step 1:
In a suitable reactor under nitrogen, tetrahydrofuran (207 L) was added to resorcinol (46 kg, 0.42 kmol, leq.) followed by addition of pyridinium tosylate (1.05 kg, 4.2 mol, O.Oleq.), and the reaction mixture was cooled down to 0 – 5 °C. Within 1 – 1.5 h ethylvinyl ether (90.4 kg, 120.5 L, 125 kmol, 3.0 eq.) was added while maintaining a temperature <5°C. After the addition was complete the reaction mixture was allowed to reach room temperature within 1.5 h. The reaction was stirred overnight, cooled down to 10-15 °C, and 138 L of aqueous 4% NaHC03 was added while maintaining the reaction solution below 20 °C. The phases were separated. The organic phase was washed once with 115 L of water and once with 125.2 kg of a 12.5% NaCl solution. The organic layer was dried by azeotropic distillation with THF to a water content value < 0.05%) (by weight) to yield bis-EOE-protected resorcinol (106.2 kg, 0.42 kmol) as a solution in THF. An advantage over previously reported protection procedures is that the bis-EOE-protected resorcinol product does not need to be isolated as a neat product. The
product-containing THF solution can be used directly in the next reaction step thus increasing throughput and reducing impurity formation.
Step 2:
Bis-EOE-protected resorcinol solution (assumption is 100% conversion) was added under inert gas protection to suitable reactor. The reaction mixture was cooled down to -10°C to -5°C and n-BuLi (117.8 kg, 25% in heptane, 1.1 eq.) was added. The reaction mixture was agitated at -5°C- 0°C for 30-40 min and then DMF (39.7 kg, 0.54 kmol, 1.3 eq.) was added at -10°C to -5°C. The reaction mixture was stirred until complete and then quenched with aqueous HC1 (1M, 488.8 kg) to give 2,6-bis(l-ethoxyethoxy)benzaldehyde. An advantage over previously reported procedures of using EOE protecting group is that the HC1 quenched solution can be used directly in the deprotection step, and 2,6-bis(l-ethoxyethoxy)benzaldehyde does not need to be isolated as a neat oil.
Step 3:
The pH of the quenched solution was adjusted to < 1 with aqueous HC1 (6M, ca 95.9 kg) and the reaction mixture stirred at ambient temperature for 16 h. After the reaction was complete the organic phase was separated and 279.7 kg of methyl tert butyl ether was added. The organic phase was washed once with aqueous IN HC1 (299 kg), once with aqueous 12.5% NaCl (205.8 kg) and once with 189 kg of water and then concentrated to a volume of ca. 69 L. To the slurry was added 164 kg of acetonitrile and the solution was concentrated in vacuo at T < 45°C to a final volume of ca. 69 L. The slurry was heated to re-dissolve the solids. The solution was seeded at 60-65 °C to initiate crystallization of the product and cooled slowly to RT over 8 hrs. The slurry was cooled down to -20 °C to -15°C and agitated at this temperature for l-2h. The product was isolated by filtration and washed with DCM (50.3 kg, pre-cooled to -20 °C to -15 °C) and dried under a stream of nitrogen to yield 2,6-dihydroxybenzaldehyde as a yellow solid. Yield: 37.8 kg (0.27 kmol, 65.4% Yield). The described telescoped approach from deprotection to crystallization increases the throughput and integrity of the product.
Example 2
Synthesis of 3-(chloromethyl)-2-(l-isopropyl-lH-pyrazol-5-yl)pyridine
dihydrochloride salt

Step 1:
An appropriately sized flask was purged with nitrogen and charged with (2-chloropyridin-3-yl)methanol (1.0 equiv), sodium bicarbonate (3.0 equiv), [1, l ‘-bis(diphenyl-phosphino)-ferrocene]dichloropalladium (5 mol %), l-isopropyl-5-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-l,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)-lH-pyrazole (1.2 equiv), and a mixture of 2-MeTHF (17.4 vol) and deionized water (5.2 vol). The resulting solution was heated to 70°C to 75°C and conversion monitored by HPLC. Once the reaction was complete, the reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature, diluted with deionized water, and the phases were separated. The organic layer was extracted with 2 N HC1 (10 vol) and the phases were separated. The aqueous phase was washed with MTBE. The pH of the aqueous phase was adjusted to 8-9 with 6 N NaOH. The product was extracted into EtOAc, treated with Darco G-60 for 30 to 60 min, dried over MgS04, filtered through Celite®, and concentrated to give (2-(l-isopropyl-lH-pyrazol-5-yl)pyridin-3-yl)methanol as a brown oil.
Step 2:
A suitably equipped reactor was charged with (2-(l-isopropyl-lH-pyrazol-5-yl)pyridin-3-yl)methanol hydrochloride salt (1 equivalent) and purified water. An aqueous sodium
bicarbonate solution (8% NaHC03) was added slowly to maintain the solution temperature between 17 °C to 25 °C. After addition was complete, the reaction mixture was stirred at 17 °C to 25 °C and dichloromethane was added and the organic layer was separated. DCM solution was then distilled under atmospheric conditions at approximately 40°C and the volume was reduced. DCM was added the reactor and the contents of the reactor are stirred at 20°C to 30°C until a clear solution is formed. The contents of the reactor were cooled to 0°C to 5°C and thionyl chloride was charged to the reactor slowly to maintain a temperature of < 5 °C. The reaction solution was stirred at 17 °C to 25 °C. When the reaction was complete, a solution of HC1 (g) in 1,4-dioxane (ca. 4 N, 0.8 equiv.) was charged to the reactor slowly to maintain the solution temperature between 17 °C and 25 °C. The product 3-(chloromethyl)-2-(l-isopropyl- lH-pyrazol-5-yl)pyridine dihydrochloride salt was filtered washed with dichloromethane and dried.
Example 3
Synthesis of 2-hydroxy-6-((2-(l-isopropyl-lH-pyrazol-5-yl)-pyridin-3-yl)methoxy)benzaldehyde
Form I

(I)
tably equipped reactor was charged with 3-(chloromethyl)-2-(l-isopropyl-lH-pyrazol-5-yl)pyridine dihydrochloride salt (1 equivalent), sodium iodide (0.05 equivalent), sodium bicarbonate (4 equivalent), l-methyl-2-pyrrolidinone (NMP), and 2,6-dihydroxy-benzaldehyde (1 to 1.05 equiv.). The reaction mixture was heated slowly to 40 °C to 50 °C and stirred until the reaction was complete. Water was then added and the reaction mixture was cooled and maintained at 17 °C to 25 °C. When the water addition was complete, the reaction mixture was stirred at 17 °C to 25 °C and slowly cooled to 0°C to 5°C and the resulting solids were collected by filtration. The solids were washed with a 0 °C to 5 °C 2: 1 water/NMP solution, followed by 0 °C to 5 °C water. The solids were filtered and dried to give 2-hydroxy-6-((2-(l-isopropyl-lH-pyrazol-5-yl)-pyridin-3-yl)methoxy)benzaldehyde as Form I or a mixture of 2-hydroxy-6-((2-(l-isopropyl-lH-pyrazol-5-yl)-pyridin-3-yl)methoxy)benzaldehyde as Form I Form I and NMP solvates.
Alternative Synthesis:
A suitably equipped reactor was charged with 3-(chloromethyl)-2-(l-isopropyl-lH-pyrazol-5-yl)pyridine bishydrochloride salt (1 equivalent), sodium iodide (0.05 equivalent), sodium bicarbonate (3 to 4 equivalent), l-methyl-2-pyrrolidinone (7 equivalent, NMP), and 2,6-dihydoxybenzaldehyde (1.05 equivalent). The reaction mixture was heated to 40 °C to 50° C and stirred until the reaction was complete. Water (5 equivalent) was then added while maintaining the contents of the reactor at 40 °C to 460 C and the resulting clear solution seeded with 2-hydroxy-6-((2-(l-isopropyl-lH-pyrazol-5-yl)-pyridin-3-yl)methoxy)benzaldehyde Form I. Additional water (5 equivalent) was added while maintaining the contents of the reactor at 40 °C to 500 C, the reactor contents cooled to 15 °C to 25 0 C, and the reactor contents stirred for at least 1 hour at 15 °C to 25 0 C. The solids were collected, washed twice with 1 :2 NMP: water and twice with water, and dried to yield 2-hydroxy-6-((2-(l-isopropyl-lH-pyrazol-5-yl)-pyridin-3-yl)methoxy)benzaldehyde Form I devoid of 2-hydroxy-6-((2-(l-isopropyl-lH-pyrazol-5-yl)-pyridin-3-yl)methoxy)benzaldehyde as NMP solvates.
Example 4
Preparation of 2-hydroxy-6-((2-(l-isopropyl-lH-pyrazol-5-yl)-pyridin-3-yl)methoxy)- benzaldehyde Form II

Step 1:
A suitably equipped reactor with an inert atmosphere was charged with crude 2-hydroxy- 6-((2-(l-isopropyl-lH-pyrazol-5-yl)-pyridin-3-yl)methoxy)benzaldehyde (from Example 3 above) and MTBE and the contents stirred at 17°C to 25°C until dissolution was achieved. The reaction solution was passed through a 0.45 micron filter and MTBE solvent volume reduced using vacuum distillation at approximately 50 °C. The concentrated solution was heated to 55°C to 60°C to dissolve any crystallized product. When a clear solution was obtained, the solution was cooled to 50 °C to 55 °C and n-heptane was added. 2-Hydroxy-6-((2-(l-isopropyl-lH-pyrazol-5-yl)-pyridin-3-yl)methoxy)benzaldehyde (e.g., Form II) seeds in a slurry of n-heptane were charged and the solution was stirred at 50°C to 55°C. The solution was cooled to 45 °C to 50 °C and n-heptane was added to the reactor slowly while maintaining a reaction solution temperature of 45°C to 50°C. The reaction solution are stirred at 45°C to 50°C and then slowly cooled to 17°C to 25°C. A sample was taken for FTIR analysis and the crystallization was considered complete when FTIR analysis confirmed 2-hydroxy-6-((2-(l-isopropyl-lH-pyrazol-5-yl)-pyridin-3-yl)methoxy)-benzaldehyde (Form II). The contents of the reactor were then cooled to 0°C to 5°C and the solids were isolated and washed with cold n-heptane and dried.
POLYMORPHS
PATENT
https://patents.google.com/patent/US20160207904
PATENT
https://patents.google.com/patent/US20160346263A1/en
-
2-Hydroxy-6-((2-(1-isopropyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)pyridin-3-yl)methoxy)benzaldehyde is a compound having the formula:
-
[0000]
-
[0003]Sickle cell disease is a disorder of the red blood cells, found particularly among those of African and Mediterranean descent. The basis for sickle cell disease is found in sickle hemoglobin (HbS), which contains a point mutation relative to the prevalent peptide sequence of hemoglobin (Hb).
-
[0004]Hemoglobin (Hb) transports oxygen molecules from the lungs to various tissues and organs throughout the body. Hemoglobin binds and releases oxygen through conformational changes. Sickle hemoglobin (HbS) contains a point mutation where glutamic acid is replaced with valine, allowing HbS to become susceptible to polymerization to give the HbS containing red blood cells their characteristic sickle shape. The sickled cells are also more rigid than normal red blood cells, and their lack of flexibility can lead to blockage of blood vessels. A need exists for therapeutics that can treat disorders that are mediated by Hb or by abnormal Hb such as HbS, such as 2-hydroxy-6-((2-(1-isopropyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)pyridin-3-yl)methoxy)benzaldehyde.
-
[0005]When used for treating humans, it is important that a crystalline form of a therapeutic agent, like 2-hydroxy-6-((2-(1-isopropyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)pyridin-3-yl)methoxy)benzaldehyde, or a salt thereof, retains its polymorphic and chemical stability, solubility, and other physicochemical properties over time and among various manufactured batches of the agent. If the physicochemical properties vary with time and among batches, the administration of a therapeutically effective dose becomes problematic and may lead to toxic side effects or to ineffective therapy, particularly if a given polymorph decomposes prior to use, to a less active, inactive, or toxic compound. Therefore, it is important to choose a form of the crystalline agent that is stable, is manufactured reproducibly, and has physicochemical properties favorable for its use as a therapeutic agent.
-
[0006]However, the art remains unable to predict which crystalline form of an agent will have a combination of the desired properties and will be suitable for human administration, and how to make the agent in such a crystalline form.
PATENT
https://patents.google.com/patent/US9447071B2/en
It has now been discovered that 2-hydroxy-6-((2-(1-isopropyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)pyridin-3-y1)methoxy)benzaldehyde (or Compound 1) i.e., the free base of Compound 1, can be obtained as one or more crystalline ansolvate forms, several of which are referred to here as crystalline Form I, Form II and Material N. In preferred embodiments, the free base of Compound 1 is a crystalline ansolvate, such as a crystalline anhydrous form. The free base of Compound 1, can be obtained from its corresponding salt form, such as the HCl salt of Compound 1.
Three anhydrous crystalline forms of the free base were identified, termed Free Base Forms I, II, and Material N. It has been discovered that nucleation of Free Base Form I generally occurs first from a slurry. Extending the slurry time can induce the transformation of Free Base Form I to Free Base Form II, a thermodynamically more stable phase relative to Form I. It has further been discovered that Free Base Material N can be stable relative to Forms I and II, at room temperature.
Synthetic Routes for Preparing Compound 1
The compound of formula (I) was synthesized as schematically described below and elaborated thereafter.
Example 1 Synthesis of Compound 15
To a solution of 2-bromobenzene-1,3-diol (5 g, 26.45 mmol) in DCM (50 ml) at 0° C. was added DIPEA (11.54 mL, 66.13 mmol) and MOMCl (4.42 mL, 58.19 mmol). The mixture was stirred at 0° C. for 1.5 h, and then warmed to room temperature. The solution was diluted with DCM, washed with sat. NaHCO3, brine, dried and concentrated to give crude product, which was purified by column (hexanes/EtOAc=4:1) to give desired product 15.58 g (90%).
Example 2 Synthesis of Compound 13 from 15
To a solution of 2-bromo-1,3-bis(methoxymethoxy)benzene (15) (19.9 g, 71.8 mmol) in THF (150 mL) at −78° C. was added BuLi (2.5 M, 31.6 mL, 79.0 mmol) dropwise. The solution was stirred at −78° C. for 25 min (resulting white cloudy mixture), then it was warmed to 0° C. and stirred for 25 min. The reaction mixture slowly turns homogenous. To the solution was added DMF at 0° C. After 25 min, HPLC showed reaction completed. The mixture was quenched with sat. NH4Cl (150 mL), diluted with ether (300 mL). The organic layer was separated, aq layer was further extracted with ether (2×200 mL), and organic layer was combined, washed with brine, dried and concentrated to give crude product, which was triturated to give 14.6 g desired product. The filtrate was then concentrated and purified by column to give additional 0.7 g, total mass is 15.3 g.
Example 3 Synthesis of Compound 13 from resorcinol 11
A three-necked round-bottom flask equipped with mechanical stirrer was charged with 0.22 mol of NaH (50% suspension in mineral oil) under nitrogen atmosphere. NaH was washed with 2 portions (100 mL) of n-hexane and then with 300 mL of dry diethyl ether; then 80 mL of anhydrous DMF was added. Then 0.09 mol of resorcinol 11, dissolved in 100 mL of diethyl ether was added dropwise and the mixture was left under stirring at rt for 30 min. Then 0.18 mol of MOMCl was slowly added. After 1 h under stirring at rt, 250 mL of water was added and the organic layer was extracted with diethyl ether. The extracts were washed with brine, dried (Na2SO4), then concentrated to give the crude product that was purified by silica gel chromatography to give compound 12 (93% yield).
A three-necked round-bottom flask was charged with 110 mL of n-hexane, 0.79 mol of BuLi and 9.4 mL of tetramethylethylendiamine (TMEDA) under nitrogen atmosphere. The mixture was cooled at −10° C. and 0.079 mol of bis-phenyl ether 12 was slowly added. The resulting mixture was left under magnetic stirring at −10° C. for 2 h. Then the temperature was raised to 0° C. and 0.067 mol of DMF was added dropwise. After 1 h, aqueous HCl was added until the pH was acidic; the mixture was then extracted with ethyl ether. The combined extracts were washed with brine, dried (Na2SO4), and concentrated to give aldehyde 13 (84%).
2,6-bis(methoxymethoxy)benzaldehyde (13): mp 58-59° C. (n-hexane); IR (KBr) n: 1685 (C═O) cm−1; 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 3.51 (s, 6H, 2 OCH3), 5.28 (s, 4H, 2 OCH2O), 6.84 (d, 2H, J=8.40 Hz, H-3, H-5), 7.41 (t, 1H, J=8.40 Hz, H-4), 10.55 (s, 1H, CHO); MS, m/e (relative intensity) 226 (M+, 3), 180 (4), 164 (14), 122 (2), 92 (2), 45 (100); Anal. Calc’d. for C11H14O5: C, 58.40; H, 6.24. Found: C, 57.98; H, 6.20.
Example 4 The Synthesis of Compound 16
To a solution of 2,6-bis(methoxymethoxy)benzaldehyde (13) (15.3 g, 67.6 mmol) in THF (105 mL) (solvent was purged with N2) was added conc. HCl (12N, 7 mL) under N2, then it was further stirred under N2 for 1.5 h. To the solution was added brine (100 mL) and ether (150 ml). The organic layer was separated and the aqueous layer was further extracted with ether (2×200 mL). The organic layer was combined, washed with brine, dried and concentrated to give crude product, which was purified by column (300 g, hexanes/EtOAc=85:15) to give desired product 16 (9.9 g) as yellow liquid.
Example 5 Synthesis of Compound 17
To a solution of 2-hydroxy-6-(methoxymethoxy)benzaldehyde (16) (10.88 g, 59.72 mmol) in DMF (120 mL) (DMF solution was purged with N2 for 10 min) was added K2CO3 (32.05 g, 231.92 mmol) and 3-(chloromethyl)-2-(1-isopropyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)pyridine hydrochloride (10) (15.78 g, 57.98 mmol). The mixture was heated at 65° C. for 1.5 h, cooled to rt, poured into ice water (800 mL). The precipitated solids were isolated by filtration, dried and concentrated to give desired product (17, 18 g).
Example 6 Synthesis of Compound (I)
To a solution of 2-((2-(1-isopropyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)pyridin-3-yl)methoxy)-6-(methoxymethoxy)benzaldehyde (17) (18 g, 47.19 mmol) in THF (135 mL, solution was purged with N2) was added conc. HCl (12N, 20 mL). The solution was stirred at rt for 3 h when HPLC showed the reaction complete. The mixture was added to a solution of NaHCO3 (15 g) in water (1.2 L), and the resulting precipitate was collected by filtration, dried to give crude solid, which was further purified by column (DCM/EtOAc=60:40) to give pure product (15.3 g).
Example 7 Synthesis of Compound I (Free Base) and its HCl Salt Form
Compound (I) free base (40 g) was obtained from the coupling of the alcohol intermediate 7 and 2,6-dihydroxybenzaldedhye 9 under Mitsunobu conditions. A procedure is also provided below:
Example 8 Synthesis of Compound (I) by Mitsunobu Coupling
Into a 2000-mL three neck round-bottom flask, which was purged and maintained with an inert atmosphere of nitrogen, was placed a solution of [2-[1-(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-5-yl]pyridin-3-yl]methanol (7) (70 g, 322.18 mmol, 1.00 equiv) in tetrahydrofuran (1000 mL). 2,6-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde (9) (49.2 g, 356.21 mmol, 1.10 equiv) and PPh3 (101 g, 385.07 mmol, 1.20 equiv) were added to the reaction mixture. This was followed by the addition of a solution of DIAD (78.1 g, 386.23 mmol, 1.20 equiv) in tetrahydrofuran (200 ml) dropwise with stirring. The resulting solution was stirred overnight at room temperature. The resulting solution was diluted with 500 ml of H2O. The resulting solution was extracted with 3×500 ml of dichloromethane and the combined organic layers were dried over sodium sulfate and concentrated under vacuum. The residue was applied onto a silica gel column with EA:PE (1:50-1:3) as eluent to yield the crude product. The crude product was re-crystallized from i-propanol/H2O in the ratio of 1/1.5. This resulted in 40 g (37%) of 2-hydroxy-6-([2-[1-(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-5-yl]pyridin-3-yl]methoxy)benzaldehyde as a light yellow solid. The compound exhibited a melting point of 80-82° C. MS (ES, m/z): 338.1 [M+1]. 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.72 (s, 1H), 10.21 (s, 1H), 8.76 (d, J=3.6 Hz, 1H), 8.24 (d, J=2.7 Hz, 1H), 7.55 (m, 3H), 6.55 (m, 3H), 5.21 (s, 2H), 4.65 (m, 1H), 1.37 (d, J=5.1 Hz, 6H). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 11.96 (s, 1H), 10.40 (s, 1H), 8.77 (dd, J=4.8, 1.5 Hz, 1H), 8.00 (d, J=7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.63 (d, J=1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.49-7.34 (m, 2H), 6.59 (d, J=8.5 Hz, 1H), 6.37 (d, J=1.8 Hz, 1H), 6.29 (d, J=8.2 Hz, 1H), 5.10 (s, 2H), 4.67 (sep, J=6.7 Hz, 1H), 1.50 (d, J=6.6 Hz, 6H).
In another approach, multiple batches of Compound (I) free base are prepared in multi gram quantities (20 g). The advantage of this route is the use of mono-protected 2,6-dihydroxybenzaldehyde (16), which effectively eliminates the possibility of bis-alkylation side product. The mono-MOM ether of 2,6-dihydroxybenzaldehyde (16) can be obtained from two starting points, bromoresorcinol (14) or resorcinol (11) [procedures described in the Journal of Organic Chemistry, 74(11), 4311-4317; 2009]. All steps and procedures are provided below. Due to the presence of phenolic aldehyde group, precautions (i.e., carry out all reactions under inert gas such as nitrogen) should be taken to avoid oxidation of the phenol and/or aldehyde group. Preparation of compound I HCl salt: A solution of compound I (55.79 g, 165.55 mmol) in acetonitrile (275 mL) was flushed with nitrogen for 10 min, then to this solution was added 3N aqueous HCl (62 mL) at room temperature. The mixture was stirred for additional 10 min after the addition, most of the acetonitrile (about 200 mL) was then removed by evaporation on a rotary evaporator at around 32° C., the remaining solution was frozen by cooling in an acetone-dry ice bath and lyophilized to afford compound I HCl salt (59.4 g).
Biological Activity
| Description | Voxelotor(GBT440, GTx011) is a novel small molecule hemoglobin modifier which increases hemoglobin oxygen affinity. |
|---|---|
| In vitro | GBT440 is a new potent allosteric effector of sickle cell hemoglobin that increases the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen and consequently inhibits its polymerization when subjected to hypoxic conditions. GBT440 inhibits these isozymes(CYP 1A2, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, and 3A4) with IC50 ranging from 7.9 to 148 μM. It is not a substrate for either P-gp or BCRP transporters[1]. It binds to the N-terminal a chain of Hb[2]. |
| In vivo | GBT440 has favorable oral bioavailability of 60, 37, and 36% in rats, dogs, and monkeys, respectively, with similar blood and plasma half-lives of approximately 20 h each. T1/2 value of GBT440 in all animal species is significantly shorter than the T1/2 of red blood cells (∼20 days), which supports that binding of GBT440 to hemoglobin is a reversible process. GBT440 is currently in Phase 3 clinical trials (NCT03036813) in SCD patients[1]. GBT440 increases haemoglobin oxygen affinity, reduces sickling and prolongs RBC half-life in a murine model of sickle cell disease. In a murine model of SCD, GBT440 extends the half-life of RBCs, reduces reticulocyte counts and prevents ex vivo RBC sickling. Importantly, oral dosing of GBT440 in animals demonstrates suitability for once daily dosing in humans and a highly selective partitioning into RBCs, which is a key therapeutic safety attribute. GBT440 shows dose proportional PK, a terminal half-life of 1.5-3 d[2]. |
GBT Receives FDA Breakthrough Therapy Designation for Voxelotor for Treatment of Sickle Cell Disease (SCD)
Voxelotor is First Investigational Treatment for SCD to Receive Breakthrough Therapy Designation
SOUTH SAN FRANCISCO, Calif., Jan. 09, 2018 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) — Global Blood Therapeutics, Inc. (GBT) (NASDAQ:GBT) today announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted Breakthrough Therapy Designation (BTD) to voxelotor (previously called GBT440) for the treatment of sickle cell disease (SCD). Voxelotor is being developed as a disease-modifying therapy for SCD and previously received European Medicines Agency (EMA) Priority Medicines (PRIME) designation for the treatment of SCD.
“The FDA’s decision to grant voxelotor the first Breakthrough Therapy designation for the treatment of sickle cell disease reflects a recognition of the promising efficacy and safety data we have collected to date for this investigational drug, as well as an acknowledgement of the overwhelming need for major advances over available therapies in the treatment of SCD patients,” said Ted W. Love, president and chief executive officer of GBT. “This designation is another significant milestone for GBT as we work to expedite the development of voxelotor.”
The FDA selectively grants BTD to expedite the development and review of drugs that have demonstrated preliminary clinical evidence indicating the potential for substantial improvement over available therapy. The BTD decision for voxelotor was based on clinical data submitted from the following studies:
- Preliminary efficacy and safety data from Part A of the Phase 3 HOPE Study (GBT440-031)
- Phase 1/2 study and open-label extension in adults (GBT440-001/024)
- Ongoing Phase 2 HOPE-KIDS 1 study in children age 6 to 17 (GBT440-007)
- Compassionate Access experience in adults with severe SCD (not eligible for the HOPE Study)
About Sickle Cell Disease (SCD)
SCD is a lifelong inherited blood disorder caused by a genetic mutation in the beta-chain of hemoglobin, which leads to the formation of abnormal hemoglobin known as sickle hemoglobin (HbS). In its deoxygenated state, HbS has a propensity to polymerize, or bind together, forming long, rigid rods within a red blood cell (RBC). The polymer rods deform RBCs to assume a sickled shape and to become inflexible, which can cause blockage in capillaries and small blood vessels. Beginning in childhood, SCD patients suffer unpredictable and recurrent episodes or crises of severe pain due to blocked blood flow to organs, which often lead to psychosocial and physical disabilities. This blocked blood flow, combined with hemolytic anemia (the destruction of RBCs), can eventually lead to multi-organ damage and early death.
About Voxelotor in Sickle Cell Disease
Voxelotor (previously called GBT440) is being developed as an oral, once-daily therapy for patients with SCD. Voxelotor works by increasing hemoglobin’s affinity for oxygen. Since oxygenated sickle hemoglobin does not polymerize, GBT believes voxelotor blocks polymerization and the resultant sickling of red blood cells. With the potential to restore normal hemoglobin function and improve oxygen delivery, GBT believes that voxelotor may potentially modify the course of SCD. In recognition of the critical need for new SCD treatments, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted voxelotor Fast Track, Orphan Drug and Rare Pediatric Disease designations for the treatment of patients with SCD. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) has included voxelotor in its Priority Medicines (PRIME) program, and the European Commission (EC) has designated voxelotor as an orphan medicinal product for the treatment of patients with SCD.
GBT is currently evaluating voxelotor in the HOPE (Hemoglobin Oxygen Affinity Modulation to Inhibit HbS PolymErization) Study, a Phase 3 clinical study in patients age 12 and older with SCD. Additionally, voxelotor is being studied in the ongoing Phase 2a HOPE-KIDS 1 Study, an open-label, single- and multiple-dose study in pediatric patients (age 6 to 17) with SCD. HOPE-KIDS 1 is assessing the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics and exploratory treatment effect of voxelotor.
About GBT
GBT is a clinical-stage biopharmaceutical company determined to discover, develop and deliver innovative treatments that provide hope to underserved patient communities. GBT is developing its lead product candidate, voxelotor, as an oral, once-daily therapy for sickle cell disease. To learn more, please visit www.gbt.com and follow the company on Twitter @GBT_news.
REFERENCES
1: Oksenberg D, Dufu K, Patel MP, Chuang C, Li Z, Xu Q, Silva-Garcia A, Zhou C, Hutchaleelaha A, Patskovska L, Patskovsky Y, Almo SC, Sinha U, Metcalf BW, Archer DR. GBT440 increases haemoglobin oxygen affinity, reduces sickling and prolongs RBC half-life in a murine model of sickle cell disease. Br J Haematol. 2016 Oct;175(1):141-53. doi: 10.1111/bjh.14214. PubMed PMID: 27378309.
2: Dufu K, Lehrer-Graiwer J, Ramos E, Oksenberg D. GBT440 Inhibits Sickling of Sickle Cell Trait Blood Under In Vitro Conditions Mimicking Strenuous Exercise. Hematol Rep. 2016 Sep 28;8(3):6637. PubMed PMID: 27757216; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC5062624.
3: Ferrone FA. GBT440 increases haemoglobin oxygen affinity, reduces sickling and prolongs RBC half-life in a murine model of sickle cell disease. Br J Haematol. 2016 Aug;174(4):499-500. doi: 10.1111/bjh.14212. PubMed PMID: 27410726.
4: Oder E, Safo MK, Abdulmalik O, Kato GJ. New developments in anti-sickling agents: can drugs directly prevent the polymerization of sickle haemoglobin in vivo? Br J Haematol. 2016 Oct;175(1):24-30. doi: 10.1111/bjh.14264. Review. PubMed PMID: 27605087; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC5035193.
////////////VOXELOTOR, GBT 440, GTx-011, Treatment of Sickle Cell Disease, phase 3, gbt, 1446321-46-5, orphan drug, breakthrough therapy designation
CC(C)n1nccc1c2ncccc2COc3cccc(O)c3C=O