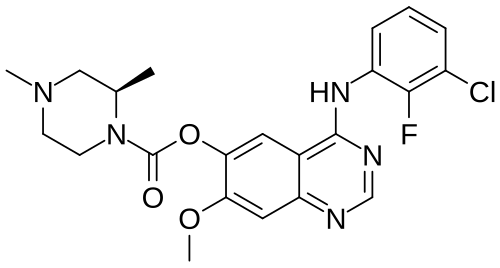
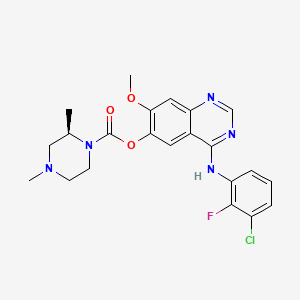
Zorifertinib
AZD 3759
CAS 1626387-80-1, 67SX9H68W2
WeightAverage: 459.91
Monoisotopic: 459.1473455
Chemical FormulaC22H23ClFN5O3
[4-(3-chloro-2-fluoroanilino)-7-methoxyquinazolin-6-yl] (2R)-2,4-dimethylpiperazine-1-carboxylate
- [4-(3-chloro-2-fluoroanilino)-7-methoxyquinazolin-6-yl] (2R)-2,4-dimethylpiperazine-1-carboxylate
- (4-(3-chloro-2-fluoroanilino)-7-methoxyquinazolin-6-yl) (2R)-2,4-dimethylpiperazine-1-carboxylate
- (R)-4-((3-chloro-2-fluorophenyl)amino)-7-methoxyquinazolin-6-yl 2,4-dimethylpiperazine-1-carboxylate
- 4-[(3-CHLORO-2-FLUOROPHENYL)AMINO]-7-METHOXYQUINAZOLIN-6-YL (2R)-2,4-DIMETHYLPIPERAZINE-1-CARBOXYLATE
China 2024, APPROVALS 2024, Alpha Biopharma, ASTRA ZENECA, Zorifer,
Zorifertinib (AZD3759) is a drug for the treatment of cancer.[1] In China, it was approved in 2024 for locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) that has epidermal growth factor receptor exon 19 deletion or exon 21 L858R substitution mutations and central nervous system (CNS) metastases.[2]
Zorifertinib is an orally available inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), with potential antineoplastic activity. Upon oral administration, zorifertinib binds to and inhibits the activity of EGFR as well as certain mutant forms of EGFR. This prevents EGFR-mediated signaling, and may lead to both induction of cell death and inhibition of tumor growth in EGFR-overexpressing cells. EGFR, a receptor tyrosine kinase mutated in many tumor cell types, plays a key role in tumor cell proliferation and tumor vascularization.
SYN
J. Med. Chem. 58 (2015) 8200–8215.
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b01073

SYN
European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 291 (2025) 117643
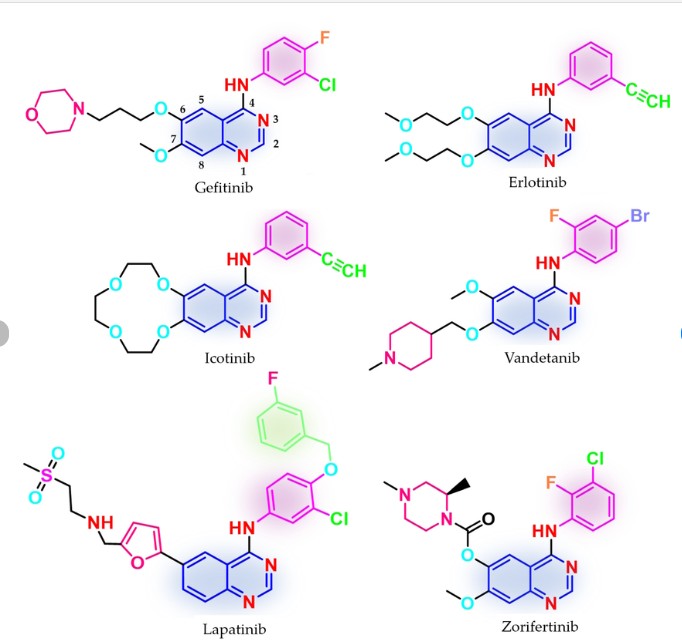
Zorifertinib, developed by AstraZeneca as AZD3759, is a novel EGFR TKI designed to effectively penetrate the blood-brain barrier (BBB) [44,45]. In 2018, Alpha Biopharma, in collaboration with AstraZeneca, advanced its development. In 2024, the NMPA gave its approval to zorifertinib hydrochloride tablets, which are sold under the brand name Zorifer. This approval is for the use of these tablets in the first-line treatment of adult patients who have the following conditions: they
have locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC with either EGFR exon 19 deletion or exon 21 L858R substitution mutations, and also have CNSmetastases [45]. Zorifertinib exerts its pharmacological action through the selective inhibition of EGFR tyrosine kinase activity, with a particular focus on mutational forms such as L858R and exon 19 deletions. In contrast to several other tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), it does not serve as a substrate for BBB efflux transporters, namely P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP). This unique property enables zorifertinib to reach elevated concentrations within brain tissue and cerebrospinal fluid. As a result, it can effectively target and
act against CNS metastases [44,45]. The clinical efficacy of zorifertinib was demonstrated in the EVEREST study (NCT03653546), a random ized, open-label, international multicenter Phase II/III trial. The study
enrolled 492 patients with EGFR-mutant NSCLC and CNS metastases. Results showed that zorifertinib significantly improved systemic PFS to 9.6 months compared to 6.9 months with first-generation EGFR-TKIs, reducing the risk of disease progression or death by 28 %. Intracranial PFS was notably extended to 15.2 months versus 8.3 months in the control group. The ORR was 68.6 % for zorifertinib compared to 58.4 % for the control. Regarding toxicity, zorifertinib exhibited a manageable safety profile. The incidence of treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) was similar between the zorifertinib and control groups (97.7 %vs. 94.0 %), with grade ≥3 TRAEs occurring in 65.9 % of patients receiving zorifertinib compared to 18.3 % in the control group. No new safety signals were identified, indicating an acceptable tolerability for patients. The approval of zorifertinib offers a significant advancement in
the treatment of EGFR-mutant NSCLC patients with CNS metastases,providing an effective therapeutic option capable of addressing both systemic and intracranial disease [44].
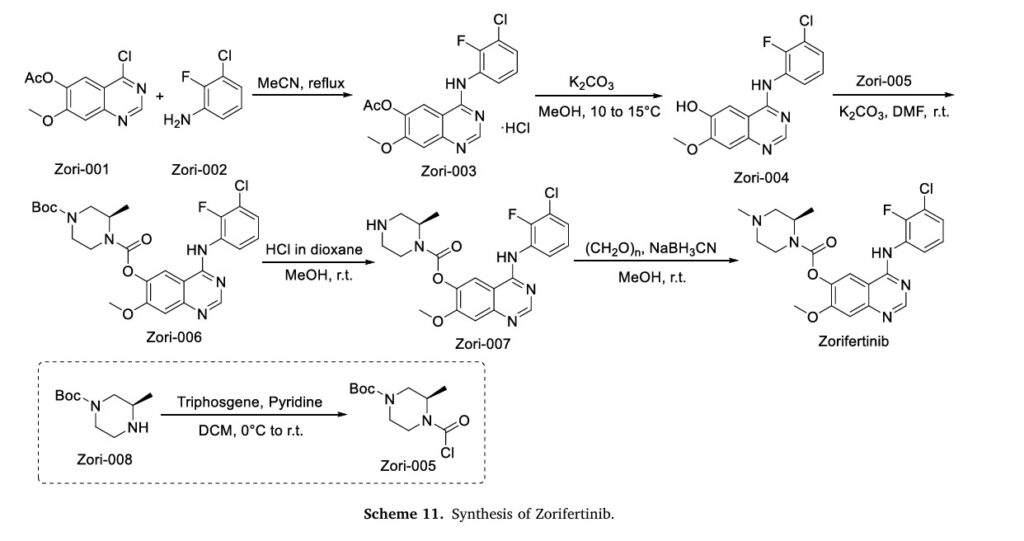
The synthesis of Zorifertinib, depicted in Scheme 11, initiates with nucleophilic substitution between Zori-001 and Zori-002 in MeCN, affording Zori-003 [46]. Hydrolysis of the ester moiety in Zori-003
yields Zori-004, which is subsequently esterified with Zori-005 in DMF to form Zori-006. Acidic deprotection of Zori-006 generates Zori-007, followed by methylation to deliver Zorifertinib. Concurrently, Zori-005 is prepared via amidation of Zori-008
[44] M. Roy-O’Reilly, D. Rogawski, The climb toward intracranial efficacy: Zorifertinib
in EGFR-mutant NSCLC with CNS metastases in the EVEREST trial, Med 6 (2025)
100525.
[45] Q. Zhou, Y. Yu, L. Xing, Y. Cheng, Y. Wang, Y. Pan, Y. Fan, J. Shi, G. Zhang, J. Cui,
J. Zhou, Y. Song, W. Zhuang, Z. Ma, Y. Hu, G. Li, X. Dong, J. Feng, S. Lu, J. Wu,
J. Li, L. Zhang, D. Wang, X. Xu, T.Y. Yang, N. Yang, Y. Guo, J. Zhao, Y. Yao,
D. Zhong, B. Xia, C.T. Yang, B. Zhu, P. Sun, B.Y. Shim, Y. Chen, Z. Wang, M.J. Ahn,
J. Wang, Y.L. Wu, First-line zorifertinib for EGFR-Mutant non-small cell lung
cancer with central nervous system metastases: the phase 3 EVEREST trial, Med 6
(2025) 100513.
[46] Q. Zeng, J. Wang, Z. Cheng, K. Chen, P. Johnstr¨om, K. Varn¨as, D.Y. Li, Z.F. Yang,
X. Zhang, Discovery and evaluation of clinical candidate AZD3759, a potent, oral
active, central nervous system-penetrant, epidermal growth factor receptor
tyrosine kinase inhibitor, J. Med. Chem. 58 (2015) 8200–8215.



AS ON JUNE2025 4.45 LAKHS VIEWS ON BLOG WORLDREACH AVAILABLEFOR YOUR ADVERTISEMENT

join me on Linkedin
Anthony Melvin Crasto Ph.D – India | LinkedIn
join me on Researchgate
RESEARCHGATE

join me on Facebook
Anthony Melvin Crasto Dr. | Facebook
join me on twitter
Anthony Melvin Crasto Dr. | twitter
+919321316780 call whatsaapp
EMAIL. amcrasto@gmail.com

……
References
- Zhou Q, Yu Y, Xing L, Cheng Y, Wang Y, Pan Y, et al. (January 2025). “First-line zorifertinib for EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer with central nervous system metastases: The phase 3 EVEREST trial”. Med. 6 (1) 100513. doi:10.1016/j.medj.2024.09.002. PMID 39389055.
- “Zorifertinib Receives NMPA Approval for EGFR+ NSCLC With CNS Metastases”. November 20, 2024.
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | AZD3759 |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | Rx in China |
| Identifiers | |
| IUPAC name | |
| CAS Number | 1626387-80-1 |
| PubChem CID | 78209992 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 10456 |
| DrugBank | DB14795 |
| ChemSpider | 38772332 |
| UNII | 67SX9H68W2 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL3623290 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H23ClFN5O3 |
| Molar mass | 459.91 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | Interactive image |
| SMILES | |
| InChI | |
//////////Zorifertinib, china 2024, APPROVALS 2024, Alpha Biopharma, ASTRA ZENECA, Zorifer, AZD 3759, 67SX9H68W2














