
Continuous Photo-Oxidation in a Vortex Reactor: Efficient Operations Using Air Drawn from the Laboratory
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.oprd.7b00153
Clark, C. A.; Lee, D. S.; Pickering, S. J.; Poliakoff, M.; George, M. W. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2016, 20, 1792-1798.

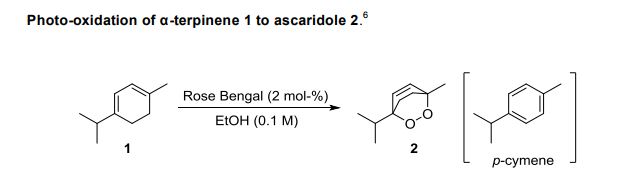
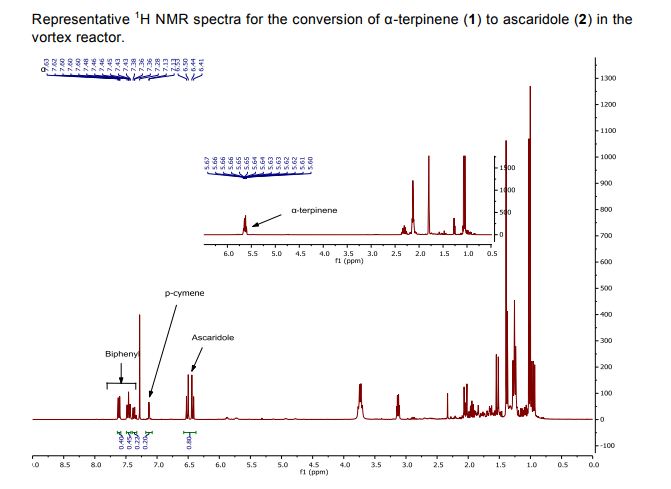
We report the construction and use of a vortex reactor which uses a rapidly rotating cylinder to generate Taylor vortices for continuous flow thermal and photochemical reactions. The reactor is designed to operate under conditions required for vortex generation. The flow pattern of the vortices has been represented using computational fluid dynamics, and the presence of the vortices can be easily visualized by observing streams of bubbles within the reactor. This approach presents certain advantages for reactions with added gases. For reactions with oxygen, the reactor offers an alternative to traditional setups as it efficiently draws in air from the lab without the need specifically to pressurize with oxygen. The rapid mixing generated by the vortices enables rapid mass transfer between the gas and the liquid phases allowing for a high efficiency dissolution of gases. The reactor has been applied to several photochemical reactions involving singlet oxygen (1O2) including the photo-oxidations of α-terpinene and furfuryl alcohol and the photodeborylation of phenyl boronic acid. The rotation speed of the cylinder proved to be key for reaction efficiency, and in the operation we found that the uptake of air was highest at 4000 rpm. The reactor has also been successfully applied to the synthesis of artemisinin, a potent antimalarial compound; and this three-step synthesis involving a Schenk-ene reaction with 1O2, Hock cleavage with H+, and an oxidative cyclization cascade with triplet oxygen (3O2), from dihydroartemisinic acid was carried out as a single process in the vortex reactor.

Darren S Lee
Catalysis, Organic Chemistry
School of Chemistry, ‡Department of Mechanical, Materials and Manufacturing Engineering, University of Nottingham, University Park, Nottingham, NG7 2RD, U.K.
/////////















