Atom- and step-economical nucleophilic arylation of azaaromatics via electrochemical oxidative cross C-C coupling reactions
DOI: 10.1039/C7GC00789B, Communication
A simple and efficient electrochemical method for the synthesis of asymmetrical bi(het)aryls through direct functionalization of the C(sp2)-H bond in azaaromatics with fragments of (hetero)aromatic nucleophiles has been developed.
Green Chemistry
Atom- and step-economical nucleophilic arylation of azaaromatics via electrochemical oxidative cross C–C coupling reactions
Abstract
The synthesis of asymmetrical bi(het)aryls through direct functionalization of the C(sp2)–H bond in azaaromatics with fragments of (hetero)aromatic nucleophiles has first been carried out under electrochemical oxidative conditions. This versatile method for C–C bond formation between two aryl fragments can be realized under very mild potential-controlled oxidative conditions, and it does require neither incorporation of any halogen atoms or other leaving groups, nor the use of metal catalysts. The use of the electrochemical SHN methodology for modification of azaaromatic compounds has first been demonstrated.
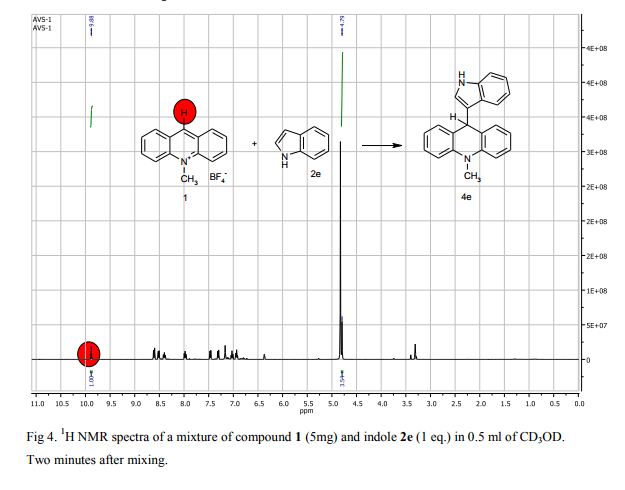
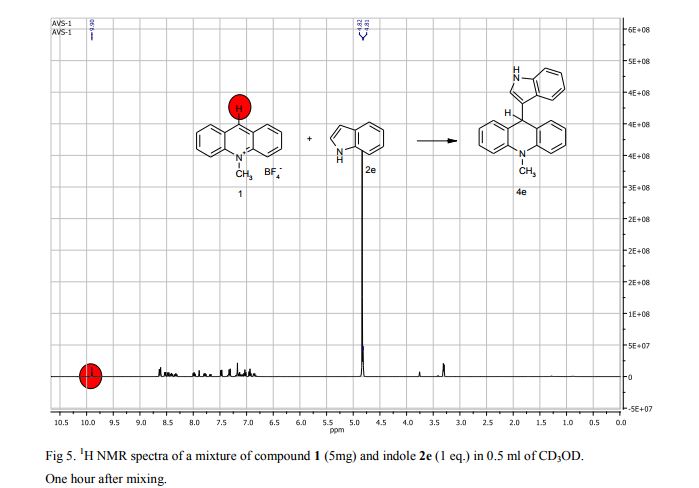
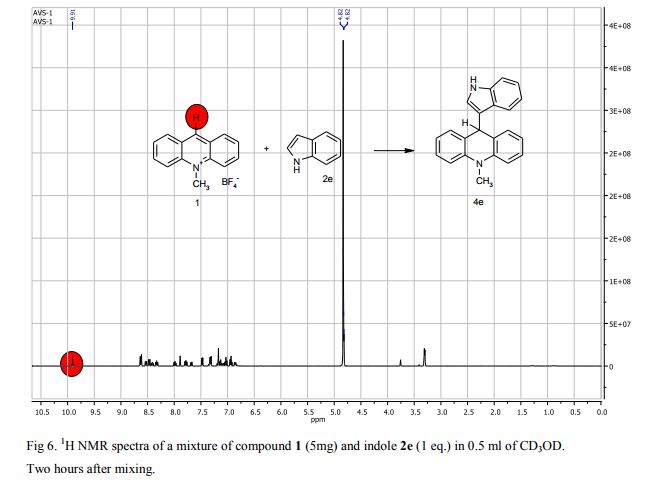
9-(1H-Indol-3-yl)-10-methylacridinium tetrafluoroborate (3e) Red crystals, 189 mg (96%). M.p.: 192-193 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, [D6]DMSO): δ 12.44 (s, 1H), 8.80 (d, 2H, J=9.5 Hz), 8.43-8.39 (m, 4H), 8.14 (d, 1H, J=2.6 Hz), 7.90-7.86 (m, 2H), 7.70 (d, 1H, J=8.2 Hz), 7.32 (t, 1H, J=7.4 Hz), 7.17-7.10 (m, 2H), 4.88 (s, 3H) ppm. 13C NMR (126 MHz, [D6]DMSO): δ 156.2, 141.2, 137.9, 136.5, 131.1, 130.5, 127.9, 127.1, 125.6, 122.9, 121.2, 119.0, 118.9, 112.7, 107.9, 38.6 ppm. Elem. Anal. Calcd. For C22H17N2BF4: C 66.69, H 4.33, N 7.07 Found: C 66.78, H 4.39, N 7.10.
///////////////