
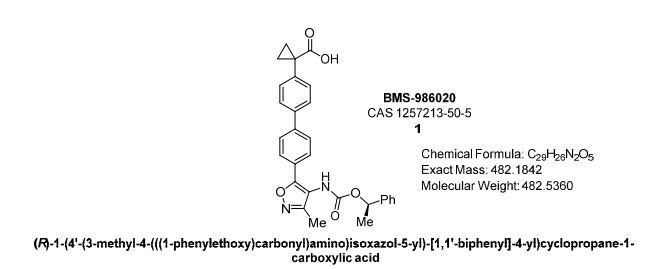
BMS-986020
AM-152; BMS-986020; BMS-986202
cas 1257213-50-5
Chemical Formula: C29H26N2O5
Molecular Weight: 482.536
(R)-1-(4′-(3-methyl-4-(((1-phenylethoxy)carbonyl)amino)isoxazol-5-yl)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-yl)cyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid
Cyclopropanecarboxylic acid, 1-(4′-(3-methyl-4-((((1R)-1-phenylethoxy)carbonyl)amino)-5-isoxazolyl)(1,1′-biphenyl)-4-yl)-
1-(4′-(3-Methyl-4-(((((R)-1-phenylethyl)oxy)carbonyl)amino)isoxazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-yl)cyclopropanecarboxylic acid
UNII: 38CTP01B4L
For treatment for pulmonary fibrosis, phase 2, The lysophosphatidic acid receptor, LPA1, has been implicated as a therapeutic target for fibrotic disorders
Lysophospholipids (LPs), including lysophosphatidic acid (LPA), sphingosine 1-phospate (S1P), lysophosphatidylinositol (LPI), and lysophosphatidylserine (LysoPS), are bioactive lipids that transduce signals through their specific cell-surface G protein-coupled receptors, LPA1-6, S1P1-5, LPI1, and LysoPS1-3, respectively. These LPs and their receptors have been implicated in both physiological and pathophysiological processes such as autoimmune diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, fibrosis, pain, cancer, inflammation, metabolic syndrome, bone formation, fertility, organismal development, and other effects on most organ systems.

- Originator Amira Pharmaceuticals
- DeveloperB ristol-Myers Squibb; Duke University
- Class Antifibrotics; Azabicyclo compounds; Carboxylic acids; Small molecules; Tetrazoles
- Mechanism of Action Lysophosphatidic acid receptor antagonists
- Orphan Drug Status Yes – Fibrosis
- Phase II Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- Phase IPsoriasis
Most Recent Events
- 05 May 2016 Bristol-Myers Squibb plans a phase I trial for Psoriasis in Australia (PO, Capsule, Liquid) (NCT02763969)
- 01 May 2016 Preclinical trials in Psoriasis in USA (PO) before May 2016
- 14 Mar 2016 Bristol-Myers Squibb withdraws a phase II trial for Systemic scleroderma in USA, Canada, Poland and United Kingdom (PO) (NCT02588625)
BMS-986020, also known as AM152 and AP-3152 free acid, is a potent and selective LPA1 antagonist. BMS-986020 is in Phase 2 clinical development for treating idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. BMS-986020 selectively inhibits the LPA receptor, which is involved in binding of the signaling molecule lysophosphatidic acid, which in turn is involved in a host of diverse biological functions like cell proliferation, platelet aggregation, smooth muscle contraction, chemotaxis, and tumor cell invasion, among others

PRODUCT PATENT
GB 2470833, US 20100311799, WO 2010141761
Hutchinson, John Howard; Seiders, Thomas Jon; Wang, Bowei; Arruda, Jeannie M.; Roppe, Jeffrey Roger; Parr, Timothy
Assignee: Amira Pharmaceuticals Inc, USA

John Hutchinson
PATENTS
WO 2011159632
WO 2011159635
PATENT
WO 2013025733
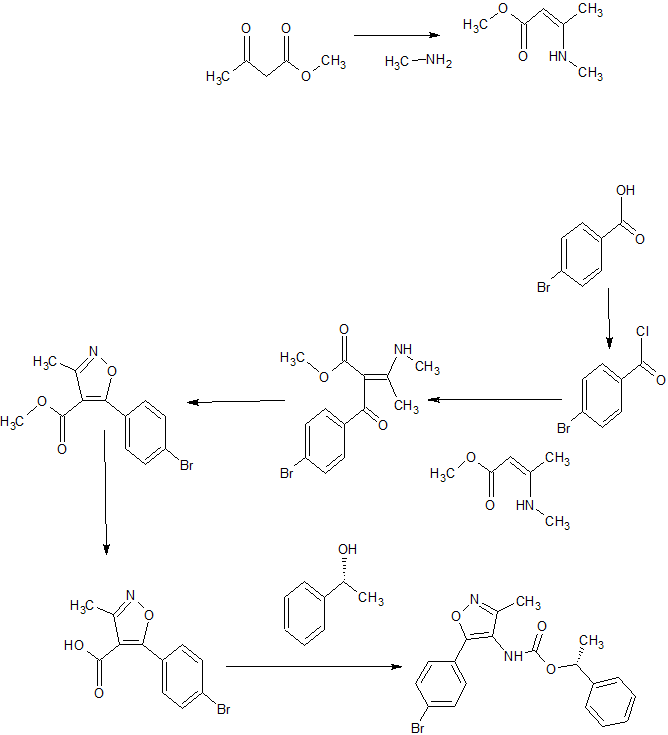
Synthesis of Compound 74
Synthetic Route (Scheme XLV)

Compound 74 Compound 74a
[0562] Compound XLV-1 was prepared by the same method as described in the synthesis of compound 1-4 (Scheme 1-A).
[0563] To a solution of compound XLV-1 (8 g, 28.08 mmol) in dry toluene (150 mL) was added compound XLV-2 (1.58 g, 10.1 mmol), triethylamine (8.0 mL) and DPPA (9.2 g, 33.6 mmol). The reaction mixture was heated to 80 °C for 3 hours. The mixture was diluted with EtOAc (50 mL), washed with brine, dried over Na2S04, filtered and concentrated. The residue was purified by column chromatography (PE/EA = 10 IX) to give compound XLV-3 (9.4 g, yield: 83 %). MS (ESI) m/z (M+H)+402.0.
[0564] Compound 74 was prepared analogously to the procedure described in the synthesis of Compound 28 and was carried through without further characterization.
[0565] Compound 74a was prepared analogously to the procedure described in the synthesis of Compound 44a. Compound 74a: 1HNMR (DMSO-d6 400MHz) δ 7.81 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.41 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.52 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.29-7.32 (m, 7 H), 5.78 (q, 1 H), 2.15 (s, 3 H), 1.52 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 3H), 1.28 (br, 2 H), 0.74 (br, 2 H). MS (ESI) m/z (M+H)+ 483.1.
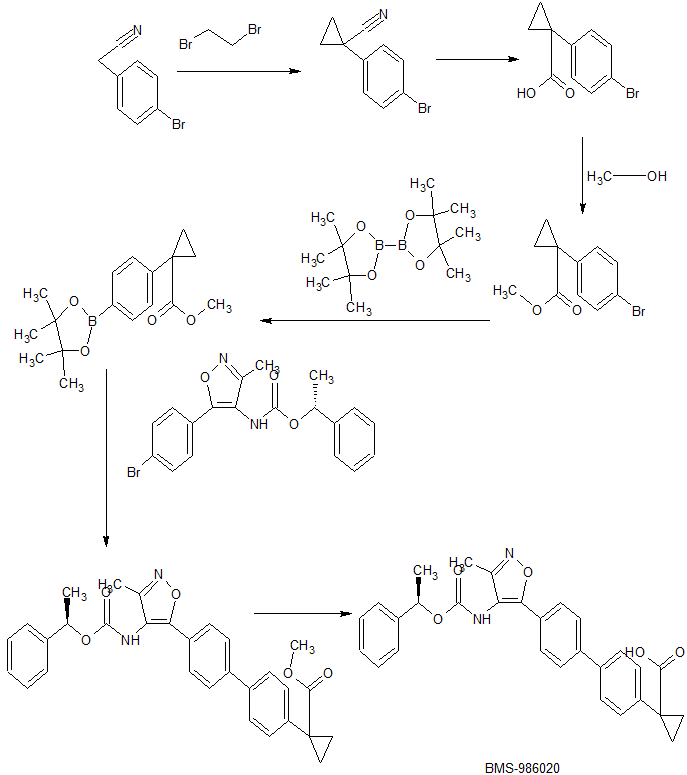
Paper
Development of a Concise Multikilogram Synthesis of LPA-1 Antagonist BMS-986020 via a Tandem Borylation–Suzuki Procedure
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.oprd.7b00301

The process development for the synthesis of BMS-986020 (1) via a palladium catalyzed tandem borylation/Suzuki reaction is described. Evaluation of conditions culminated in an efficient borylation procedure using tetrahydroxydiboron followed by a tandem Suzuki reaction employing the same commercially available palladium catalyst for both steps. This methodology addressed shortcomings of early synthetic routes and was ultimately used for the multikilogram scale synthesis of the active pharmaceutical ingredient 1. Further evaluation of the borylation reaction showed useful reactivity with a range of substituted aryl bromides and iodides as coupling partners. These findings represent a practical, efficient, mild, and scalable method for borylation.
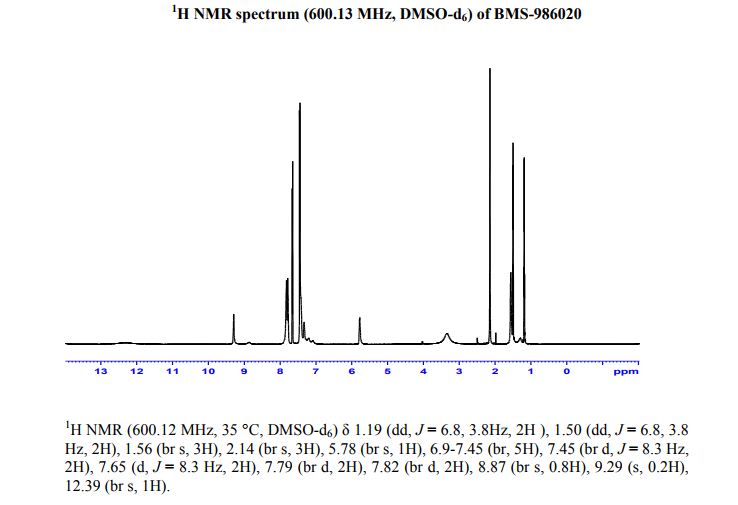
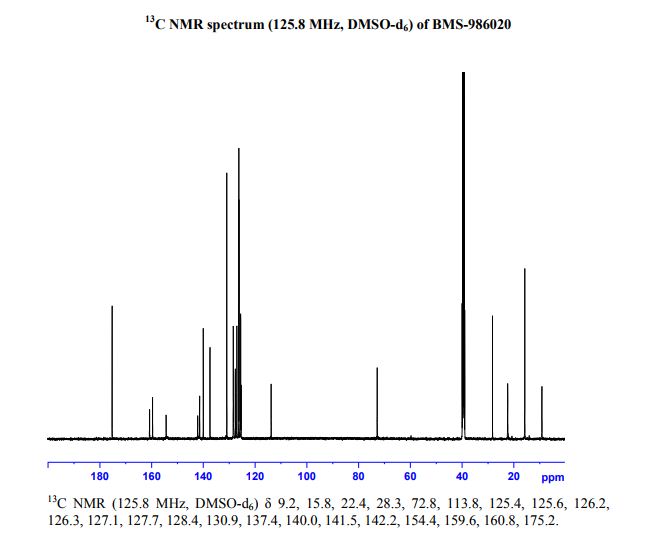
1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 1.19 (dd, J = 6.8, 3.8 Hz, 2H), 1.50 (dd, J = 6.8, 3.8 Hz, 2H), 1.56 (br s, 3H), 2.14 (br s, 3H), 5.78 (br s, 1H), 6.9–7.45 (br, 5H), 7.45 (br d, J = 8.3 Hz, 2H), 7.65 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 2H), 7.79 (br d, 2H), 7.82 (br d, 2H), 8.87 (br s, 0.8H), 9.29 (s, 0.2H), 12.39 (br s, 1H). 13C NMR (126 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.2, 15.8, 22.4, 28.3, 72.8, 113.8, 125.4, 125.6, 126.2, 126.3, 127.1, 127.7, 128.4, 130.9, 137.4, 140.0, 141.5, 142.2, 154.4, 159.6, 160.8, 175.2. HRMS (ESI+) Calculated M + H 483.19145, found 483.19095.
REFERENCES
1: Kihara Y, Mizuno H, Chun J. Lysophospholipid receptors in drug discovery. Exp
Cell Res. 2015 May 1;333(2):171-7. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2014.11.020. Epub 2014
Dec 8. Review. PubMed PMID: 25499971; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4408218.
//////////////BMS-986020, AM 152, BMS 986020, BMS 986202, Orphan Drug, BMS, Amira Pharmaceuticals, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Duke University, Antifibrotics, PHASE 2, pulmonary fibrosis
O=C(C1(C2=CC=C(C3=CC=C(C4=C(NC(O[C@H](C)C5=CC=CC=C5)=O)C(C)=NO4)C=C3)C=C2)CC1)O















