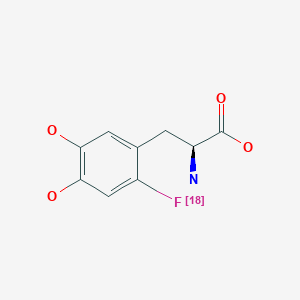
Fluorodopa F 18
2019/10/10, fda 2019,
| Formula |
C9H10FNO4
|
|---|---|
| Cas |
92812-82-3
|
| Mol weight |
215.1784
|
Diagnostic aid (brain imaging), Radioactive agent, for use in positron emission tomography (PET)
CAS 92812-82-3
フルオロドパ (18F)
Fluorodopa, also known as FDOPA, is a fluorinated form of L-DOPA primarily synthesized as its fluorine-18isotopologue for use as a radiotracer in positron emission tomography (PET).[1] Fluorodopa PET scanning is a valid method for assessing the functional state of the nigrostriatal dopaminergic pathway. It is particularly useful for studies requiring repeated measures such as examinations of the course of a disease and the effect of treatment
In October 2019, Fluorodopa was approved in the United States for the visual detection of certain nerve cells in adult patients with suspected Parkinsonian Syndromes (PS).[2][3]
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Fluorodopa F 18 based on evidence from one clinical trial of 56 patients with suspected PS.[2] The trial was conducted at one clinical site in the United States.[2]
PAPER
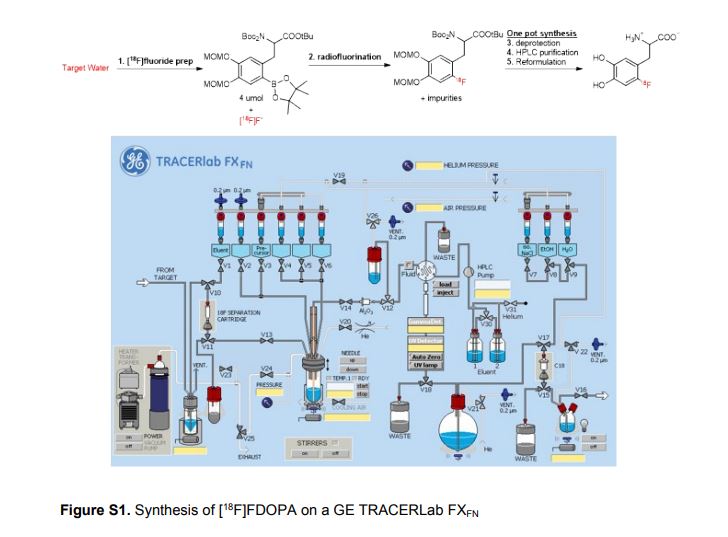
A one-pot two-step synthesis of 6-[18F]fluoro-L-DOPA ([18F]FDOPA) has been developed involving Cu-mediated radiofluorination of a pinacol boronate ester precursor. The method is fully automated, provides [18F]FDOPA in good activity yield (104 ± 16 mCi, 6 ± 1%), excellent radiochemical purity (>99%) and high molar activity (3799 ± 2087 Ci mmol−1), n = 3, and has been validated to produce the radiotracer for human use.
![Graphical abstract Graphical abstract: One-pot synthesis of high molar activity 6-[18F]fluoro-l-DOPA by Cu-mediated fluorination of a BPin precursor](https://pubs.rsc.org/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=C9OB01758E&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2019)
PATENT
KR 2019061368
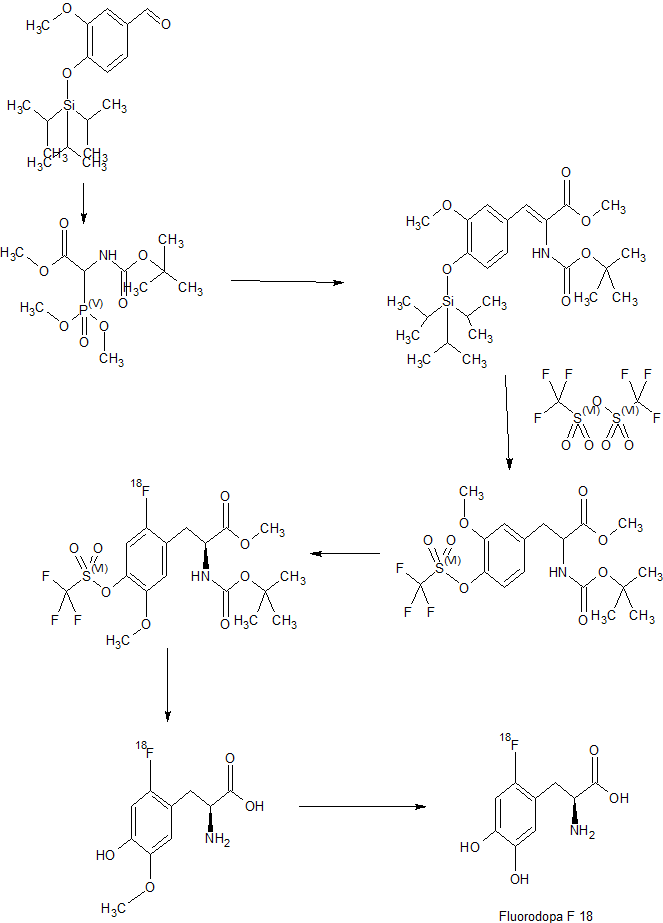
The present invention relates to an L-dopa precursor compd., a method for producing the same, and a method for producing 18F-labeled L-dopa using the same. The method of prepg. 18F-labeled L-dopa I using the L-dopa precursor II [A = halogen-(un)substituted alkyl; W, X, Y = independently protecting group] can improve the labeling efficiency of 18F. After the labeling reaction, sepn. and purifn. steps of the product can be carried out continuously and it can be performed with on-column labeling (a method of labeling through the column). The final product I, 18 F-labeled L-dopa, can be obtained at a high yield relative to conventional methods. Further, it has an advantage that it is easy to apply various methods such as bead labeling.
PAPER
Science (Washington, DC, United States) (2019), 364(6446), 1170-1174.
PAPER
European Journal of Organic Chemistry (2018), 2018(48), 7058-7065.
PATENT
WO 2018115353
CN 107311877
References
- ^ Deng WP, Wong KA, Kirk KL (June 2002). “Convenient syntheses of 2-, 5- and 6-fluoro- and 2,6-difluoro-L-DOPA”. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry. 13 (11): 1135–1140. doi:10.1016/S0957-4166(02)00321-X.
- ^ Jump up to:a b c “Drug Trials Snapshots: Fluorodopa F 18”. U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 27 November 2019. Archived from the original on 27 November 2019. Retrieved 27 November 2019.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - ^ “Drug Approval Package: Fluorodopa F18”. U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 20 November 2019. Archived from the original on 27 November 2019. Retrieved 26 November 2019.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 6-fluoro-L-DOPA, FDOPA |
| License data |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C9H10FNO4 |
| Molar mass | 215.18 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
//////////////////Fluorodopa F 18, フルオロドパ (18F), FDA 2019, флуородопа (18F) , فلورودوبا (18F) , 氟[18F]多巴 , radio labelled
N[C@@H](CC1=CC(O)=C(O)C=C1[18F])C(O)=O