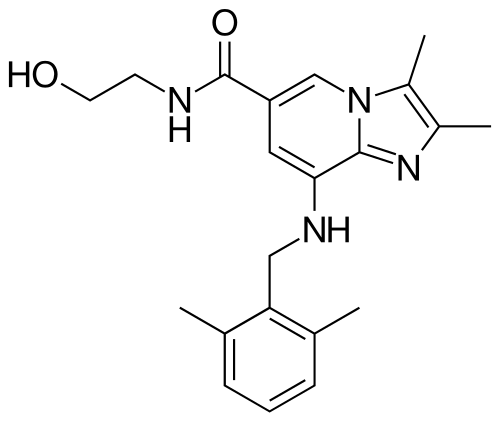
Linaprazan
CHINA 2024, APPROVALS 2024, AstraZeneca, CINCLUS, GERD, linaprazan glurate, for the treatment of moderate to severe GERD,
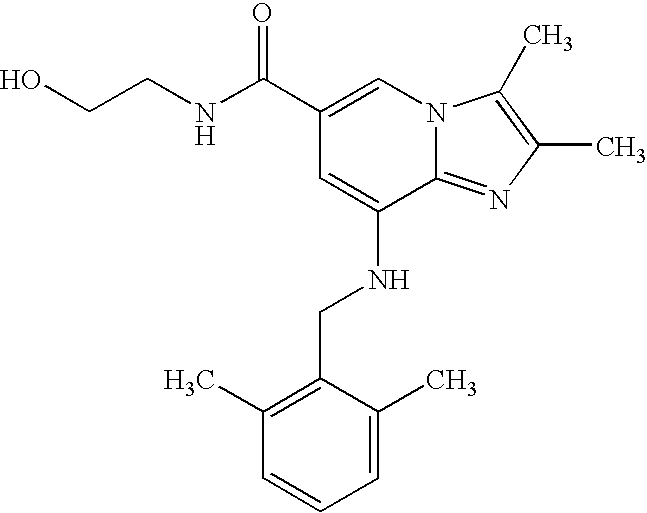
8-[(2,6-dimethylphenyl)methylamino]-N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-2,3-dimethylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-6-carboxamide
- CAS 248919-64-4
- AZD-0865
- E0OU4SC8DP
- DTXSID90870279
366.5 g/mol, C21H26N4O2- CS-5725
- MS-25870
- DB-302288
- HY-100412
- F85407
- Q27276714
- 8-(2,6-dimethylbenzylamino)-N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-2,3-dimethylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-6-carboxamide
- 8-[(2,6-dimethylphenyl)methylamino]-N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-2,3-dimethyl-imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-6-carboxamide
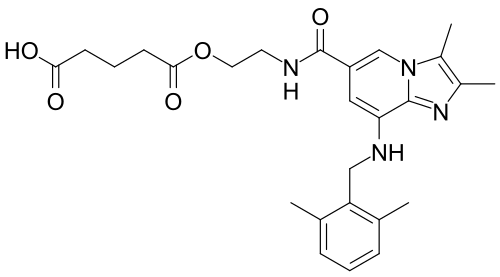
Chemical structure of linaprazan glurate CAS No.: 1228559-81-6 , X842
| Molecular formula | C26H32N4O5 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | 480.556086540222 |
| Accurate quality | 480.237 |
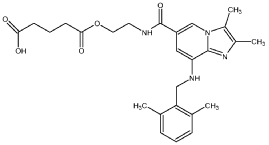
5-[2-[[8-[(2,6-dimethylphenyl)methylamino]-2,3-dimethylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-6-carbonyl]amino]ethoxy]-5-oxopentanoic acid
- OriginatorAstraZeneca
- DeveloperCinclus Pharma; Jiangsu Sinorda Biomedicine Co., Ltd; Shanghai Pharmaceutical Group
- Class2 ring heterocyclic compounds; Amines; Aminopyridines; Anti-inflammatories; Antibacterials; Antiulcers; Glutarates; Imidazoles; Pentanoic acids; Pyridines; Small molecules; Toluenes
- Mechanism of ActionPotassium-competitive acid blockers
- RegisteredReflux oesophagitis
- Phase IIDuodenal ulcer; Erosive oesophagitis; Helicobacter infections
- Phase IGastro-oesophageal reflux
- 28 Aug 2025No recent reports of development identified for phase-I development in Gastro-oesophageal-reflux(In volunteers) in Sweden (PO, Tablet)
- 29 Jun 2025Cinclus Pharma Holding plans a phase III trial for Gastro-oesophageal-reflux in the US, Bulgaria, Czech Republic, Georgia, Germany, Hungary, Poland (PO) (NCT07037875)
- 13 Jun 2025Cinclus Pharma secures EMA and FDA pediatric study waivers for linaprazan glurate in H. pylori infection
Linaprazan is a lipophilic, weak base with potassium-competitive acid blocking (P-CAB) activity. Linaprazan concentrates highly in the gastric parietal cell canaliculus and on entering this acidic environment is instantly protonated and binds competitively and reversibly to the potassium binding site of the proton pump hydrogen-potassium adenosine triphosphatase (H+/K+ ATPase), thereby inhibiting the pump’s activity and the parietal cell secretion of H+ ions into the gastric lumen, the final step in gastric acid production.
Linaprazan is an experimental drug for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Unlike the proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs) which are typically used to treat GERD, linaprazan is a potassium-competitive acid blocker (P-CAB).[1][2] Linaprazan was developed by AstraZeneca, but it was not successful in clinical trials.[3]
The drug was then licensed to Cinclus Pharma,[4] which is now investigating linaprazan glurate, a prodrug of linaprazan which is expected to have a longer biological half-life than linaprazan itself.[4]
Linaprazan glurate inhibits exogenously or endogenously stimulated gastric acid secretion. Linaprazan glurate exhibits several favorable properties, such as rapid onset of action, high in vivo potency, and/or prolonged duration of action. Linaprazan glurate is useful in the research of gastrointestinal inflammatory diseases and peptic ulcer disease (disclosed in patent WO2010063876A1).
- Imidazo pyridine derivatives which inhibit gastric acid secretionPublication Number: WO-9955706-A9Priority Date: 1998-04-29
- Imidazo pyridine derivatives which inhibit gastric acid secretion.Publication Number: ZA-200005797-BPriority Date: 1998-04-29
- Imidazo pyridine derivatives which inhibit gastric acid secretionPublication Number: KR-20050121760-APriority Date: 1998-04-29
- Imidazopyridine derivatives which inhibit gastric acid secretion, pharmaceutical formulation containing such derivatives, processes for their preparation, use thereof, and intermediates.Publication Number: NO-317262-B1Priority Date: 1998-04-29
- Imidazo pyridine derivatives which inhibit gastric acid secretionPublication Number: PL-195000-B1Priority Date: 1998-04-29
- Imidazo pyridine derivatives which inhibit gastric acid secretionPublication Number: US-6313137-B1Priority Date: 1998-04-29Grant Date: 2001-11-06
- Imidazo pyridine derivatives which inhibit gastric acid secretionPublication Number: WO-9955706-A1Priority Date: 1998-04-29
SYN
WO2010063876
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/WO2010063876
Examples
Example 1
Preparation of 5- {2-[( {8-[(2,6-dimethylbenzyl)amino]-2,3-dimethylimidazo[ 1 ,2-a]pyridin-6-yl}carbonyl)amino]ethoxy}-5-oxopentanoic acid
2,3-dimethyl-8-(2,6-dimethylbenzylamino)-N-hydroxyethyl-imidazo[l,2-a]pyridi-ne-6-carboxamide (obtained using the process according to WO02/20523) (2.0 g,
5.46 mmol) and glutaric anhydride (0.95 g, 8.33 mmol) was added to DMF (10 ml). The mixture was heated to 80 0C and stirred 16 h at this temperature.
Acetone (20 ml) was added to the reaction mixture whereby the product started to crystallize. The mixture was cooled to room temperature. After 4 h the product was filtered off and washed with acetone (20 ml). 2.25 g (86%) of the title compound was obtained. The structure of the compound was confirmed with 1H- NMR spectrum.
1H-NMR (300 MHz, DMSO): δ 1.73 (m, 2H), 2.2-2.4 (m, 16H), 3.52 (m,2H), 4.18 (t, 2H), 4.36 (d, 2H), 4.99 (t, IH), 6.67 (s, IH), 7.0-7.2 (m, 3H), 8.04 (s, IH), 8.56 (t, IH), 12.10 (bs, IH).
SYN
US6900324B2.
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=US40374322&_cid=P12-MEXO1E-18626-1
Example 1.16
| Synthesis of 8-[(216-dimethylbenzyl)amino]-N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-2,3-dimethylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-6-carboxamide |
Example 2.1
Example 2.2
Example 2.3
SYN
European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 291 (2025) 117643
Linaprazan is a potassium-competitive acid blocker (P-CAB) initially developed by AstraZeneca between 2001 and 2005 for treating gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Subsequently, Cinclus Pharma ac
quired the rights to linaprazan and developed linaprazan glurate. In 2024, the NMPA approved linaprazan glurate for the treatment of moderate to severe GERD, marking Cinclus Pharma’s first marketing approval in China. Linaprazan glurate is a P-CAB that inhibits gastric acid secretion by reversibly blocking the potassium-binding site of the gastric H+/K +-ATPase enzyme, leading to rapid and sustained acid suppression [94]. Clinical efficacy was demonstrated in Phase III trials NCT04567810), showing superior acid suppression and symptom relief compared to PPIs in GERD patients. Regarding toxicity, linaprazan was generally well tolerated in clinical studies. However, some issues were
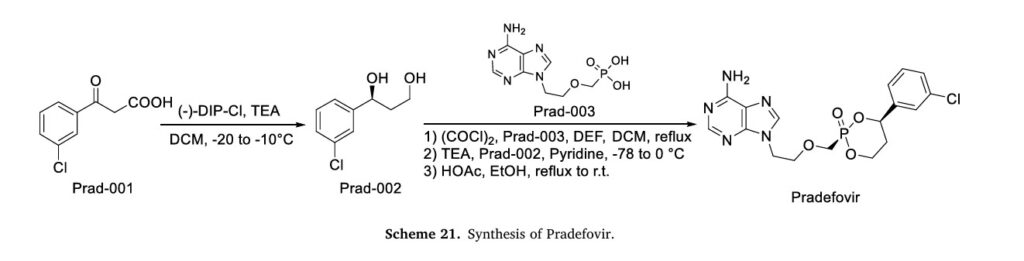
noted, such as elevated liver transaminases in a few patients, which were addressed in the development of linaprazan glurate by achieving lower peak plasma concentrations (Cmax) to minimize liver load 95,96]. The synthetic route of Linaprazan, shown in Scheme 22 [97], initiates with condensative Cyclization between Lina-001 and Lina-002 to yield Lina-003. This intermediate undergoes nucleophilic substitution with Lina-004 under basic conditions to generate Lina-005. Final thermolytic amidation of Lina-005 at 100 DEG CENT affords Linaprazan
[95] C. Scarpignato, R.H. Hunt, Potassium-competitive acid blockers: current clinical use and future developments, Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 26 (2024) 273–293.
[96] J.F. Willart, M. Durand, L.E. Briggner, A. Marx, F. Dan`ede, M. Descamps, Solid-state amorphization of linaprazan by mechanical milling and evidence of polymorphism, J Pharm Sci 102 (2013) 2214–2220.
[97] B. Elman, S. Erback, E. Thiemermann, Process for Preparing a Substituted Imidazopyridine Compound, 2002. US6900324B2.



AS ON JUNE2025 4.45 LAKHS VIEWS ON BLOG WORLDREACH AVAILABLEFOR YOUR ADVERTISEMENT

join me on Linkedin
Anthony Melvin Crasto Ph.D – India | LinkedIn
join me on Researchgate
RESEARCHGATE

join me on Facebook
Anthony Melvin Crasto Dr. | Facebook
join me on twitter
Anthony Melvin Crasto Dr. | twitter
+919321316780 call whatsaapp
EMAIL. amcrasto@gmail.com

……
References
- Rawla P, Sunkara T, Ofosu A, Gaduputi V (December 2018). “Potassium-competitive acid blockers – are they the next generation of proton pump inhibitors?”. World Journal of Gastrointestinal Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 9 (7): 63–68. doi:10.4292/wjgpt.v9.i7.63. PMC 6305499. PMID 30595950.
- “Linaprazan”. Inxight Drugs. National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences.
- Tong A (4 March 2020). “Can reformulation of an AstraZeneca castoff rival Takeda’s new heartburn drug? Here’s a $26M bet on yes”. endpts.com.
- “Linaprazan glurate”. Cinclus Pharma.
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | AZD-0865 |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | Investigational |
| Identifiers | |
| IUPAC name | |
| CAS Number | 248919-64-4 |
| PubChem CID | 9951066 |
| UNII | E0OU4SC8DP |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H26N4O2 |
| Molar mass | |
////////////Linaprazan, CHINA 2024, APPROVALS 2024, AstraZeneca, CINCLUS, GERD, linaprazan glurate, moderate to severe GERD, 248919-64-4, AZD 0865, E0OU4SC8DP, DTXSID90870279, X 842














