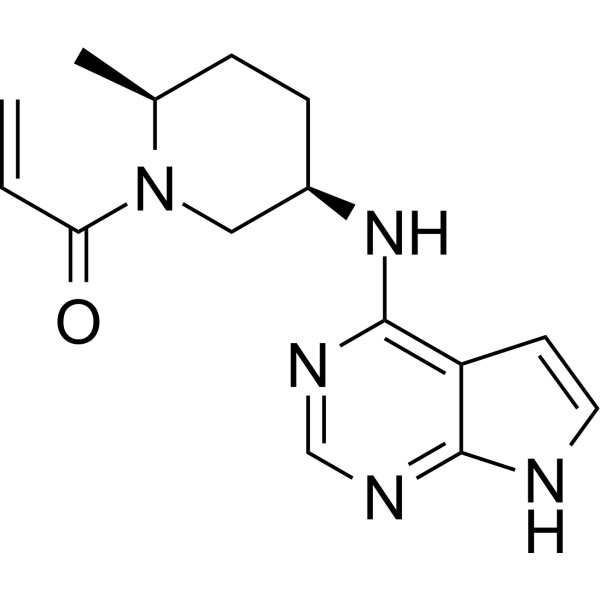
Ritlectinib
PF-06651600
CAS 1792180-81-4
C₁₅H₁₉N₅O, 285.34, UNII-2OYE00PC25
1-((2S,5R)-5-((7H-Pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)amino)-2-methylpiperidin-1-yl)prop-2-en-1-one

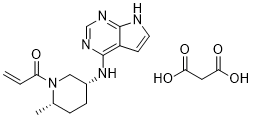
1-[(2S,5R)-2-Methyl-5-(7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-ylamino)-1-piperidinyl]-2-propen-1-one malonate
PF-06651600 malonate
CAS: 2140301-97-7 (malonate)
Chemical Formula: C18H23N5O5
Molecular Weight: 389.412
PHASE 2 alopecia areata, rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s disease, and ulcerative colitis.
PF-06651600 is a potent and selective JAK3 inhibitor. PF-06651600 is a potent and low clearance compound with demonstrated in vivo efficacy. The favorable efficacy and safety profile of this JAK3-specific inhibitor PF-06651600 led to its evaluation in several human clinical studies. JAK3 was among the first of the JAKs targeted for therapeutic intervention due to the strong validation provided by human SCID patients displaying JAK3 deficiencies
Pfizer has established a leading kinase research capability with multiple unique kinase inhibitors in development as potential medicines. PF-06651600 is a highly selective and orally bioavailable Janus Kinase 3 (JAK3) inhibitor that represents a potential immunomodulatory therapy. With the favorable efficacy, safety profile, and ADME properties, this JAK3-specific covalent inhibitor has been under clinical investigation for the treatment of alopecia areata, rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s disease, and ulcerative colitis. Supported by positive results from a Phase 2 study, 1 was granted Breakthrough Therapy designation by the FDA on Sept. 5, 2018 for treatment of alopecia areata.
SYN
PAPER
J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60 (5), 1971–1993, DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b01694
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b01694
Paper
Process Development and Scale Up of a Selective JAK3 Covalent Inhibitor PF-06651600,
Yong Tao*

A scalable process for PF-06651600 (1) has been developed through successful enabling of the first generation syntheis. The synthesis highlights include the following: (1) replacement of costly PtO2 with a less expensive 5% Rh/C catalyst for a pyridine hydrogenation, (2) identification of a diasteroemeric salt crystallization to isolate the enantiomerically pure cis-isomer directly from a racemic mixture of cis/trans isomers, (3) a high yielding amidation via Schotten–Baumann conditions, and (4) critical development of a reproducible crystallization procedure for a stable crystalline salt (1·TsOH), which is suitable for long-term storage and tablet formulation. All chromatographic purifications, including two chiral SFC chromatographic separations, were eliminated. Combined with other improvements in each step of the synthesis, the overall yield was increased from 5% to 14%. Several multikilogram batches of the API have been delivered to support clinical studies.
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.oprd.9b00198
1-((2S,5R)-5-((7H-Pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)amino)-2-methylpiperidin-1-yl)prop-2-en-1-one p-Toluenesulfonate (1·TsOH)
1·TsOH (4.41 kg, 9.64 mol) as a white powder in 89.6% yield (accounting for the amount of seed charged). Achiral HPLC purity: 99.6% with 0.22% of dimer 15. Chiral SFC purity: >99.7%. Mp 199 °C. Rotomers observed for NMR spectroscopies. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ ppm 12.68 (brs, 1H), 9.22 (brs, 1H), 8.40 (s, 1H), 7.50 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 2H), 7.45 (m, 1H), 7.12 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 2H), 6.94 (d, J = 1.2 Hz, 1H), 6.84 (m, 1H), 6.13 (m, 1H), 5.70 (m, 1H), 4.81 (m, 0.5H), 4.54 (m, 0.5H), 4.41 (m, 0.5H), 4.12 (m, 0.5H), 3.99 (m, 1H), 3.15 (m, 0.5H), 2.82 (m, 0.5H), 2.29 (s, 3H), 1.91–1.72 (m, 4H), 1.24–1.17 (m, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ ppm 165.52, 165.13, 150.50, 145.64, 143.06, 138.48, 129.51, 129.24, 128.67, 127.99, 127.73, 125.97, 125.02, 102.30, 49.53, 48.92, 47.27, 43.83, 42.96, 29.37, 28.41, 25.22, 21.28, 16.97, 15.51. HRMS (ESI) m/z: calculated for C15H20N5O [M + H]+286.1668; observed 286.1692.
PAPER
PATENT
WO 2015083028
https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2015083028A1
PATENT
WO 2020084435
1 -((2S,5R)-5-((7H-Pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)amino)-2-methylpiperidin-1 -yl)prop-2-en-1 -one has the structural formula:
The synthesis of 1 -((2S,5R)-5-((7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)amino)-2-methylpiperidin-1 -yl)prop-2-en-1 -one is described in WO2015/083028, commonly assigned to the assignee of the present invention and which is incorporated herein by reference in its entirety. 1 -((2S,5R)-5-((7H-Pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)amino)-2-methylpiperidin-1 -yl)prop-2-en-1 -one is useful as an inhibitor of protein kinases, such as the enzyme Janus Kinase (JAK) and as such is useful therapy as an immunosuppressive agent for organ transplants, xeno transplantation, lupus, multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, Type I diabetes and complications from diabetes, cancer, asthma, atopic dermatitis, autoimmune thyroid disorders, ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease, alopecia, vitiligo, Alzheimer’s disease, leukemia and other indications where immunosuppression would be desirable. See ACS Chem. Biol. , 2016, 11 (12), pp 3442-3451 . The present invention relates to a novel p-toluenesulfonic acid salt and crystalline solid form of the said salt of 1 -((2S,5R)-5-((7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)amino)-2-methylpiperidin-1 -yl)prop-2-en-1 -one that demonstrate improved properties for use in a pharmaceutical dosage form, particularly for oral dosage forms.
Preparations
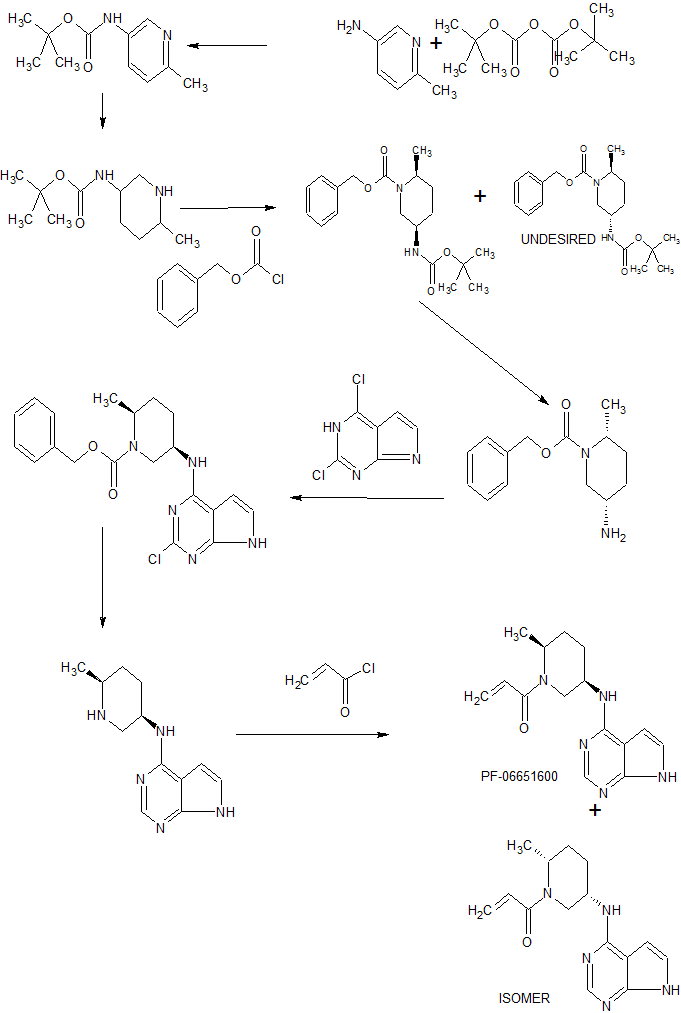
Scheme 1. Synthesis of 1
Scheme 2. Alternate Synthesis of Intermediates 7 and 10
1. K2C03, MIBK/water 1. H2, H2O
2. EtOAc, aq. NaCI Pd(OH)2/C (wet)
3. MeOH, H20 2. NaOH, MeOH
7 + 8 – ► 9 – – 10 . H2O
89% 89%
Scheme 3. First Alternate Preparation of 1
Scheme 4. Second Alternate Preparation of 1
Preparation 1
ferf-Butyl (6-methylpyridin-3-yl)carbamate (3). To a 3000L reactor was charged 2 (72.00 kg, 665.8 mol) and THF (660 kg). A solution of NH4CI (1 .07 kg , 20 mol) in water (72 kg, 4000 mol) was added. The mixture was heated to 57 °C and Di-f-butyl dicarbonate (220.0 kg, 1003 mol) was added slowly with rinse of THF (45 kg) while maintaining the temperature between 55 – 60 °C. The mixture was stirred at 55 – 60 °C for 10 h. Upon reaction completion, the slurry was cooled to 20 °C and ethyl acetate (654 kg) and water (367 kg) were added. The organic phase was separated, washed by water (2 x 360 kg) and stirred with active carbon (22 kg) for 5 h. The mixture was filtered through a layer of diatomaceous earth (22 kg) with THF rinse and the filtrates were concentrated under vacuum at <40 °C to a residual volume of ~370 L. n-Heptane (500 kg) was added slowly over 1 h and the resulting slurry was cooled to 20 °C and stirred for 2 h. The solid was collected by centrifuge with an n-heptane wash (420 kg), then dried at 45 °C under vacuum for 20 h to give 3 (131 .15 kg, 629.7 mol) as a white powder in 94.5% yield. HPLC purity: 99.9%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-c/6): d ppm 9.42 (brs, 1 H), 8.48 (d, J = 1 .9 Hz, 1 H), 7.75 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 1 H), 7.13 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 1 H), 2.38 (s, 3H), 1 .49 (s, 9H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6y d ppm 153.34, 151 .56, 139.75, 134.13, 126.10, 123.09, 79.87, 28.56, 23.70. HRMS (ESI) m/z: calculated for C11H17N2O2 [M + H]+ 209.1290; observed 209.1285.
Preparation 2
ferf-Butyl (6-methylpiperidin-3-yl)carbamate (rac-4). To a 3000L reactor was charged 3 (137.0 kg, 667.8 mol), ethanol (988 kg) and acetic acid (139 kg). The reactor was purged with nitrogen three times and 5 wt% Rhodium on carbon (wet, 27.4 kg, 20 wt% loading relative to 3) was added. The reactor was purged with nitrogen three times and then with hydrogen three times. The hydrogen pressure was adjusted to 0.34 – 0.38 MPa and the reactor temperature was adjusted to 47 °C. The mixture was stirred at 45 – 60 °C under hydrogen pressure at 0.34 – 0.38 MPa for 10 h. Upon reaction completion, the reactor was cooled to 20 °C and flushed with nitrogen. The mixture was filtered through a layer of diatomaceous earth (20 kg) with an ethanol rinse (1320 kg) and the filtrates were concentrated under vacuum at <50 °C to a residual volume of ~350 L. n-Heptane (571 kg) was added and the mixture was concentrated under vacuum at <50 °C to a residual volume of~350 L. This operation was repeated twice until the residual acetic acid <8.0%. Ethanol (672 kg) was added and the mixture was concentrated under vacuum at <50 °C to a residual volume of ~350 L. This operation was repeated twice until the residual n-heptane was <0.2% and water was <0.2%. Ethanol (889 kg) was added and the solution (1254 kg) was transferred to drums for use in the subsequent classical resolution step. Achiral HPLC assay indicated that the solution contained 10.8 wt% of the total reduced product (rac-4) in 96% mass recovery and chiral SFC showed that the solution contained 36.3% of the desired stereoisomer cis-4.
Preparation 3
ferf-Butyl ((3R,6S)-6-methylpiperidin-3-yl)carbamate (R)-2-(3,5-dinitrobenzamido)-2-phenylacetic acid salt (15). To a 2000L reactor (R1 ) was charged rac-4 as a 10.8 wt% solution in ethanol (620.5 kg, ~312.7 mol. of all 4 isomers). The solution was concentrated under vacuum at <45 °C to a residual volume of ~210 L and then cooled to 20 °C. To a 3000 L reactor (R2) was charged (R)-2-(3,5-dinitrobenzamido)-2-phenylacetic acid 14 (47.0 kg, 136.1 mol) and ethanol (1 125 kg). With high speed agitation, reactor R2 was heated to 70 °C, stirred at 68 – 70 °C for ~2 h to dissolve all solid 14, and then seeded with crystalline 15 (1 1 g). The solution containing 4 in reactor R1 was slowly transferred to reactor R2 over 30 min with ethanol rinse (160 kg). Reactor R2 was stirred at ~74 °C for 3 h and then cooled to 22 °C with a linear cooling rate over a period of 5 h and stirred for 16 h. The solid was collected by centrifuge with ethanol wash (2 x 200 kg). The wet cake (with 97.1 % e.e.) was charged back to reactor R2. The slurry was heated to 74 °C and the mixture was stirred for 17 h. The mixture was then cooled to 22 °C with a linear cooling rate over a period of 5 h and stirred for 4 h. The solid was collected by centrifuge with ethanol wash (2 x 200 kg) and dried at 35 °C under vacuum for 25 h to give 15 (56.05 kg, 100.2 mol) as a white powder in 30.7% yield over 2 steps. Chiral HPLC purity: 99.1 %. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): d ppm 9.46 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 1 H), 9.07 (d, J = 2.2 Hz, 2H), 8.96 (t, J = 2.2 Hz, 1 H), 7.49 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 2H), 7.30 (t, J = 7.3 Hz, 2H), 7.23 (t, J = 7.3, 1 H), 7.1 1 (m, 1 H), 5.31 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 1 H), 3.66 (m, 1 H), 2.98 (m, 3H), 1 .63 (m, 2H), 1 .45 (m, 2H), 1 .40 (s, 9H), 1 .1 1 (d, J = 6.7 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): d ppm 172.71 , 161 .71 , 155.42, 148.51 , 141 .27, 137.70, 128.29, 128.25, 128.02, 127.05, 121 .12, 78.49, 59.74, 50.66, 46.29, 43.34, 28.66, 26.88, 26.1 1 , 18.60.
Preparation 4
Benzyl (2S,5R)-5-amino-2-methylpiperidine-1 -carboxylate hydrochloride (7»HCI) -telescoped process. To a 2000L reactor was charged 15 (70.0 kg, 125 mol) and MTBE (500 kg). The mixture was cooled to 12 °C and 6.9 wt% aqueous NaOH solution (378 kg, 652 mol) was added slowly while maintaining the temperature between 10 – 25 °C. The mixture was stirred at 18 °C for 1 h . The organic phase was separated and washed with 3.8 wt% aqueous NaOH solution (2 x 221 kg) and then 25 wt% aqueous NaCI solution (2 x 220 kg). The organic layer (containing the free base cis-4) was concentrated under vacuum at <40 °C to a residual volume of ~300 L and then cooled to 20 °C. NaHCOs (53 kg, 632 mol) and water (200 kg) were added and the mixture was cooled to 7 °C. Benzyl chloroformate (32.30 kg, 189.3 mol) was added slowly while maintaining the temperature between 5 – 20 °C. The mixture was stirred at 17 °C for 20 h. Upon reaction completion, the mixture was cooled to 12 °C, 25 wt% aqueous ammonium hydroxide solution (79 kg, 1 160 mol) was added slowly while maintaining the temperature between 10 – 20 °C, and the mixture was stirred at 15 °C for 1 h. The organic phase was separated and washed with 25 wt% aqueous NaCI solution (3 x 90 kg). The organic layer (containing 5) was concentrated under vacuum at <45 °C to a residual volume of ~150 L. Isopropyl acetate (310 kg) was added and the mixture was concentrated under vacuum at <45 °C to a residual volume of ~150 L. This operation was repeated twice to meetthe criteria of water <0.1 % (by KF). Isopropyl acetate (130 kg) was then added and the mixture was cooled to -3 °C. 4-5N HCI in methanol (181 kg, ~730 mol) was added slowly while maintaining the temperature between -5 to 5 °C, and the mixture was stirred at 3 °C for 12 h. Upon reaction completion, the mixture was cooled to -3 °C and MTBE (940 kg) was added slowly while maintaining the temperature between -5 to 5 °C. The resulting slurry was stirred at 3 °C for 3 h. The solid was collected by centrifuge with MTBE washes (4 x 70 kg), and then dried at 45 °C under vacuum for 20 h to give 7»HCI (28.60 kg, 100.4 mol) as a white powder in 80.3% yield. Achiral HPLC purity: 100%. Chiral SFC purity: 99.8% e.e. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): d ppm 8.36 (brs, 3H), 7.37 (m, 5H), 5.09 (s, 2H), 4.31 (m, 1 H), 4.16 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 1 H), 3.00 (m, 2H), 1 .82 (m, 2H), 1 .59 (m, 2H), 1 .1 1 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): d ppm 154.71 , 137.24, 128.92, 128.34, 128.00, 66.89, 47.20, 45.66, 40.68, 28.16, 23.02, 15.67. HRMS (ESI) m/z. calculated for C H N O [M + H]+ 249.1603; observed 249.1598.
Preparation 5
Benzyl (2S, 5R)-5-((2-chloro-7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)amino)-2 -methyl-piperidine-1 -carboxylate (9). To a 2000L reactor was charged 7»HCI (88.6 kg, 31 1 .12 mol), 8 (56.0 kg, 298 mol), K2C03 (133.0 kg, 962.3 mol), water (570 kg) and MIBK (101 kg). The mixture was heated to 90 °C and stirred at this temperature for 22 h. Upon reaction completion, the mixture was cooled to 56 °C and ethyl acetate (531 kg) was added. After cooling the mixture to 22 °C, the organic phase was separated, washed with water (570 kg) and concentrated under vacuum at <40 °C to a residual volume of ~220 L. Methanol (360 kg) was added slowly over a period of 1 h and the mixture concentrated under vacuum at <50 °C to a residual volume of ~220 L. This operation was repeated three times until residual MIBK reached <5 wt%. Methanol (270 kg) was added, followed by seeding with 9 (120 g). The mixture was stirred at 22 °C for >4 h and water (286 kg) was added slowly over 4 h. The slurry was stirred for 10 h and the solid was then collected by centrifuge. The wet cake (165.6 kg) was charged back to a clean reactor and water (896 kg) was added. The slurry was heated to 55 °C and stirred at this temperature for 7 h; and then cooled to 22 °C and stirred at this temperature for 2 h. The solid was collected by centrifuge with water wash (3 x 170 kg) and dried at 55 °C under vacuum for 20 h to give 9 (106.62 kg, 266.6 mol) as a white powder in 89.5% yield. Achiral HPLC purity: 99.7%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): d ppm 1 1 .71 (brs, 1 H), 7.72 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 1 H), 7.38 (m, 5H), 7.10 (s, 1 H), 6.57 (d, J = 2.7 Hz, 1 H), 5.1 1 (m, 2H), 4.39 (m, 1 H), 4.17 (m, 1 H), 4.01 (m, 1 H), 3.36 (s, 2H), 2.77 (m, 1 H), 1 .73-1 .81 (m, 4H), 1 .16 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): d ppm 156.65, 154.74, 153.04, 151 .31 , 137.43, 128.89, 128.27, 127.96, 122.13, 101 .65, 99.51 , 66.75, 49.10, 47.32, 45.64, 42.98, 29.05, 25.08. HRMS (ESI) m/z. calculated for C20H22CIN5O2 [M + H]+ 400.1540; observed 400.1535.
Preparation 6
N-((3R,6S)-6-methylpiperidin-3-yl)-7H-pyrrolo[2,3-dlpyrimidin-4-amine monohydrate (10·H2O) To a 1600L reactor was charged water (570 kg). The reactor was purged with nitrogen three times. 10% Pd(OH)2/C (wet, 3.2 kg) and 9 (53.34 kg, 133.2 mol) were added with water rinses (2 x 55 kg). The reactor was purged with nitrogen three times and then with hydrogen three times. The hydrogen pressure was adjusted to 0.34 – 0.38 MPa and the reactor temperature was adjusted to 77 °C. The mixture was stirred at 75 – 80 °C under a hydrogen pressure of 0.34 -0.38 MPa for 10 h. Upon reaction completion, the reactor was cooled to 20 °C and purged with nitrogen. The mixture was filtered through a layer of diatomaceous earth (8 kg) with a water rinse (460 kg), and the filtrates were transferred to a 3000L reactor. Methanol (260 kg) was added, followed by slow addition of 50 wt% aqueous sodium hydroxide (12.0 kg , 150 mol) while maintaining the temperature between 15 – 25 °C. The slurry was heated to 55 °C and stirred for 2 h; then cooled to 22 °C and stirred for 10 h. The solid was collected by centrifuge with a 10:1 water/methanol wash (3 x 1 10 kg) and then dried at 55 °C under vacuum for 20 h to give 10·H2O (30.90 kg, 266.6 mol) as a white powder in 89.1 % yield. Achiral HPLC purity: 99.7%. Chiral SFC
purity: 99.8% e.e. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): d ppm 1 1 .48 (brs, 1 H), 8.08 (s, 1 H), 7.07 (s, 1 H), 6.85 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 1 H), 6.64 (s, 1 H), 4.16 (m, 1 H), 3.35 (brs, 2H), 2.96 (d, J = 12.7 Hz, 1 H), 2.82 (d, J = 12.7 Hz, 1 H), 2.67 (m, 1 H), 2.04 (brs, 1 H), 1 .92 (m, 1 H), 1 .63 (m, 1 H), 1 .44 (m, 1 H), 1 .33 (m, 1 H), 1 .03 (d, J = 6.2 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): d ppm 155.95, 151 .87, 150.74, 121 .20, 102.97, 99.20, 51 .27, 49.94, 44.78, 29.97, 28.69, 22.35. HRMS (ESI) m/z\ calculated for C12H17N5 [M + H]+ 232.1562; observed 232.1558.
Preparation 7
1 -((2S,5R)-5-((7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)amino)-2-methylpiperidin-1 -yl)prop-2-en-1 -one (1 ). To a 100L reactor was charged water (18.0 L), 10·H2q (3.60 kg, 14.4 mol) and THF (36.0 L). The mixture was heated to 53 °C and stirred for 15 min to dissolve all the solids. The solution was then cooled to 18 °C and K3PO4 (6.38 kg, 30.1 mol) was added. The mixture was stirred at 18 °C for 10 min to dissolve all the solids, and then cooled to 10 °C. 3-Chloropropionyl chloride (2.20 kg, 17.3 mol) was added while maintaining the temperature <20 °C. The mixture was then stirred at 20 °C for 2 h. Upon reaction completion, 2 N aqueous NaOH solution (23.50 kg, 43.76 mol) was added while maintaining the temperature <25 °C. The mixture was stirred at 22 °C for >12 h until the elimination reaction was complete (11 <0.2%). KH2PO4 (10.32 kg, 75.8 mol) was added and the mixture was stirred at 20 °C for 10 min. The organic phase was separated and then washed with 23.5 wt% aqueous NaCI solution (2 x 8.5 kg). The isolated organic phase was concentrated under vacuum at <30 °C to a residual volume of ~10 L, whereupon MEK (39.6 L) was added. This operation was repeated once or twice until residual THF was <1 % and water was <2%. MgS04 (0.96 kg), Silica gel (4.90 kg) and Darco™ G-60 (0.48 kg) were added to the MEK solution, and the mixture was stirred at 20 °C for 1 h, then filtered through a layer of Diatomaceous Earth with a MEK rinse (76 L). The combined filtrates were concentrated under vacuum at <30 °C to a residual volume of ~8 L. The concentration of the residual solution was measured by qNMR, and the solution was transferred to a container with a rinse using the calculated amount of MEK to adjust the final concentration to 30 wt%. Thus, a 30 wt% solution of 1 in MEK (1 1 .09 kg, 1 1 .66 mol of 1) with 98.7% purity was obtained in 81 % yield, which was stored in a cold room (2 – 8 °C) for the next step.
Preparation 8
1 -((2S,5R)-5-((7H-pyrrolo[2,3-cdpyrimidin-4-yl)amino)-2-methylpiperidin-1 -yl)prop-2-en-1 -one p-toluenesulfonate (1»TsOH). To a 20L reactor was charged a 30 wt% solution of 1 in MEK (9.80 kg, 10.30 mol of 1) and silica gel (0.74 kg). The mixture was stirred at 22 °C for 15 min and filtered through a 0.45 micron Teflon cartridge filter with a MEK rinse (7.89 kg, 9.8 L), collecting in a 100L reactor. Water (1 .27 L) was added, followed by a solution of p-toluenesulfonic acid monohydrate (2.18 kg, 1 1 .3 mol) in MEK (4.75 kg, 5.9 L) with a MEK rinse (3.14 kg, 3.9 L), followed by the addition of 1 »TsOH seed (188 g, 0.41 mol). The mixture was stirred at 22 °C for
4 h to form a slurry and MEK (31 .56 kg, 39.2 L) was added slowly over a period of 3 h. The slurry was stirred at 22 °C for an additional 2 h and then filtered. The cake was washed with MEK (4.02 kg, 5 L) and then dried at 50 °C under vacuum for 10 h to give 1 »TsOH (4.41 kg, 9.64 mol) as a white powder in 89.6% yield (accounting for the amount of seed charged). Achiral HPLC purity: 99.6% with 0.22% of dimer 15. Chiral SFC purity: >99.7%. m.p. 199 °C. Rotomers observed for NMR spectroscopies. Ή NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): d ppm 12.68 (brs, 1 H), 9.22 (brs, 1 H), 8.40 (s, 1 H), 7.50 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 2H), 7.45 (m, 1 H), 7.12 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 2H), 6.94 (d, J = 1 .2 Hz, 1 H), 6.84 (m, 1 H), 6.13 (m, 1 H), 5.70 (m, 1 H), 4.81 (m, 0.5H), 4.54 (m, 0.5H), 4.41 (m, 0.5H), 4.12 (m, 0.5H), 3.99 (m, 1 H), 3.15 (m, 0.5H), 2.82 (m, 0.5H), 2.29 (s, 3H), 1 .91 -1 .72 (m, 4H), 1 .24-1 .17 (m, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-c/6): d ppm 165.52, 165.13, 150.50, 145.64, 143.06, 138.48, 129.51 , 129.24, 128.67, 127.99, 127.73, 125.97, 125.02, 102.30, 49.53, 48.92, 47.27, 43.83, 42.96, 29.37, 28.41 , 25.22, 21 .28, 16.97, 15.51 . HRMS (ESI) m/z: calculated for Ci5H2oN50 [M + H]+ 286.1668; observed 286.1692.
Comparative Example
Preparation of 1 -((2S,5R)-5-((7H-Pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)amino)-2-methyl-piperidin-1 -yl)prop-2-en-1 -one Malonic Acid Salt (Form 1 )
A 250 ml_ round bottom flask was charged with 1 -((2S,5R)-5-((7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)amino)-2-methylpiperidin-1 -yl)prop-2-en-1 -one (4.10 g, 14.4 mmol), MEK (Methyl Ethyl Ketone (15.0 ml_/g, 687 mmol, 49.5 g, 61 .5 ml_)). To the solution, malonic acid (0.950 equiv. 13.7 mmol, 1 .42 g) was added in one portion. The mixture was heated to 50 °C and stirred at 50 °C for 15min. The heating was turned off and the slurry was stirred for 16 hours. The resulting white slurry was filtered. The filter cake was washed with MEK (2 X 5 ml_) and dried in a vacuum oven (40 °C) for 2 hours give 1 -((2S,5R)-5-((7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)amino)-2-methylpiperidin-1 -yl)prop-2-en-1 -one malonic acid salt (Form 1) (4.48 g, 1 1 .5 mmol, 4.48 g, 80.1 % Yield) as white powder.
REFERENCES
1: D’Amico F, Fiorino G, Furfaro F, Allocca M, Danese S. Janus kinase inhibitors for the treatment of inflammatory bowel diseases: developments from phase I and phase II clinical trials. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2018 Jul;27(7):595-599. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2018.1492547. Epub 2018 Jul 6. Review. PubMed PMID: 29938545.
2: Robinette ML, Cella M, Telliez JB, Ulland TK, Barrow AD, Capuder K, Gilfillan S, Lin LL, Notarangelo LD, Colonna M. Jak3 deficiency blocks innate lymphoid cell development. Mucosal Immunol. 2018 Jan;11(1):50-60. doi: 10.1038/mi.2017.38. Epub 2017 May 17. PubMed PMID: 28513593; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC5693788.
3: Thorarensen A, Dowty ME, Banker ME, Juba B, Jussif J, Lin T, Vincent F, Czerwinski RM, Casimiro-Garcia A, Unwalla R, Trujillo JI, Liang S, Balbo P, Che Y, Gilbert AM, Brown MF, Hayward M, Montgomery J, Leung L, Yang X, Soucy S, Hegen M, Coe J, Langille J, Vajdos F, Chrencik J, Telliez JB. Design of a Janus Kinase 3 (JAK3) Specific Inhibitor 1-((2S,5R)-5-((7H-Pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)amino)-2-methylpiperidin-1-yl)prop -2-en-1-one (PF-06651600) Allowing for the Interrogation of JAK3 Signaling in Humans. J Med Chem. 2017 Mar 9;60(5):1971-1993. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b01694. Epub 2017 Feb 16. PubMed PMID: 28139931.
4: Telliez JB, Dowty ME, Wang L, Jussif J, Lin T, Li L, Moy E, Balbo P, Li W, Zhao Y, Crouse K, Dickinson C, Symanowicz P, Hegen M, Banker ME, Vincent F, Unwalla R, Liang S, Gilbert AM, Brown MF, Hayward M, Montgomery J, Yang X, Bauman J, Trujillo JI, Casimiro-Garcia A, Vajdos FF, Leung L, Geoghegan KF, Quazi A, Xuan D, Jones L, Hett E, Wright K, Clark JD, Thorarensen A. Discovery of a JAK3-Selective Inhibitor: Functional Differentiation of JAK3-Selective Inhibition over pan-JAK or JAK1-Selective Inhibition. ACS Chem Biol. 2016 Dec 16;11(12):3442-3451. Epub 2016 Nov 10. PubMed PMID: 27791347.
5: Walker G, Croasdell G. The European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) – 17th Annual European Congress of Rheumatology (June 8-11, 2016 – London, UK). Drugs Today (Barc). 2016 Jun;52(6):355-60. doi: 10.1358/dot.2016.52.6.2516435. PubMed PMID: 27458612.
////////////PF-06651600, PF 06651600, PF06651600, Breakthrough Therapy designation, PHASE 2, alopecia areata, rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis,
C=CC(N1[C@@H](C)CC[C@@H](NC2=C3C(NC=C3)=NC=N2)C1)=O














