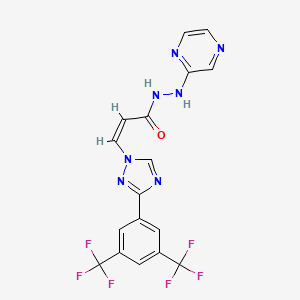
Selinexor
セリネクソル
KPT-330
UNII-31TZ62FO8F
(Z)-3-[3-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl]-N‘-pyrazin-2-ylprop-2-enehydrazide
| Formula |
C17H11F6N7O
|
|---|---|
| CAS |
1393477-72-9
|
| Mol weight |
443.306
|
FDA, APPROVED 2019/7/3, Xpovio
CAS : 1393477-72-9 (free base) 1421923-86-5 (E-isomer) 1621865-82-4 (E-isomer) Unknown (HCl)
Treatment of cancer, Antineoplastic, Nuclear export inhibitor
Selinexor (INN, trade name Xpovio; codenamed KPT-330) is a selective inhibitor of nuclear export used as an anti-cancer drug. It works by quasi-irreversibly binding to exportin 1 and thus blocking the transport of several proteins involved in cancer-cell growth from the cell nucleus to the cytoplasm, which ultimately arrests the cell cycle and leads to apoptosis.[1] It is the first drug with this mechanism of action.[2][3]
Selinexor was granted accelerated approval by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in July 2019, for use as a drug of last resort in people with multiple myeloma. In clinical trials, it was associated with a high incidence of severe side effects, including low platelet counts and low blood sodium levels.[3][4]
Selinexor is an orally available, small molecule inhibitor of CRM1 (chromosome region maintenance 1 protein, exportin 1 or XPO1), with potential antineoplastic activity. Selinexor modifies the essential CRM1-cargo binding residue cysteine-528, thereby irreversibly inactivates CRM1-mediated nuclear export of cargo proteins such as tumor suppressor proteins (TSPs), including p53, p21, BRCA1/2, pRB, FOXO, and other growth regulatory proteins. As a result, this agent, via the approach of selective inhibition of nuclear export (SINE), restores endogenous tumor suppressing processes to selectively eliminate tumor cells while sparing normal cells. CRM1, the major export factor for proteins from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, is overexpressed in a variety of cancer cell types.
Selinexor has been used in trials studying the treatment of AML, Glioma, Sarcoma, Leukemia, and Advanced, among others.
Selinexor, also known as KPT-330, is an orally bioavailable, potent and selective XPO1/CRM1 Inhibitor. Selinexor is effective in acquired resistance to ibrutinib and synergizes with ibrutinib in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Selinexor potentiates the antitumor activity of gemcitabine in human pancreatic cancer through inhibition of tumor growth, depletion of the antiapoptotic proteins, and induction of apoptosis. Selinexor has strong activity against primary AML cells while sparing normal stem and progenitor cells.
SYN
Medical uses
Selinexor is restricted for use in combination with the steroid dexamethasone in people with relapsed or refractory multiple myelomawhich has failed to respond to at least four or five other therapies (so-called “quad-refractory” or “penta-refractory” myeloma),[5] for whom no other treatment options are available.[3][4] It is the first drug to be approved for this indication.[6]
Adverse effects
In the clinical study used to support FDA approval, selinexor was associated with high rates of pancytopenia, including leukopenia(28%), neutropenia (34%, severe in 21%), thrombocytopenia (74%, severe in 61% of patients), and anemia (59%).[4][7] The most common non-hematological side effects were gastrointestinal reactions (nausea, anorexia, vomiting, and diarrhea), hyponatremia (low blood sodium levels, occurring in up to 40% of patients), and fatigue.[7][8] More than half of all patients who received the drug developed infections, including fatal cases of sepsis.[7] However, these data are from an open-label trial, and thus cannot be compared to placebo or directly attributed to treatment.
Mechanism of action
Schematic illustration of the Ran cycle of nuclear transport. Selinexor inhibits this process at the nuclear export receptor (upper right).
Like other so-called selective inhibitors of nuclear export (SINEs), selinexor works by binding to exportin 1 (also known as CRM1). CRM1 is a karyopherin which performs nuclear transport of several proteins, including tumor suppressors, oncogenes, and proteins involved in governing cell growth, from the cell nucleus to the cytoplasm; it is often overexpressed and its function misregulated in several types of cancer.[1] By restoring nuclear transport of these proteins to normal, SINEs lead to a buildup of tumor suppressors in the nucleus of malignant cells and reduce levels of oncogene products which drive cell proliferation. This ultimately leads to cell cycle arrest and death of cancer cells by apoptosis.[1][2][7] In vitro, this effect appeared to spare normal (non-malignant) cells.[1][8]
Because CRM1 is a pleiotropic gene, inhibiting it affects many different systems in the body, which explains the high incidence of adverse reactions to selinexor.[2] Thrombocytopenia, for example, is a mechanistic and dose-dependent effect, occurring because selinexor causes a buildup of the transcription factor STAT3 in the nucleus of hematopoietic stem cells, preventing their differentiation into mature megakaryocytes (platelet-producing cells) and thus slowing production of new platelets.[2]
Chemistry
Selinexor is a fully synthetic small-molecule compound, developed by means of a structure-based drug design process known as induced-fit docking. It binds to a cysteine residue in the nuclear export signal groove of exportin 1. Although this bond is covalent, it is not irreversible.[1]
History
Selinexor was developed by Karyopharm Therapeutics of Newton, Massachusetts, a pharmaceutical company devoted entirely to the development of drugs that target nuclear transport. It was approved by the FDA on July 3, 2019, on the basis of a single uncontrolled clinical trial. The decision was controversial, and overruled the previous recommendation of an FDA Advisory Panel which had voted 8–5 against approving the drug, due to concerns about efficacy and toxicity.[3]
Research
Under the codename KPT-330, selinexor was tested in several preclinical animal models of cancer, including pancreatic cancer, breast cancer, non-small-cell lung cancer, lymphomas, and acute and chronic leukemias.[9] In humans, early clinical trials (phase I) have been conducted in non-Hodgkin lymphoma, blast crisis, and a wide range of advanced or refractory solid tumors, including colon cancer, head and neck cancer, melanoma, ovarian cancer, and prostate cancer.[9] Compassionate use in patients with acute myeloid leukemia has also been reported.[9]
The pivotal clinical trial which served to support approval of selinexor for people with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma was an open-label study of 122 patients known as the STORM trial.[7] In all of the enrolled patients, selinexor was used as fifth-line or sixth-line therapy after conventional chemotherapy, targeted therapy with bortezomib, carfilzomib, lenalidomide, pomalidomide, and a monoclonal antibody (daratumumab or isatuximab)[5]; nearly all had also undergone hematopoietic stem cell transplantation to no effect.[7] The overall response rate was 25%, and no patients had a complete response.[7] However, the response rate was higher in patients with high-risk myeloma (cytogenetic abnormalities associated with a worse prognosis).[5] The median time to progression was 2.3 months overall and 5 months in patients who responded to the drug.[2]
As of 2019, phase I/II and III trials are ongoing,[3][9] including the use of selinexor in other cancers and in combinations with other drugs used for multiple myeloma.[2]
PATENT
WO 2013019561
WO 2013019548
US 9079865
PATENT
WO 2016025904 A
https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2016025904A1/tr
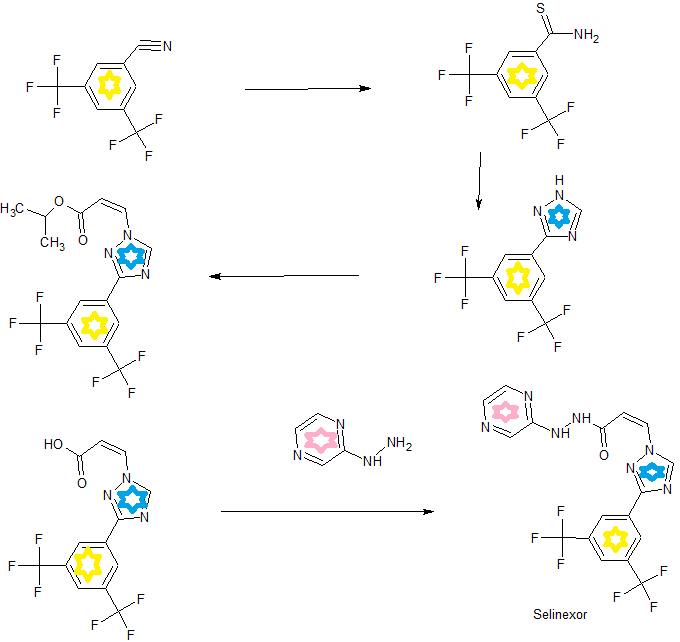
International Publication No. WO 2013/019548 describes a series of compounds that are indicated to have inhibitory activity against chromosomal region maintenance 1 (CRM1, also referred to as exportin 1 or XPO1) and to be useful in the treatment of disorders associated with CRM1 activity, such as cancer. (Z)-3-(3-(3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-N’-(pyrazin-2-yl)acrylohydrazide (also referred to as selinexor) is one of the compounds disclosed in International Publication No. WO 2013/019548. Selinexor has the chemical structure shown in Structural Formula I:
Example 1. Preparation of Selinexor Lot No.1305365 (Form A).
[00274] Selinexor for Lot No. 1305365 was made in accordance with the following reaction scheme:
[00275] A solution of propane phosphonic acid anhydride (T3P®, 50% in ethyl acetate, 35Kg) in THF (24.6Kg) was cooled to about -40 °C. To this solution was added a solution of KG1 (13.8Kg) and diisopropylethylamine (12.4Kg) in tetrahydrofuran (THF, 24.6Kg). The resulting mixture was stirred at about -40°C for approximately 2.5 hours.
[00276] In a separate vessel, KJ8 (4.80Kg) was mixed with THF (122.7Kg), and the resulting mixture cooled to about -20°C. The cold activated ester solution was then added to the KJ8 mixture with stirring, and the reaction was maintained at about -20°C. The mixture was warmed to about 5°C, water (138.1Kg) was added and the temperature adjusted to about 20°C. After agitating for about an hour, the lower phase was allowed to separate from the mixture and discarded. The upper layer was diluted with ethyl acetate (EtOAc). The organic phase was then washed three times with potassium phosphate dibasic solution (~150Kg), then with water (138.6Kg).
[00277] The resulting organic solution was concentrated under reduced pressure to 95L, EtOAc (186.6Kg) was added and the distillation repeated to a volume of 90L. Additional EtOAc (186.8Kg) was added and the distillation repeated a third time to a volume of 90L. The batch was filtered to clarify, further distilled to 70L, then heated to about 75°C, and slowly cooled to 0 to 5°C. The resulting slurry was filtered and the filter cake washed with a mixture of EtOAc (6.3Kg) and toluene (17.9Kg) before being dried in a vacuum oven to provide selinexor designated Lot No. 1305365 (Form A).
Example 2. Preparation of Selinexor Lot No.1341-AK-109-2 (Form A).
[00278] The acetonitrile solvate of selinexor was prepared in accordance with Example 6.
[00279] The acetonitrile solvate of selinexor (2.7g) was suspended in a mixture of isopropanol (IPA, 8mL) and water (8mL), and the resulting mixture heated to 65 to 70 °C to effect dissolution. The solution was cooled to 45 °C, and water (28mL) was added over 15 minutes, maintaining the temperature between 40 and 45 °C. The slurry was cooled to 20 to 25 °C over an hour, then further cooled to 0 to 5 °C and held at that temperature for 30 minutes before being filtered. The filter cake was washed with 20% v/v IPA in water and the product dried under suction overnight, then in vacuo (40°C).
Example 3. Preparation of SelinexorSelinexorSelinexor Lot No. PC-14-005 (Form A).
[00280] The acetonitrile solvate of selinexor (Form D) was prepared in accordance with the procedure described in Example 6.
[00281] The acetonitrile solvate of selinexor (1.07Kg) was suspended in a mixture of IPA (2.52Kg) and water (3.2Kg) and the mixture heated to 70 to 75 °C to dissolve. The temperature was then adjusted to 40 to 45 °C and held at that temperature for 30 minutes. Water (10.7Kg) was added while maintaining the temperature at 40 to 45 °C, then the batch was cooled to 20 to 25 °C and agitated at that temperature for 4 hours before being further cooled to 0 to 5 °C. After a further hour of agitation, the slurry was filtered and the filter cake washed with a cold mixture of IPA (0.84Kg) and water (4.28Kg) before being dried.
Example 4. Preparation of SelinexorSelinexorSelinexor Lot No. PC-14-009 (Form A).
[00282] The acetonitrile solvate of selinexor (Form D) was prepared in accordance with the procedure described in Example 6.
[00283] The acetonitrile solvate of selinexor (1.5Kg) was suspended in IPA (3.6Kg) and water (4.5Kg) and warmed to 37 to 42 °C with gentle agitation. The suspension was agitated at that temperature for 4 hours, and was then cooled to 15 to 20 °C over 1 hour. Water (15.1Kg) was added, maintaining the temperature, then the agitation was continued for 1 hour and the batch was filtered. The filter cake was washed with a mixture of IPA (1.2Kg) and water (6Kg), then dried under a flow of nitrogen.
Example 5. Preparation of Selinexor Lot Nos.1339-BS-142-1, 1339-BS-142-2 and PC-14-008 (Form A).
[00284] A reactor, under nitrogen, was charged with KG1 (1Kg, 1.0 Eq), KJ8 (0.439 Kg, 1.4 Eq) and MeTHF (7L, 7 parts with respect to KG1). Diisopropylethylamine (0.902Kg, 2.45 Eq with respect to KG1) was added to the reaction mixture at -20 °C to -25 °C with a MeTHF rinse. To the reaction mixture, 50% T3P® in ethyl acetate (2.174Kg, 1.2 Eq with respect to KG1) was then charged, maintaining the temperature at -20 °C to -25 °C with a MeTHF rinse. After the completion of the addition, the reaction mixture was stirred briefly
and then warmed to 20 °C to 25 °C. Upon completion, the reaction mixture was washed first with water (5L, 5 parts with respect to KG1) and then with dilute brine (5L, 5 parts with respect to KG1). The organic layer was concentrated by vacuum distillation to a volume of 5 L (5 parts with respect to KG1), diluted with acetonitrile (15L, 15 parts with respect to KG1) at approximately 40 °C and concentrated again (5L, 5 parts with respect to KG1). After solvent exchange to acetonitrile, the reaction mixture was then heated to approximately 60 °C to obtain a clear solution. The reaction mixture was then cooled slowly to 0-5 °C, held briefly and filtered. The filter cake was washed with cold acetonitrile (2L, 5 parts with respect to KG1) and the filter cake was then dried under a stream of nitrogen to provide the acetonitrile solvate of selinexor (Form D) as a slightly off-white solid.
[00285] Form D of selinexor (0.9Kg) was suspended in IPA (2.1Kg, 2.7L, 3 parts with respect to Form D) and water (2.7Kg, 2.7L, 3 parts with respect to Form D) and warmed to approximately 40 °C. The resulting suspension was agitated for about 4 hours, selinexor, cooled to approximately 20 °C, and diluted with additional water (9Kg, 10 parts with respect to Form D). The mixture was stirred for a further 4-6 hours, then filtered, and the cake washed with a mixture of 20% IPA and water (4.5L, 5 parts with respect to Form D). The filter cake was then dried under vacuum to provide selinexor designated Lot No. PC-14-008 as a white crystalline powder with a >99.5% a/a UPLC purity (a/a=area to area of all peaks; UPLC-ultra performance HPLC).
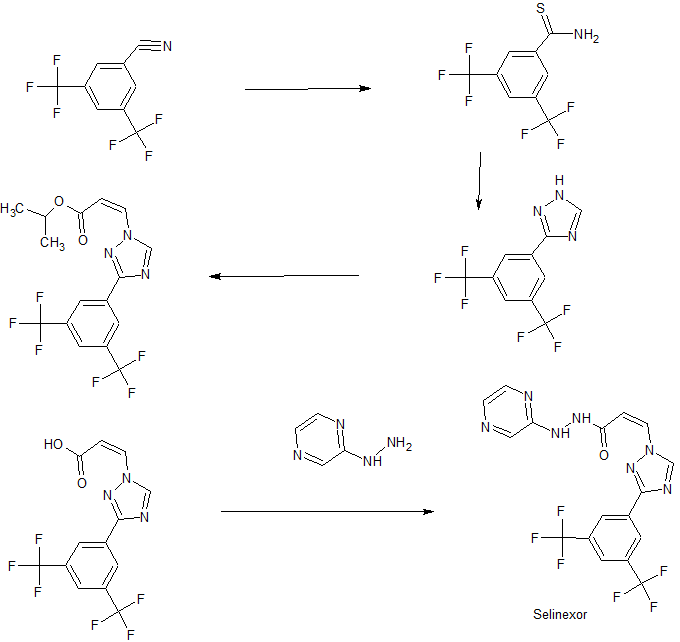
Example 6. Preparation of Selinexor Lot No.1405463 (Form A).
[00286] Selinexor Lot No. 1405463 was prepared in accordance with the following reaction scheme:
.
[00287] A reactor was charged with KG1 (15.8Kg), KJ8 (6.9Kg) and MeTHF (90Kg). Diisopropylethylamine (14.2Kg) was added to the reaction mixture over approximately 35 minutes at about -20 °C. Following the addition of the diisopropylethylamine, T3P® (50%
solution in EtAOc, 34.4Kg) was added maintaining the temperature at -20 °C. The mixture stirred to complete the reaction first at -20 °C, then at ambient temperature.
[00288] Upon completion of the reaction, water (79Kg) was added over about 1 hour. The layers were separated and the organic layer was washed with a mixture of water (55Kg) and brine (18Kg), The mixture was filtered, and the methyl-THF/ethyl acetate in the mixture distillatively replaced with acetonitrile (volume of approximately 220L). The mixture was warmed to dissolve the solids, then slowly cooled to 0 to 5 °C before being filtered. The filter cake was washed with acetonitrile to provide the acetonitrile solvate of
selinexorSelinexorSelinexor (Form D).
[00289] The acetonitrile solvate of selinexorSelinexorSelinexor was dried, then mixed with isopropanol (23Kg) and water (55Kg). The slurry was warmed to about 38 °C and held at that temperature for approximately 4 hours before being cooled to 15 to 20 °C. Water (182Kg) was added. After a further 5 hours of agitation, the mixture was filtered and the filter cake washed with a mixture of isopropanol (14Kg) and water (73Kg), before being dried under vacuum (45 °C). The dried product was packaged to provide
selinexorSelinexorSelinexor Lot No. 1405463 (Form A).
Example 7. Polymorphism Studies of Selinexor.
[00290] A comprehensive polymorphism assessment of selinexor was performed in a range of different solvents, solvent mixtures and under a number of experimental conditions based on the solubility of selinexor. Three anhydrous polymorphs of
selinexorSelinexorSelinexor were observed by XRPD investigation, designated Form A, Form B and Form C. Form A is a highly crystalline, high-melting form, having a melting point of 177 °C, and was observed to be stable from a physico-chemical point of view when exposed for 4 weeks to 25 °C/97% relative humidity (RH) and to 40 °C/75% RH. A solvated form of selinexor was also observed in acetonitrile, designated Form D. A competitive slurry experiment confirmed Form A as the stable anhydrous form under the conditions investigated, except in acetonitrile, in which solvate formation was observed. It was further found that in acetonitrile, below 50 °C, only Form D is observed, at 50 °C both Form A and Form D are observed, and at 55 °C, Form A is observed .
PATENT
CN 106831731
https://patents.google.com/patent/CN106831731A/en
Selinexor is an orally bioavailable selective nuclear export inhibitors, 2012 for the first time in clinical, so far carried out a total of 21 trials, indications include chronic myelogenous leukemia, acute myelogenous leukemia, acute lymphatic leukemia, prostate cancer, melanoma, non-small cell lung cancer, glioma, neuroblastoma into, gynecological cancer, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, squamous cell carcinoma, colorectal cancer and the like. May 2014, FDA granted orphan drug designation Selinexor treatment of acute myeloid leukemia and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, in June 2014, EMA is also granted orphan drug designation Selinexor treatment of both diseases. January 2015, received FDA orphan drug to treat multiple myeloma identified.
[0003] Currently, the synthesis process has been disclosed, the following reaction equation:
[0006] wherein the compound is 5 Selinexor drug.
[0007] In this method, however, easy to produce Intermediate 1-2 double bond is easily reversed when synthetically produced from trans impurities, in addition to more difficult to impact yield; Intermediate 3 Intermediate 4 Synthesis APIs 5 when required ultra-low temperature, and the product was purified by column required, only a yield of 20%.
SUMMARY
[0008] The object of the present invention to provide a novel compound Selinexor drug synthesis of 5, in order to solve technical problems.
[0009] – novel synthetic method of Se species I inexor drug, comprising the steps of:
Synthesis [0010] A, Compound 7
[0011] Compound 6, dichloromethane and ethyl acetate mixture, stirred and dissolved, compound 4, T3P (n-propyl phosphoric anhydride) and DIPEA (N, N- diisopropylethylamine) at a low temperature; the reaction was stirred for 25-35min at a low temperature, dichloromethane and water were added after the completion of the reaction, liquid separation, the organic phase was evaporated to dryness to give crude compound 7, crude without purification cast down;
[0012] B, Synthesis of Compound 8
[0013] the compound obtained in Step 7, and mixed sodium iodide acetic acid, warmed to 110-120 ° C, the reaction 2.5-3.5h; After completion of the reaction, the system cooled to room temperature, water and dichloromethane were added, stirred for 8 after -15min, standing layered organic phase was washed with saturated sodium bicarbonate and saturated sodium chloride, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and distilled to give crude compound 8, was dissolved in DMF (dimethyl fumarate) to give compound in DMF 8;
Synthesis [0014] C, of Compound 5
[0015] Compound 1, DBAC0 (triethylenediamine), the DMF mixed and dissolved with stirring, dropwise adding to the reaction system of the compound obtained in DMF step 8, after the addition was complete, stirring was continued for 3-4 hours; the reaction after completion, water and ethyl acetate were added to the system, the organic phase is evaporated to dryness and petroleum ether and recrystallized from ethyl acetate to give compound 5.
[0016] Preferably, said step A, the low temperature is 0-2 ° C.
[0017] Preferably, said step B in DMF, the crude compound 8 concentration of less than 1%.
[0018] The novel synthetic methods of the present invention Selinexor drug, the chemical equation is as follows:
〇
[0020] The present invention has the following advantages: novel synthetic method Selinexor drug of the present invention to overcome the conventional synthesis process, is easy to produce trans impurities, more difficult in addition, the influence the yield and the need for ultra-low temperature, and the product requires problems purified by column, the yield is very low, reducing the synthetic steps, increased yield, there is provided a new process for the synthesis of the drug Selinexor.
[0021] In addition to the above-described objects, features and advantages of the present invention as well as other objects, features and advantages. Below the invention will be described in further detail present.
Example 1
[0024] – novel synthetic method of Se species I inexor drug, comprising the steps of:
Synthesis [0025] A, Compound 7
[0026] 50ml three □ flask, 15ml of dichloromethane and 0.2g compound 6,15ml ethyl acetate, stirred and dissolved, was added 0.3g of compound 4 and 3gT3P, 0.75gDIPEA at 0 ° C; the system at 0 ° C the reaction was stirred for 30min, 50ml of dichloromethane and 30ml of water were added after the completion of the reaction, liquid separation, the organic phase was evaporated to dryness to give crude compound 7, crude without purification cast down;
[0027] B, Synthesis of Compound 8
[0028] 50ml three-necked flask, added the compound obtained in Step 7,40ml of glacial acetic acid and 1.38g of sodium iodide was heated to 115. (:, The reaction 3H; After completion of the reaction, cooled to room temperature system, the system will be transferred to 500ml flask, 50ml of water was added and IOOml dichloromethane, after stirring IOmin, standing separation, the organic phase was washed with saturated sodium bicarbonate and saturated washed with sodium chloride, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and distilled to give crude compound 8, was dissolved in IOmL DMF to give DMF solution of compound 8;
Synthesis [0029] C, of Compound 5
[0030] After 50ml 3-necked flask was added 0.2g compound 1,0.24gDBAC0,20mlDMF, dissolved with stirring, dropwise adding to the reaction system in DMF compound obtained in Step 8, after the addition was complete, stirring continued for 3.5 hours; after completion of the reaction, 20ml water was added to the system and 50ml ethyl acetate, the organic phase is evaporated to dryness and petroleum ether to ethyl acetate to give 0.158g of compound 5, yield 50.9%.
[0031] Example 2
[0032] – new type Se Iinexor drug synthesis, comprising the steps of:
Synthesis [0033] A, Compound 7
[0034] 50ml three □ flask, 15ml of dichloromethane and 0.2g compound 6,15ml ethyl acetate, stirred and dissolved, was added 0.3g of compound 4 and 3gT3P, 0.75gDIPEA at 1 ° C; system at 1 ° C the reaction was stirred for 35min, 50ml of dichloromethane and 30ml of water were added after the completion of the reaction, liquid separation, the organic phase was evaporated to dryness to give crude compound 7, crude without purification cast down;
[0035] B, Synthesis of Compound 8
Three-neck flask [0036] 50ml of addition of the compound obtained in Step 7,40ml glacial acetic acid and 1.38g of sodium iodide was heated to 120. (:, The reaction for 2.5 h; After completion of the reaction, cooled to room temperature system, the system will be transferred to 500ml flask, 60ml water and 120ml dichloromethane was added, after stirring for 15min, allowed to stand for separation, the organic phase was washed with saturated sodium bicarbonate and washed with saturated sodium chloride, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and distilled to give crude compound 8, 12mLDMF was dissolved in DMF to give a solution of compound 8;
Synthesis [0037] C, of Compound 5
[0038] After 50ml 3-necked flask was added 0.2g compound 1,0.24gDBAC0,20mlDMF, dissolved with stirring, dropwise adding to the reaction system of the compound obtained in DMF step 8, after the addition was complete, stirring continued for 3 hours; after completion of the reaction, 25ml of water and 50ml of ethyl acetate was added to the system, the organic phase is evaporated to dryness and petroleum ether to ethyl acetate to give 0.152g of compound 5, yield 49.0% billion
[0039] Example 3
[0040] – novel synthetic method of Se species I inexor drug, comprising the steps of:
Synthesis [0041] A, Compound 7
Three [0042] 50ml of flask, 15ml of dichloromethane and 0.2g compound 6,15ml ethyl acetate, stirred and dissolved, was added 0.3g of compound 4 and 3gT3P, 0.75gDIPEA at 2 ° C; system from 0 ° C the reaction was stirred for 25min, 40ml of dichloromethane and 35ml of water were added after the completion of the reaction, liquid separation, the organic phase was evaporated to dryness to give crude compound 7, crude without purification cast down;
[0043] B, Synthesis of Compound 8
Three-neck flask [0044] 50ml of addition of the compound obtained in Step 7,35ml glacial acetic acid and 1.38g of sodium iodide was heated to 110. (:, The reaction for 3.5 h; After completion of the reaction, cooled to room temperature system, the system will be transferred to 500ml flask, 50ml of water was added and dichloromethane IOOml After Smin of stirring, standing separation, the organic phase was washed with saturated sodium bicarbonate and washed with saturated sodium chloride, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and distilled to give crude compound 8, was dissolved in IOmL DMF to give DMF solution of compound 8;
Synthesis [0045] C, of Compound 5
[0046] 50ml three-neck flask was added 0.2g compound 1,0.24gDBA⑶, 20mlDMF, and dissolved with stirring, dropwise adding to the reaction system of the compound obtained in DMF step 8, after the addition was complete, stirring was continued for 4 hours; after completion of the reaction, 20ml of water and 40ml ethyl acetate were added to the system, the organic phase is evaporated to dryness and petroleum ether to ethyl acetate to give 0.155g of compound 5, yield 49.9% billion
PATENT
WO 2017118940
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=WO2017118940&tab=PCTDESCRIPTION
The drug compound having the adopted name “Selinexor” has chemical name:(Z)-3-(3-(3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-IH-l,2,4-triazol-1 -yl)-N’-(pyrazin-2yl) acrylohydrazide as below.
Selinexor (KPT-330) is a first-in-class, oral Selective Inhibitor of Nuclear Export / SINE™ compound. Selinexor functions by binding with and inhibiting the nuclear export protein XP01 (also called CRM1 ), leading to the accumulation of tumor suppressor proteins in the cell nucleus. This reinitiates and amplifies their tumor suppressor function and is believed to lead to the selective induction of apoptosis in cancer cells, while largely sparing normal cells. Over 1 ,200 patients have been treated with Selinexor in company and investigator-sponsored Phase 1 and Phase 2 clinical trials in advanced hematologic malignancies and solid tumors. Karyopharm has initiated four later-phase clinical trials of Selinexor, including one in older patients with acute myeloid leukemia (SOPRA), one in patients with Richter’s transformation (SIRRT), one in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (SADAL) and a single-arm trial of Selinexor and lose-dose dexamethasone in patients with multiple myeloma (STORM). Patients may receive a twice-weekly combination of Selinexor in combination with low dose dexamethasone. Randomized 1 :1 , Selinexor will be dosed either at 60mg + dexamethasone or at 100 mg + dexamethasone.
US 8999996 B2 discloses Selinexor and a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, pharmaceutical compositions and use for treating disorders associated with CRM1 activity. Further, it discloses preparative methods for the preparation of compounds disclosed therein including Selinexor by reacting (Z)-3-(3- (3,5-
bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-IH-l,2,4-triazol-l-yl)acrylic acid in 1 :1 CH2CI2: AcOEt with 2-Hydrazinopyrazine at -40 °C followed by addition of T3P[Propylphosphonic anhydride] (50%) and DIPEA. After 30 minutes, the reaction mixture was concentrated and the crude oil was purified by preparative TLC using 5% MeOH in CH2CI2 as mobile phase (under ammonia atmosphere) to afford 40 mg of Selinexor with purity: 95.78%. However, it is not disclosed about the nature of the compound obtained therein.
WO 2016025904 A1 discloses various crystalline forms of Selinexor namely Form A, Form B, Form C, Form D, compositions and MoU thereof for the treatment of disorder associated with CRM1 activity and their preparative processes.
Prior art process for the preparation of Selinexor suffers from disadvantages interms of process such as the use of lengthy procedures to practice and resulting in low yields, which may not be viable at industrial scale. Synthetic product obtained therein has very low purity and contains significant amounts of unreacted starting materials and trans-isomer of Selinexor, which are further purified by time consuming and expensive chromatographic separations leading to loss of yield. Hence, there remains a need for improved process for the preparation of Selinexor which is industrially viable and reproducible. Particularly, it is desirable to have a process avoiding purification steps still meeting desired pharmaceutical quality.
EXAMPLES
Example-1 : Preparation of isopropyl (Z)-3-(3-(3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl) phenyl)-1 H- -triazol-1 -yl)acrylate
3-(3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-1 H-1 ,2,4-triazole (250 g) was dissolved in tetrahydrofuran (2 I) under nitrogen atmosphere at 27°C and cooled to -5°C. 1 ,4- diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane (DABCO, 1 99.5 g) was added to the reaction mixture at -5°C and stirred at the same temperature for 40 minutes. Isopropyl (Z)-3- iodoacrylate (234.8 g in 500 mL of tetrahydrofuran) was added drop wise to the reaction mixture in 1 hour 1 0 minutes at -5°C and stirred at the same temperature for 2 hours. After the completion of the reaction, the reaction mixture was added to ice cold water (2 I) and separated the organic layer. The aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl acetate (2 x 1 I). The combined organic layer was washed with brine solution (1 I) and dried over sodium sulphate. The dried solution was evaporated completely under vacuum at 40°C to obtain crude product with HPLC purity of 93.53% The crude product was triturated with hexane (700 mL) and stirred for 20 minutes at -30°C and filtered the solid. Trituration of crude product with hexane was repeated for three times and dried under vacuum to obtain the title compound with HPLC purity of 97.46% and trans-isomer content of 0.66%. Yield: 297 g Example-2: Preparation of (Z)-3-(3-(3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-1 H-1 ,2,4- triazol-1 -yl)acr lic acid.
To a mixture of tetrahydrofuran (300 mL) and water (300 mL), Isopropyl (Z)-3-(3- (3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-1 H-1 ,2,4-triazol-1 -yl)acrylate (30 g) was added and cooled to 0°C. Lithium hydroxide monohydrate (16.03 g) under cooling condition at 0°C was added to the reaction mixture and stirred the reaction mixture at same temperature for 7 hours. After completion of the reaction, 2 N HCI (180 mL) was added to adjust the pH of the reaction mixture to 2 and extracted it with ethyl acetate (300 mL). Organic layer was dried over sodium sulphate and evaporated under vacuum at 40°C. The crude compound was stirred with hexane (150 mL) and filtered the solid. Dried the compound under vacuum at 40°C for 0.5 hour to obtain the title compound with HPLC purity of 97.25% with trans-isomer content of 3 %. Yield: 24 g
Example-3: Purification of (Z)-3-(3-(3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-1 H-1 ,2,4- tria
A mixture of (Z)-3-(3-(3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-1 H-1 ,2,4-triazol-1 -yl)acrylic acid (24 g) and acetone (240 mL) was stirred for complete dissolution at 30°C. Dicyclohexyl amine (1 5 mL) was added drop wise for 20 minutes under stirring at the same temperature. Acetone (50 mL) was added to the reaction mixture and stirred for 2 hours at 27°C. Filtered the solid and washed with hot acetone (150 mL) and dried in vacuum drier at 30°C for 1 hour to obtain the Dicyclohexyl amine salt of (Z)-3-(3-(3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-1 H-1 ,2,4-triazol-1 -yl)acrylic acid. To the above salt, dichloromethane (150 mL) and water (1 00 mL) was added and stirred for complete dissolution at 30and adjusted the pH of the solution with 2 N sulphuric acid (100 mL) to 2. Filtered the reaction mixture and washed the product with water (1 00 mL) and then with hexane (150 mL). The solid was dried under vacuum at 40°C for 0.5 hour to obtain title compound with HPLC purity 99.98% with no detectable content of trans-isomer. Yield: 17 g
Example-4: Preparation of Selinexor
(Z)-3-(3-(3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-1 H-1 ,2,4-triazol-1 -yl)acrylic acid (10 g) was combined with a mixture of acetonitrile (1 00 mL) and ethyl acetate (50 mL) then added the 2-hydrazinylpyrazine (3.76 g) and stirred for 5 min. Reaction mixture was cooled to 0°C and diisopropyl ethyl amine (16.63 ml) and then Propylphosphonic anhydride (T3P, 33.31 mL) was added at 0°C and stirred the reaction mixture for 2.5 hours at the same temperature. After completion of the reaction, the reaction mixture was quenched with cold water (100 mL) and extracted the product with ethyl acetate (2 x 150 mL). The combined organic layer was dried over sodium sulphate and evaporated the solvent under vacuum at 40°C to obtain the crude product as yellow syrup. The obtained crude product was combined with dichloromethane (1 00 mL) and filtered the solid and washed with dichloromethane (2 x 50 mL). The solid was dried under vacuum at 40°C to obtain the title compound with purity by HPLC of 99.86%. Yield : 7 g
PATENT
WO 2018129227
References
- ^ Jump up to:a b c d e Fung HY, Chook YM (2014). “Atomic basis of CRM1-cargo recognition, release and inhibition”. Semin Cancer Biol. 27: 52–61. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2014.03.002. PMC 4108548. PMID 24631835.
- ^ Jump up to:a b c d e f Gandhi UH, Senapedis W, Baloglu E, Unger TJ, Chari A, Vogl D; et al. (2018). “Clinical implications of targeting XPO1-mediated nuclear export in multiple myeloma”. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 18 (5): 335–345. doi:10.1016/j.clml.2018.03.003. PMID 29610030.
- ^ Jump up to:a b c d e Feuerstein, Adam (2019-07-03). “FDA approves new multiple myeloma drug despite toxicity concerns”. STAT. Retrieved 2019-07-06.
- ^ Jump up to:a b c Mulcahy, Nick (2019-07-03). “FDA Approves Selinexor for Refractory Multiple Myeloma”. Medscape. Retrieved 2019-07-06.
- ^ Jump up to:a b c Chim CS, Kumar SK, Orlowski RZ, Cook G, Richardson PG, Gertz MA; et al. (2018). “Management of relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma: novel agents, antibodies, immunotherapies and beyond”. Leukemia. 32 (2): 252–262. doi:10.1038/leu.2017.329. PMC 5808071. PMID 29257139.
- ^ Barrett, Jennifer (2019-07-03). “New Treatment for Refractory Multiple Myeloma Granted FDA Approval”. Pharmacy Times. Retrieved 2019-07-07.
- ^ Jump up to:a b c d e f g “XPOVIO Prescribing Information” (PDF). Newton, MA: Karyopharm Therapeutics. 2019-07-03. Retrieved 2019-07-06.
- ^ Jump up to:a b Chen C, Siegel D, Gutierrez M, Jacoby M, Hofmeister CC, Gabrail N (2018). “Safety and efficacy of selinexor in relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma and Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia”. Blood. 131 (8): 855–863. doi:10.1182/blood-2017-08-797886. PMID 29203585.
- ^ Jump up to:a b c d Parikh K, Cang S, Sekhri A, Liu D; et al. (2014). “Selective inhibitors of nuclear export (SINE)—a novel class of anti-cancer agents”. J Hematol Oncol. 7: 78. doi:10.1186/s13045-014-0078-0. PMC 4200201. PMID 25316614.
REFERENCES
1: Wang AY, Weiner H, Green M, Chang H, Fulton N, Larson RA, Odenike O, Artz AS, Bishop MR, Godley LA, Thirman MJ, Kosuri S, Churpek JE, Curran E, Pettit K, Stock W, Liu H. A phase I study of selinexor in combination with high-dose cytarabine and mitoxantrone for remission induction in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. J Hematol Oncol. 2018 Jan 5;11(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s13045-017-0550-8. PubMed PMID: 29304833.
2: Crochiere ML, Hannus S, Hansen K, Becker F, Baloglu E, Lee M, Kauffman M, Shacham S, Landesman Y. XPO1 target occupancy measurements confirm the selinexor recommended phase 2 dose. Oncotarget. 2017 Nov 30;8(66):110503-110516. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22801. eCollection 2017 Dec 15. PubMed PMID: 29299164; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC5746399.
3: Chim CS, Kumar SK, Orlowski RZ, Cook G, Richardson PG, Gertz MA, Giralt S, Mateos MV, Leleu X, Anderson KC. Management of relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma: novel agents, antibodies, immunotherapies and beyond. Leukemia. 2017 Jan 16. doi: 10.1038/leu.2017.329. [Epub ahead of print] Review. PubMed PMID: 29257139.
4: Bobillo S, Abrisqueta P, Carpio C, Raheja P, Castellví J, Crespo M, Bosch F. Promising activity of selinexor in the treatment of a patient with refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and central nervous system involvement. Haematologica. 2017 Dec 14. pii: haematol.2017.181636. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2017.181636. [Epub ahead of print] PubMed PMID: 29242296.
5: Chen C, Siegel D, Gutierrez M, Jacoby M, Hofmeister CC, Gabrail N, Baz R, Mau-Sorensen M, Berdeja JG, Savona M, Savoie L, Trudel S, Areethamsirikul N, Unger TJ, Rashal T, Hanke T, Kauffman M, Shacham S, Reece D. Safety and efficacy of selinexor in relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma and Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia. Blood. 2017 Dec 4. pii: blood-2017-08-797886. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-08-797886. [Epub ahead of print] PubMed PMID: 29203585.
6: Corno C, Stucchi S, De Cesare M, Carenini N, Stamatakos S, Ciusani E, Minoli L, Scanziani E, Argueta C, Landesman Y, Zaffaroni N, Gatti L, Perego P. FoxO-1 contributes to the efficacy of the combination of the XPO1 inhibitor selinexor and cisplatin in ovarian carcinoma preclinical models. Biochem Pharmacol. 2018 Jan;147:93-103. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2017.11.009. Epub 2017 Nov 16. PubMed PMID: 29155058.
7: Azmi AS, Li Y, Muqbil I, Aboukameel A, Senapedis W, Baloglu E, Landesman Y, Shacham S, Kauffman MG, Philip PA, Mohammad RM. Exportin 1 (XPO1) inhibition leads to restoration of tumor suppressor miR-145 and consequent suppression of pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and migration. Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 17;8(47):82144-82155. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.19285. eCollection 2017 Oct 10. PubMed PMID: 29137251; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC5669877.
8: Chen Y, Zhang L, Huang J, Hong X, Zhao J, Wang Z, Zhang K. Dasatinib and chemotherapy in a patient with early T-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia and NUP214-ABL1 fusion: A case report. Exp Ther Med. 2017 Nov;14(5):3979-3984. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.5046. Epub 2017 Aug 28. PubMed PMID: 29067094; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC5647690.
9: Body S, Esteve-Arenys A, Miloudi H, Recasens-Zorzo C, Tchakarska G, Moros A, Bustany S, Vidal-Crespo A, Rodriguez V, Lavigne R, Com E, Casanova I, Mangues R, Weigert O, Sanjuan-Pla A, Menéndez P, Marcq B, Picquenot JM, Pérez-Galán P, Jardin F, Roué G, Sola B. Cytoplasmic cyclin D1 controls the migration and invasiveness of mantle lymphoma cells. Sci Rep. 2017 Oct 24;7(1):13946. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-14222-1. PubMed PMID: 29066743; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC5654982.
10: Broccoli A, Argnani L, Zinzani PL. Peripheral T-cell lymphomas: Focusing on novel agents in relapsed and refractory disease. Cancer Treat Rev. 2017 Nov;60:120-129. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2017.09.002. Epub 2017 Sep 18. Review. PubMed PMID: 28946015.
11: Soung YH, Kashyap T, Nguyen T, Yadav G, Chang H, Landesman Y, Chung J. Selective Inhibitors of Nuclear Export (SINE) compounds block proliferation and migration of triple negative breast cancer cells by restoring expression of ARRDC3. Oncotarget. 2017 May 18;8(32):52935-52947. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17987. eCollection 2017 Aug 8. PubMed PMID: 28881784; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC5581083.
12: Garg M, Kanojia D, Mayakonda A, Ganesan TS, Sadhanandhan B, Suresh S, S S, Nagare RP, Said JW, Doan NB, Ding LW, Baloglu E, Shacham S, Kauffman M, Koeffler HP. Selinexor (KPT-330) has antitumor activity against anaplastic thyroid carcinoma in vitro and in vivo and enhances sensitivity to doxorubicin. Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 29;7(1):9749. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-10325-x. PubMed PMID: 28852098; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC5575339.
13: Conforti F, Zhang X, Rao G, De Pas T, Yonemori Y, Rodriguez JA, McCutcheon JN, Rahhal R, Alberobello AT, Wang Y, Zhang YW, Guha U, Giaccone G. Therapeutic Effects of XPO1 Inhibition in Thymic Epithelial Tumors. Cancer Res. 2017 Oct 15;77(20):5614-5627. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-1323. Epub 2017 Aug 17. PubMed PMID: 28819023.
14: Arango NP, Yuca E, Zhao M, Evans KW, Scott S, Kim C, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Janku F, Ueno NT, Tripathy D, Akcakanat A, Naing A, Meric-Bernstam F. Selinexor (KPT-330) demonstrates anti-tumor efficacy in preclinical models of triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2017 Aug 15;19(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s13058-017-0878-6. PubMed PMID: 28810913; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC5557476.
15: Schaffer M, Chaturvedi S, Davis C, Aquino R, Stepanchick E, Versele M, Liu Y, Yang J, Lu R, Balasubramanian S. Identification of potential ibrutinib combinations in hematological malignancies using a combination high-throughput screen. Leuk Lymphoma. 2017 Jul 28:1-10. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2017.1349899. [Epub ahead of print] PubMed PMID: 28750570.
16: Muz B, Azab F, de la Puente P, Landesman Y, Azab AK. Selinexor Overcomes Hypoxia-Induced Drug Resistance in Multiple Myeloma. Transl Oncol. 2017 Aug;10(4):632-640. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2017.04.010. Epub 2017 Jun 29. PubMed PMID: 28668761; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC5496204.
17: Gupta A, Saltarski JM, White MA, Scaglioni PP, Gerber DE. Therapeutic Targeting of Nuclear Export Inhibition in Lung Cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2017 Sep;12(9):1446-1450. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2017.06.013. Epub 2017 Jun 21. PubMed PMID: 28647672; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC5572747.
18: Machlus KR, Wu SK, Vijey P, Soussou TS, Liu ZJ, Shacham E, Unger TJ, Kashyap T, Klebanov B, Sola-Visner M, Crochiere M, Italiano JE Jr, Landesman Y. Selinexor-induced thrombocytopenia results from inhibition of thrombopoietin signaling in early megakaryopoiesis. Blood. 2017 Aug 31;130(9):1132-1143. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-11-752840. Epub 2017 Jun 19. PubMed PMID: 28630120; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC5580272.
19: Podar K, Pecherstorfer M. Current and developing synthetic pharmacotherapy for treating relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2017 Aug;18(11):1061-1079. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2017.1340942. Epub 2017 Jul 5. Review. PubMed PMID: 28604120.
20: Tandon N, Kumar SK. Highlights of Multiple Myeloma at the Annual Meeting of American Society of Hematology, 2016. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus. 2017 Jun;33(2):153-158. doi: 10.1007/s12288-017-0796-x. Epub 2017 Feb 28. Review. PubMed PMID: 28596644; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC5442069.
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Xpovio |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 95% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic oxidation, glucuronidation, and conjugation, by CYP3A4, UGTand GST |
| Elimination half-life | 6–8 h |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H11F6N7O |
| Molar mass | 443.313 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
Karyopharm’s Selinexor Receives Fast Track Designation from FDA for the Treatment of Patients with Penta-Refractory Multiple Myeloma
NEWTON, Mass., April 10, 2018 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) — Karyopharm Therapeutics Inc. (Nasdaq:KPTI), a clinical-stage pharmaceutical company, today announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted Fast Track designation to the Company’s lead, oral Selective Inhibitor of Nuclear Export (SINE) compound selinexor for the treatment of patients with multiple myeloma who have received at least three prior lines of therapy. The FDA’s statement, consistent with the design of Karyopharm’s Phase 2b STORM study, noted that the three prior lines of therapy include regimens comprised of an alkylating agent, a glucocorticoid, Velcade® (bortezomib), Kyprolis® (carfilzomib), Revlimid® (lenalidomide), Pomalyst® (pomalidomide) and Darzalex® (daratumumab). In addition, the patient’s disease must be refractory to at least one proteasome inhibitor (Velcade or Kyprolis), one immunomodulatory agent (Revlimid or Pomalyst), glucocorticoids and to Darzalex, as well as to the most recent therapy. The Company expects to report top-line data from the STORM study at the end of April 2018.
The FDA’s Fast Track program facilitates the development of drugs intended to treat serious conditions and that have the potential to address unmet medical needs. A drug program with Fast Track status is afforded greater access to the FDA for the purpose of expediting the drug’s development, review and potential approval. In addition, the Fast Track program allows for eligibility for Accelerated Approval and Priority Review, if relevant criteria are met, as well as for Rolling Review, which means that a drug company can submit completed sections of its New Drug Application (NDA) for review by FDA, rather than waiting until every section of the NDA is completed before the entire application can be submitted for review.
“The designation of Fast Track for selinexor represents important recognition by the FDA of the potential of this anti-cancer agent to address the significant unmet need in the treatment of patients with penta-refractory myeloma that has continued to progress despite available therapies,” said Sharon Shacham, PhD, MBA, Founder, President and Chief Scientific Officer of Karyopharm. “We are fully committed to working closely with the FDA as we continue development of this potential new, orally-administered treatment for patients who currently have no other treatment options of proven benefit.”
About the Phase 2b STORM Study
In the multi-center, single-arm Phase 2b STORM (Selinexor Treatment of Refractory Myeloma) study, approximately 122 patients with heavily pretreated, penta-refractory myeloma receive 80mg oral selinexor twice weekly in combination with 20mg low-dose dexamethasone, also dosed orally twice weekly. Patients with penta-refractory disease are those who have previously received an alkylating agent, a glucocorticoid, two immunomodulatory drugs (IMiDs) (Revlimid® (lenalidomide) and Pomalyst® (pomalidomide)), two proteasome inhibitors (PIs) (Velcade® (bortezomib) and Kyprolis® (carfilzomib)), and the anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody Darzalex® (daratumumab), and their disease is refractory to at least one PI, at least one IMiD, Darzalex, glucocorticoids and their most recent anti-myeloma therapy. Overall response rate is the primary endpoint of the study, with duration of response and clinical benefit rate being secondary endpoints. All responses will be adjudicated by an Independent Review Committee (IRC).
About Selinexor
Selinexor (KPT-330) is a first-in-class, oral Selective Inhibitor of Nuclear Export (SINE) compound. Selinexor functions by binding with and inhibiting the nuclear export protein XPO1 (also called CRM1), leading to the accumulation of tumor suppressor proteins in the cell nucleus. This reinitiates and amplifies their tumor suppressor function and is believed to lead to the selective induction of apoptosis in cancer cells, while largely sparing normal cells. To date, over 2,300 patients have been treated with selinexor, and it is currently being evaluated in several mid- and later-phase clinical trials across multiple cancer indications, including in multiple myeloma in a pivotal, randomized Phase 3 study in combination with Velcade® (bortezomib) and low-dose dexamethasone (BOSTON), in combination with low-dose dexamethasone (STORM) and as a potential backbone therapy in combination with approved therapies (STOMP), and in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (SADAL), and liposarcoma (SEAL), among others. Additional Phase 1, Phase 2 and Phase 3 studies are ongoing or currently planned, including multiple studies in combination with one or more approved therapies in a variety of tumor types to further inform Karyopharm’s clinical development priorities for selinexor. Additional clinical trial information for selinexor is available at www.clinicaltrials.gov.
About Karyopharm Therapeutics
Karyopharm Therapeutics Inc. (Nasdaq:KPTI) is a clinical-stage pharmaceutical company focused on the discovery, development and subsequent commercialization of novel first-in-class drugs directed against nuclear transport and related targets for the treatment of cancer and other major diseases. Karyopharm’s SINE compounds function by binding with and inhibiting the nuclear export protein XPO1 (or CRM1). In addition to single-agent and combination activity against a variety of human cancers, SINE compounds have also shown biological activity in models of neurodegeneration, inflammation, autoimmune disease, certain viruses and wound-healing. Karyopharm, which was founded by Dr. Sharon Shacham, currently has several investigational programs in clinical or preclinical development.
/////////Selinexor, FDA 2019, セリネクソル ,KPT-330, KPT 330 , KPT330, AML, Glioma, Sarcoma, Leukemia, Fast Track, CANCER