Synthesis of ureas in the bio-alternative solvent Cyrene
Green Chem., 2017, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C7GC00908A, Communication
DOI: 10.1039/C7GC00908A, Communication
Liam Mistry, Kopano Mapesa, Thomas W. Bousfield, Jason E. Camp
The bio-alternative solvent Cyrene was shown to be an alternative to toxic oil-derived solvents for the synthesis of ureas.
The bio-alternative solvent Cyrene was shown to be an alternative to toxic oil-derived solvents for the synthesis of ureas.
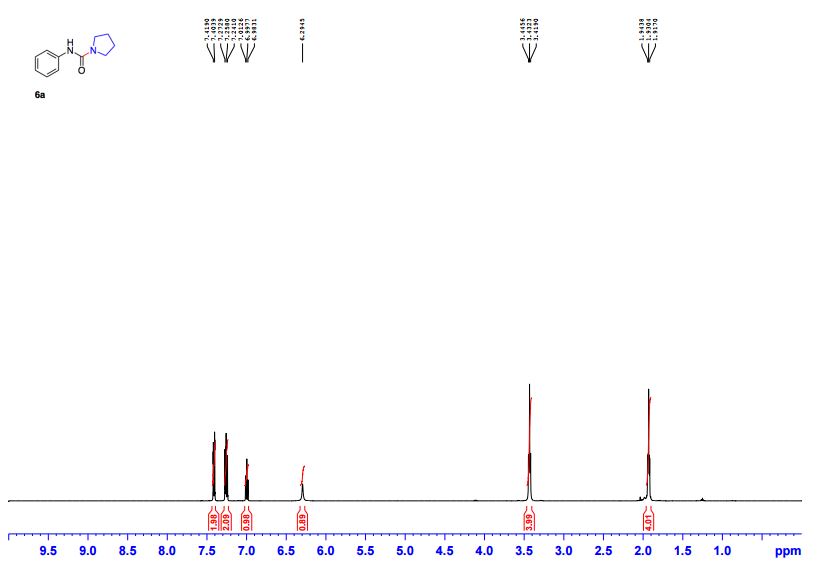
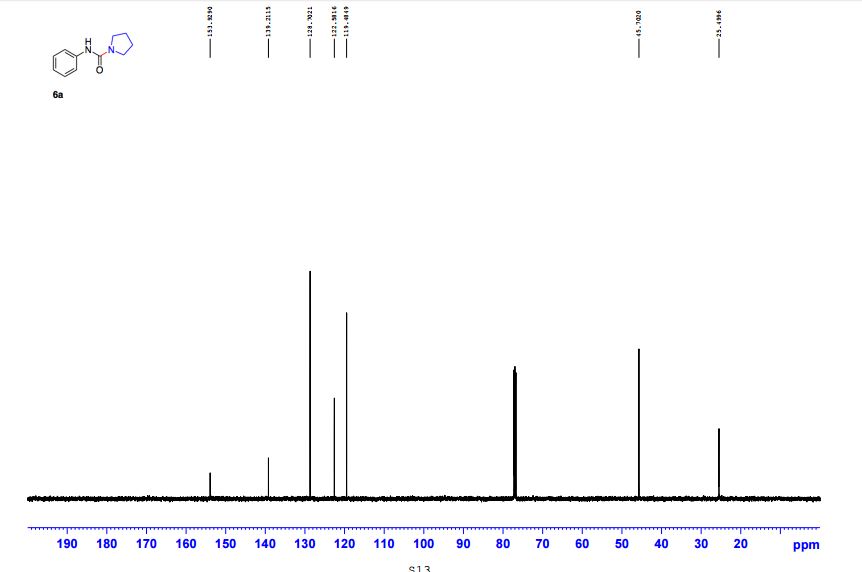
N-Phenylpyrrolidine-1-carboxamide (6a) 1
Method A: To a stirred solution of pyrrolidine (42 µL, 0.5 mmol) in Cyrene (0.5 mL, 1 M) at 0 °C was added phenyl isocyanate (4a, 55 µL, 0.5 mmol). The resultant mixture was allowed to warm to r.t. over 1 h. Water (5 mL) was added and the mixture was stirred for 30 min. The solvent was removed by Buchner filtration and the filtrate was washed with water (60 mL). The residue was dissolved in EtOAc (20 mL), dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure to give N-phenylpyrrolidine-1-carboxamide (6a, 76 mg, 80%), as a white solid.
Method B: To a stirred solution of pyrrolidine (42 µL, 0.5 mmol) in Cyrene (0.5 mL, 1 M) at 0 °C was added phenyl isocyanate (4a, 55 µL, 0.5 mmol). The resultant mixture was allowed to warm to r.t. over 1 h. Water (5 mL) was added and the mixture was stirred for 30 min. Water (25 mL) and EtOAc (25 mL) were added. The organic layer was dried over MgSO4 (10.0 g), filtered with the aid of EtOAc (10 mL). Silica gel (100 mg) was added and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by flash column chromatography on silica gel (100 g; EtOAc:hexane, 9:1) to to give N-phenylpyrrolidine-1- carboxamide (6a, 92 mg, 97%), as a white solid. mp. (o C) 133-134 [Lit.1 133-134];
IR (neat): 3292, 2971, 2871, 1639, 1532, 1438, 1373, 1239, 759 cm-1 ;
1 H NMR (CDCl3, 500 MHz) δ 1.92-1.94 (m, 4H), 3.42-3.45 (m, 4H), 6.29 (br. s, 1H), 6.98-7.01 (m, 1H), 7.24-2.28 (m, 2H), 7.40-7.42 (m, 2H);
13C NMR (CDCl3, 125 MHz) δ 25.5, 45.7, 119.5, 122.6, 128.7, 139.2, 153.9;
HRMS (ESI) m/z Calcd for [C11H15N2O] + 191.1184; found 191.1179.
Synthesis of ureas in the bio-alternative solvent Cyrene
Abstract
Cyrene as a bio-alternative solvent: a highly efficient, waste minimizing protocol for the synthesis of ureas from isocyanates and secondary amines in the bio-available solvent Cyrene is reported. This method eliminated the use of toxic solvents, such as DMF, and established a simple work-up procedure for removal of the Cyrene, which led to a 28-fold increase in molar efficiency versus industrial standard protocols.
. References 1 Y. Wei, J. Liu, S. Lin, H. Ding, F. Liang and B. Zhao, Org. Lett., 2010, 12, 4220-4223.
////////////