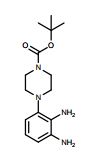
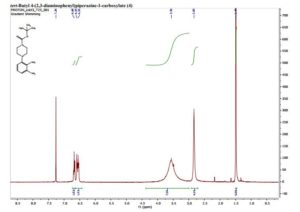
tert-Butyl 4-(2,3-diaminophenyl)piperazine-1- carboxylate (4)
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δ in ppm = 6.68 (t, 1H), 6.59 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 6.55 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 3.56 (br s, 8H), 2.83 (s, 4H), 1.49 (s, 9H). This is consistent with literature data.1
Abstract
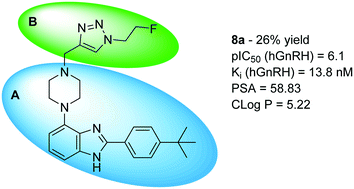
In this communication, we report the synthesis and characterization of a library of small molecule antagonists of the human gonadotropin releasing hormone receptor based upon the 2-(4-tert-butylphenyl)-4-piperazinyl-benzimidazole scaffold via Cu-catalysed azide alkyne cycloaddition. Our main purpose was to find a more soluble compound based on the WAY207024 lead with nanomolar potency to inhibit the GnRH receptor. A late stage diversification by the use of click chemistry was, furthermore developed to allow for expansion of the library in future optimisations. All compounds were tested in a functional assay to determine the individual potency of inhibiting stimulation of the receptor by the endogenous agonist GnRH. In conclusion, we found that compound 8ashowed improved solubility compared to WAY207024 and nanomolar affinity to GnRH receptor.
//////////////
References 1. Pelletier, J. C.; Chengalvala, M.; Cottom, J.; Feingold, I.; Garrick, L.; Green, D.; Hauze, D.; Huselton, C.; Jetter, J.; Kao, W.; Kopf, G. S.; Lundquist, J. T. t.; Mann, C.; Mehlmann, J.; Rogers, J.; Shanno, L.; Wrobel, J., 2-phenyl-4-piperazinylbenzimidazoles: orally active inhibitors of the gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) receptor. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry 2008, 16 (13), 6617-40.