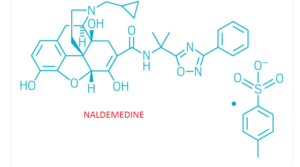
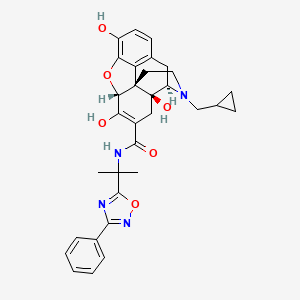
Naldemedine
- Molecular FormulaC32H34N4O6
- Average mass570.636 Da
| CAS Number |
|---|
FDA APPROVED 2017

Naldemedine (INN, USAN; S-297,995, Symproic) is a peripherally–selective μ-opioid receptor antagonist developed by Shionogi which is approved for the treatment of opioid-induced constipation in adult patients with chronic non-cancer pain.[1] Clinical studies have thus far found it to possess statistically significant effectiveness for these indications and to be generally well-tolerated with predominantly mild to moderate gastrointestinal side effects.[2][3] No effects indicative of central opioid withdrawal or impact on the analgesic or mydriatic effects of co-administered opioids have been observed.[2]


ナルデメジントシル酸塩
Commercialization
Naldemedine is manufactured by Shionogi Inc., a U.S. based subsidiary of Shionogi & Co., Ltd. Shionogi & Co., Ltd. (SGIOF) is a Japanese pharmaceutical company founded in 1878 based in Osaka, Japan. Shionogi Inc. is fully funded by its parent company, Shionogi & Co., Ltd. The parent company specializes in pharmaceuticals, diagnostic reagents and medical devices in Japan and internationally. Naldemedine is their only gastroenterology product in the United States.
In the US market, Shionogi Inc. has partnered with Purdue Pharma in a joint venture for US commercialization of Symproic.[4] Purdue Pharma LP is a privately held pharmaceutical company based in the United States that specializes in chronic pain disorders.[5]
Purdue Pharma appealed to remove the Class II scheduling of Symproic as accordant to the Controlled Substances Act. The appeal was posted to the Federal Register on July 12, 2017.[6] The Drug Enforcement Administration officially removed the Class II scheduling in September 2017.[7]
SYN
US 8084460
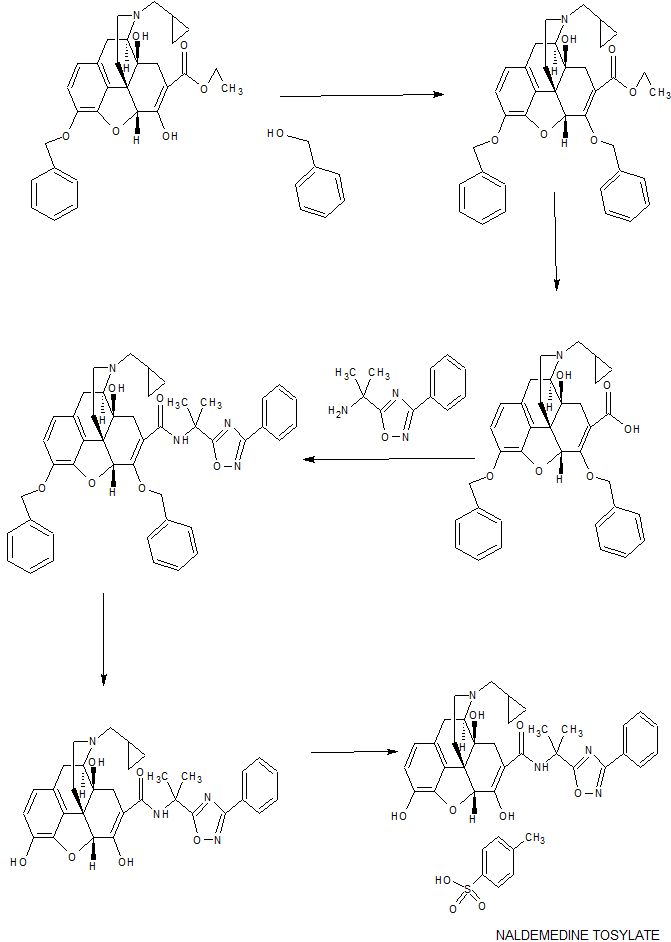
WO 2012063933

Manufacturer Finances
Since 2015, Shionogi & Co., Ltd. has produced increasing net income. At the end of fiscal year 2016, Shionogi & Co., Ltd. had a net income of $66,687,000. At the end of fiscal year 2017, they increased their net income to $83,879,000.[8] How much of this is attributed to sales of Symproic is unknown. Shionogi & Co., Ltd. ends their fiscal year on March 31 of each year. Considering the drug was only FDA approved on March 23 of 2017, the true valuation of the drug is yet to be seen. Purdue Pharma has begun advertising for the medication to be available by October 2017.[9]
Intellectual Property
There are currently three patents issued for naldemedine tosylate by the United States Patent and Trademark Office. All patents are owned by Shionogi Inc. and will expire from 2026-2031.[10] Naldemedine tosylate has 46 other patents in 18 different countries.[11]
Preclinical Trials
12 Phase I clinical trials were reported for the use of naldemedine in healthy volunteers.[12] In a single ascending dose study, subjects received one dose of naldemedine (0.1–100 mg) or one dose of a placebo. In a multiple ascending dose study, subjects received once daily naldemedine (3–30 mg) or placebo for 10 days. Maximum plasma concentrations were reached within 0.5-0.75 hours. There were no reported major safety concerns, even at doses 150-500 times the available dose of 0.2 mg. In both studies, gastrointestinal events occurred more frequently with naldemedine, but researchers concluded these to be treatment related.[13]
Clinical Trials
The approval of naldemedine came from the results of the COMPOSE program, a phase three clinical studies program conducted in adults 18–80 years of age with chronic non-cancer pain opioid induced constipation. COMPOSE-I and COMPOSE-II were 12-week double blind randomized controlled trials comparing the use of naldemedine to placebo in the patient population. COMPOSE-I began in August 2013 until January 2015 in 68 outpatient clinic in seven countries. COMPOSE-II began in November 2013 until June 2015 taking place in 69 outpatient clinics in six countries. In both trials, patients were randomly assigned to receive either naldemedine 0.2 mg or placebo once daily for 12 weeks. A responder had at least three spontaneous bowel movements per week with an increase of one spontaneous bowel movement for nine of the 12 weeks, including three of the final four weeks of the study. In COMPOSE-I and COMPOSE-II, the proportion of responders were significantly higher in the naldemedine group than the placebo group. Adverse events were similar in both trials, however, patients in the naldemedine group had slightly higher rates of adverse events.[14]
COMPOSE-III was a 52 week clinical trial examining the long term safety with naldemedine in patients with non cancer chronic pain. Results from this trial showed statistical significance for increased weekly bowel movements and no opioid withdrawal symptoms. The study also concluded adverse effects were more similar between two groups.[12]
All trials were conducted following Good Clinical Practice guidelines.[12]
FDA Orange Book Patents
| FDA Orange Book Patents: 1 of 3 (FDA Orange Book Patent ID) | |
|---|---|
| Patent | 9108975 |
| Expiration | Nov 11, 2031 |
| Applicant | SHIONOGI INC |
| Drug Application | N208854 (Prescription Drug: SYMPROIC. Ingredients: NALDEMEDINE TOSYLATE) |
| FDA Orange Book Patents: 2 of 3 (FDA Orange Book Patent ID) | |
|---|---|
| Patent | RE46375 |
| Expiration | Oct 5, 2026 |
| Applicant | SHIONOGI INC |
| Drug Application | N208854 (Prescription Drug: SYMPROIC. Ingredients: NALDEMEDINE TOSYLATE) |
| FDA Orange Book Patents: 3 of 3 (FDA Orange Book Patent ID) | |
|---|---|
| Patent | RE46365 |
| Expiration | Jan 11, 2028 |
| Applicant | SHIONOGI INC |
| Drug Application | N208854 (Prescription Drug: SYMPROIC. Ingredients: NALDEMEDINE TOSYLATE) |
References
- Jump up^ “FDA Approves Symproic (naldemedine) for the Treatment of Opioid-Induced Constipation – Chemdiv”. Chemdiv. 2017-03-27. Retrieved 2017-04-05.
- ^ Jump up to:a b De Sarro, Giovambattista; Kelly S. Sprawls; Egilius L.H. Spierings; Dustin Tran (2012-03-07). “Drugs in Development for Opioid-Induced Constipation” (PDF). In Catto-Smith G., Anthony. Constipation – Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment. p. 7. doi:10.5772/30377. ISBN 978-953-51-0237-3. Retrieved 12 May 2012.
- Jump up^ Shionogi (2009-03-27). “Research and Development at Shionogi (as of March 2009)”(PDF). Retrieved 2012-05-12.
- Jump up^ “SHIONOGI AND PURDUE PHARMA ESTABLISH ALLIANCE FOR JOINT U.S. COMMERCIALIZATION OF NALDEMEDINE”. Purdue Pharma. Purdue Pharma. Retrieved 31 October 2017.
- Jump up^ “FDA Approves Symproic® (naldemedine) Once-Daily Tablets C-II for the Treatment of Opioid-Induced Constipation in Adults with Chronic Non-Cancer Pain”. Purdue Pharma. Purdue Pharma. Retrieved 31 October 2017.
- Jump up^ “Schedules of controlled substances: removal of naldemedine from control” (PDF). Federal Register. Federal Register. Retrieved 1 November 2017.
- Jump up^ “Symproic Now Available for Opioid-Induced Constipation”. MPR. 2017-10-12. Retrieved 2017-11-08.
- Jump up^ “Shionogi & Co., Ltd”. Yahoo Finance. Yahoo Finance. Retrieved 31 October 2017.
- Jump up^ “Opioid Induced Constipation”. Opioid Induced Constipation. Purdue Pharma. Retrieved 31 October 2017.
- Jump up^ “Generic Symproic Availability”. Drugs.com. Drugs.com. Retrieved 31 October 2017.
- Jump up^ “Naldemedine tosylate – generic drug details”. Drug Patent Watch. Drug Patent Watch. Retrieved 31 October 2017.
- ^ Jump up to:a b c “Center for Drug Evaluaiton and Research Medication Review” (PDF). FDA. FDA. Retrieved 31 October 2017.
- Jump up^ Fukumura, K; Yokota, T; Baba, Y; Arjona Ferreira, JC (27 September 2017). “Phase 1, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Studies on the Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of Naldemedine in Healthy Volunteers”. Clinical pharmacology in drug development. doi:10.1002/cpdd.387. PMID 28960888.
- Jump up^ Hale, M; Wild, J; Reddy, J; Yamada, T; Arjona Ferreira, JC (August 2017). “Naldemedine versus placebo for opioid-induced constipation (COMPOSE-1 and COMPOSE-2): two multicentre, phase 3, double-blind, randomised, parallel-group trials”. The Lancet. Gastroenterology & Hepatology. 2 (8): 555–564. doi:10.1016/S2468-1253(17)30105-X. PMID 28576452.
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C32H34N4O6 |
| Molar mass | 570.63556 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
//////////S-297995, Naldemedine, FDA 2017, ナルデメジントシル酸塩 , Symproic
CC(C)(C1=NC(=NO1)C2=CC=CC=C2)NC(=O)C3=C(C4C56CCN(C(C5(C3)O)CC7=C6C(=C(C=C7)O)O4)CC8CC8)O