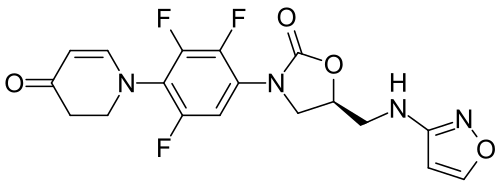

Contezolid
- MRX-I
- 1112968-42-9
- MRX-1
- B669M62ELP
- (5S)-5-[(1,2-oxazol-3-ylamino)methyl]-3-[2,3,5-trifluoro-4-(4-oxo-2,3-dihydropyridin-1-yl)phenyl]-1,3-oxazolidin-2-one
- 4(1H)-Pyridinone, 2,3-dihydro-1-(2,3,6-trifluoro-4-((5S)-5-((3-isoxazolylamino)methyl)-2-oxo-3-oxazolidinyl)phenyl)-
- (5S)-5-[(1,2-oxazol-3-ylamino)methyl]-3-[2,3,5-trifluoro-4-(4-oxo-2,3-dihydropyridin-1-yl)phenyl]-1,3-oxazolidin-2-one
- 4(1H)-Pyridinone, 2,3-dihydro-1-[2,3,6-trifluoro-4-[(5S)-5-[(3-isoxazolylamino)methyl]-2-oxo-3-oxazolidinyl]phenyl]-
- 1-{2,3,6-trifluoro-4-[(5S)-5-{[(1,2-oxazol-3-yl)amino]methyl}-2-oxo-1,3-oxazolidin-3-yl]phenyl}-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyridin-4-one
- 5-((isoxazol-3-ylamino)methyl)-3-(2,3,5-trifluoro-4-(4-oxo-3,4-dihydropyridin-1(2H)-yl)phenyl)oxazolidin-2-one
- コンテゾリド;
WeightAverage: 408.337
Monoisotopic: 408.104539468
Chemical FormulaC18H15F3N4O4
Shanghai MicuRx Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd
Contezolid was approved for use by the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) of China in 2021
- OriginatorMicuRx Pharmaceuticals
- ClassAntibacterials; Oxazolidinones; Skin disorder therapies
- Mechanism of ActionProtein synthesis inhibitors
- Phase IIIDiabetic foot; Skin and soft tissue infections
- No development reportedGram-positive infections
- 28 Jan 2025No recent reports of development identified for phase-I development in Gram-positive-infections(In volunteers) in China (IV)
- 28 Jan 2025No recent reports of development identified for phase-I development in Gram-positive-infections(In volunteers) in China (PO)
- 29 Nov 2024Phase-III clinical trials in Skin and soft tissue infections in China (IV), prior to November 2024
Contezolid (trade name Youxitai) is an antibiotic of the oxazolidinone class.[1][2] It is effective against Staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus agalactiae, and other bacteria.[3]
In 2021, it was approved by the National Medical Products Administration of China for the treatment of complicated skin and soft tissue infections (cSSTI).[3][4]
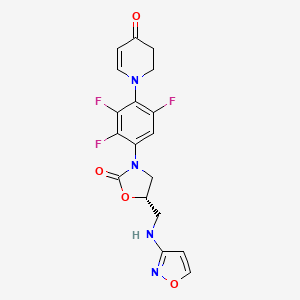
A prodrug of contezolid, contezolid acefosamil, which is formulated for IV administration[5] is in Phase III clinical trials for diabetic foot infection.[6]

Chemical structure of contezolid acefosamil
SYN
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acsmedchemlett.2c00191
Abstract

New oral antibiotic contezolid (CZD) is effective against Gram-positive infections but unsuitable for intravenous (IV) administration due to its modest solubility. To address the medical need for an IV form of CZD, its isoxazol-3-yl phosphoramidate derivatives have been explored, and contezolid acefosamil (CZA, 8), the first representative of a novel O-acyl phosphoramidate prodrug class, has been identified. CZA exhibits high aqueous solubility (>200 mg/mL) and good hydrolytic stability at media pH suitable for IV administration. CZA rapidly converts into the active drug CZD in vivo. In a pharmacokinetic (PK) rat model, the exposure of active drug CZD after IV administration of the prodrug CZA was similar to or higher than that from the IV administration of CZD. The prodrug CZA is bioequivalent to or better than CZD in several preclinical infection models. CZA is likewise active upon its oral administration. To date, CZA has been evaluated in Phase 1 and Phase 2 clinical trials in the USA. It is advancing into further clinical studies including step-down therapy with in-hospital intravenous CZA administration followed by outpatient oral CZD treatment.
SYN
Contezolid (Youxitai). Contezolid (4), also referred to as MRX-I, is an orally administered oxazolidinone
antibacterial agent developed by Shanghai MicuRx Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. Contezolid was developed to overcome the myelosuppression and monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibition limitations of the structurally similar linezolid. 32 Contezolid is used to treat complicated skin and soft tissue infections arising
from multidrug-resistant Gram-positive bacterial infections including methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA), methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus agalactiae, and vancomycin-resistant enterococci.3334 Contezolid was approved for use by the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) of China in 2021.
As with most antibacterial oral therapies, high 35 dosage is required; the drug is given twice daily for 7−14 days.36,37
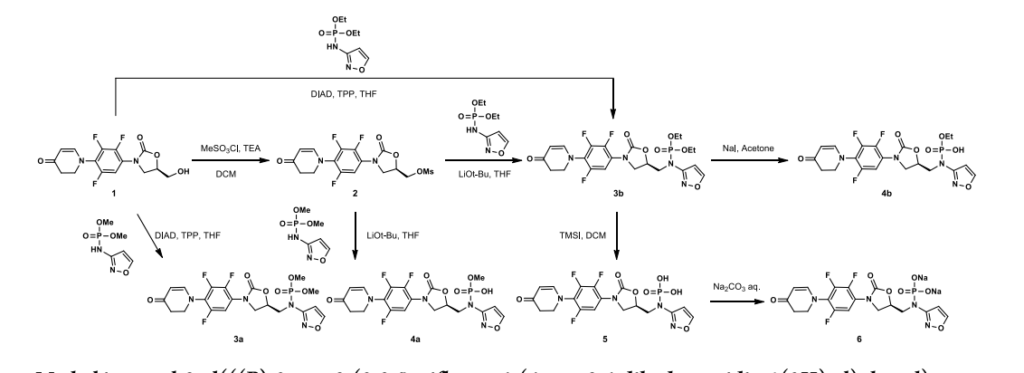
The synthesis of contezolid builds on prior research from other groups.
A sequence developed by Pharmaciawith a facile SN38began Ar reaction between polyfluorinated nitro
benzene 4.1 and piperidine-4-one 4.2 to furnish 4.3 in good yield (Scheme 9). Silyl enol ether formation afforded 4.4, which was subjected to Tsuji’s 39 method to give the α,βunsaturated ketone in excellent yield. Subsequent reduction of the nitro group gave aryl amine 4.5. Treatment of 4.5 with isobutyl chloroformate gave carbamate 4.6, which was treated with optically pure epoxide 4.7 to give xazolidinone 4.8. 38Mesylation of the free alcohol and displacement with N-Bocaminoisoxazole 4.9 afforded the Boc-protected contezolid 4.10. Simple acidic removal of the Boc group provided contezolid 4.
(32) Wang, W.; Voss, K. M.; Liu, J.; Gordeev, M. F. Nonclinical
evaluation of antibacterial oxazolidinones contezolid and contezolid
acefosamil with low serotonergic neurotoxicity. Chem. Res. Toxicol.
2021, 34, 1348−1354.
(33) Hoy, S. M. Contezolid: First approval. Drugs 2021, 81, 1587−
1591.
(34) MicuRx Pharmaceuticals. China NMPA approves MicuRx’s
contezolid for treatment of drug-resistant bacterial infection. http://www.
micurx.com/703.html (accessed 2023-06).
(35) MSD Pharmaceuticals. Usual dosages of commonly prescribed
antibiotics. https://www.msdmanuals.com/en-jp/professional/
multimedia/table/usual-dosages-of-commonly-prescribed-antibioticsa
(accessed 2023-06).
(36) Barbachyn, M. R.; Hutchinson, D. K.; Brickner, S. J.; Cynamon,
M. H.; Kilburn, J. O.; Klemens, S. P.; Glickman, S. E.; Grega, K. C.;
Hendges, S. K.; Toops, D. S.; et al. Identification of a novel
oxazolidinone (U-100480) with potent antimycobacterial activity. J.
Med. Chem. 1996, 39, 680−685.
(37) Im, W. B.; Choi, S. H.; Park, J. Y.; Choi, S. H.; Finn, J.; Yoon, S.
H. Discovery of torezolid as a novel 5-hydroxymethyl-oxazolidinone
antibacterial agent. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 1027−1039.
(38) Manninen, P. R.; Brickner, S. J. Preparation of N-aryl-5R
hydroxymethyl-2-oxazolidinones from N-aryl carbamates: N-phenyl
(5R)-hydroxymethyl-2-oxazolidinone. Organic Synth 2005, 81, 112.
(39) Tsuji, J.; Minami, I.; Shimizu, I. A novel palladium-catalyzed
preparative method of α,β-unsaturated ketones and aldehydes from
saturated ketones and aldehydes via their silyl enol ethers. Tetrahedron
Lett. 1983, 24, 5635−5638.




AS ON JUNE2025 4.45 LAKHS VIEWS ON BLOG WORLDREACH AVAILABLEFOR YOUR ADVERTISEMENT

join me on Linkedin
Anthony Melvin Crasto Ph.D – India | LinkedIn
join me on Researchgate
RESEARCHGATE

join me on Facebook
Anthony Melvin Crasto Dr. | Facebook
join me on twitter
Anthony Melvin Crasto Dr. | twitter
+919321316780 call whatsaapp
EMAIL. amcrasto@gmail.com

……
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Youxitai |
| Other names | MRX-I |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | Rx in China |
| Identifiers | |
| IUPAC name | |
| CAS Number | 1112968-42-9 |
| PubChem CID | 25184541 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 10795 |
| DrugBank | DB12796 |
| ChemSpider | 34217570 |
| UNII | B669M62ELP |
| KEGG | D11297 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL3287379 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DTXSID901353186 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H15F3N4O4 |
| Molar mass | 408.337 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | Interactive image |
| SMILES | |
| InChI | |
References
- Gordeev MF, Yuan ZY (June 2014). “New Potent Antibacterial Oxazolidinone (MRX-I) with an Improved Class Safety Profile”. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 57 (11): 4487–4497. doi:10.1021/jm401931e. PMID 24694071.
- Zhao X, Huang H, Yuan H, Yuan Z, Zhang Y (May 2022). “A Phase III multicentre, randomized, double-blind trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of oral contezolid versus linezolid in adults with complicated skin and soft tissue infections”. The Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. 77 (6): 1762–1769. doi:10.1093/jac/dkac073. PMID 35265985.
- Hoy SM (September 2021). “Contezolid: First Approval”. Drugs. 81 (13): 1587–1591. doi:10.1007/s40265-021-01576-0. PMC 8536612. PMID 34365606.
- Mak E (3 June 2021). “Micurx wins China approval for antibacterial contezolid”. BioWorld.
- Liu J, Wang W, Wang C, Zhang L, Zhang X, Liu S, et al. (July 2022). “Discovery of Antibacterial Contezolid Acefosamil: Innovative O-Acyl Phosphoramidate Prodrug for IV and Oral Therapies”. ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 13 (7): 1030–1035. doi:10.1021/acsmedchemlett.2c00191. PMC 9290071. PMID 35859881.
- “Contezolid acefosamil by MicuRx Pharmaceuticals for Diabetic Foot Infection (DFI): Likelihood of Approval”. GlobalData. 31 May 2023 – via Pharmaceutical Technology.
/////////Contezolid, CHINA 2021, APPROVALS 2021, MRX-I, 1112968-42-9, MRX 1, B669M62ELP, コンテゾリド ,














