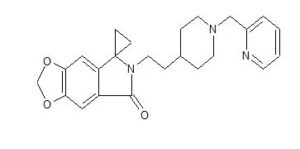
AD 35
IND-120499
MF C24 H27 N3 O3
- Molecular Weight, 405.49
- Spiro[cyclopropane-1,5′-[5H-1,3]dioxolo[4,5-f]isoindol]-7′(6′H)-one, 6′-[2-[1-(2-pyridinylmethyl)-4-piperidinyl]ethyl]-
6′-[2-[1-(2-Pyridinylmethyl)-4-piperidinyl]ethyl]spiro[cyclopropane-1,5′-[5H-1,3]dioxolo[4,5-f]isoindol]-7′(6’H)-one
1531586-58-9 CAS FREE FORM
1531586-64-7 PHOSPHATE
1531586-62-5 HYDROCHLORIDE
Zhejiang Hisun Pharmaceutical Co Ltd

AD-35 is known to be a neuroprotectant, useful for treating Alzheimer’s diseases.
Zhejiang Hisun Pharmaceutical is developing an oral tablet formulation of AD-35, for treating Alzheimers disease . By August 2017, the phase I multiple doses trial had been completed in the US and would be completed in China soon

CAS 1531586-64-7 PHOSPHATE
6′-[2-[1-(Pyridin-2-ylmethyl)piperidin-4-yl]ethyl]spiro[cyclopropane-1,5′-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-f]isoindol]-7′(6’H)-one phosphate
| Molecular Formula |
C24 H27 N3 O3 . H3 O4 P |
| Molecular Weight |
503.4847 |

With the rapid growth of the elderly population, the number of people suffering from Alzheimer’s disease (Alzheimer’s disease) also will be increased dramatically.Alzheimer’s disease is also known as Alzheimer-type dementia (Alzheimer type dementia), or the Alzheimer type senile dementia (senile dementia of the Alzheimer type). At present, although the prevalence of this disease on a global scale is still unknown, but according to the latest report from the US Alzheimer’s Association (the Alzheimer’s Association), and in 2011 the United States there are about 540 million people suffer from Alcatel the number of Alzheimer’s disease, and in 2050, in the United States suffering from the disease will increase to about 13.5 million. Therefore, the development of better efficacy and fewer side effects of new drugs to treat the disease it is a priority.
Alzheimer’s disease is the most common form of senile dementia, it has become the sixth leading cause of death of Americans, and 65 years and the fifth leading cause of death in Americans over 65 years. Although scientists have this disease carried out extensive and in-depth research, but so far, the exact cause of the disease remains unclear. Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive disease that continues to kill nerve cells, destroying nerve connections in the brain, resulting in brain tissue is damaged, leading to patients gradually lose memory, consciousness and judgment, and cause mood disorders and behavioral disorders in patients.
Alzheimer’s is an irreversible disease, and now there is no any drug can prevent the disease, and no drugs can cure the disease or slow the disease process. Drugs currently used to treat the disease can only alleviate or ameliorate symptoms of the disease. These drugs are FDA approved for use in the United States a total of five, four of which are acetylcholinesterase (acetylcholinesterase) inhibitors. Acetylcholine (acetylcholine) is a neurotransmitter, a chemical released by nerves, if produced in the brain acetylcholine system, i.e. damaged cholinergic system, it can result in associated with Alzheimer’s disease memory disorders; and acetylcholinesterase function is to catalyze the hydrolysis of acetylcholine, acetylcholine is decomposed. Because Alzheimer’s disease is accompanied
Attenuation of acetylcholine activity, thus inhibiting acetylcholinesterase is one way to treat this disease. As described above, in the present 5 treatment of Alzheimer’s disease drugs in clinical use, there are four acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, including acetylcholinesterase inhibitors such as donepezil (donepezil), tacrine (tacrine ), rivastigmine (rivastigmine), and galantamine (galantamine), wherein donepezil (Sugimoto et al US4895841 and 5100901;.. Pathi et al WO 2007077443;. Parthasaradhi et al WO 2005003092;. Dubey et al WO 2005076749; Gutman . et al WO 200009483;… Sugimoto et al J. Med Chem 1995, 38, 481) is a first-line treatment of Alzheimer’s disease drugs. However, donepezil and the other four drugs can only improve the patient’s symptoms, and this is the only improvement of symptoms is short, only lasting about 6-12 months, and the patient response rates to these drugs only about 50% (Alzheimer’s Association, 201 1 Alzheimer ‘Disease Facts and Figures, Alzheimer’s & Dementia, 201 1, 7 (2), 208). The present invention provides a new class of inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase, which is dioxole between a new class of derivatives of benzo, is more effective than donepezil and fewer side effects in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease drug.
PATENT
WO 2014005421
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=WO2014005421&recNum=1&maxRec=&office=&prevFilter=&sortOption=&queryString=&tab=PCTDescription
Example 42: 6- [2- [l- (2-Pyridylmethyl) -4-piperidinyl] ethyl] spiro [[1,3] dioxolo [4,5-f ] Isoindole-7, Γ-cyclopropane-5-one (Compound No. 1-29)

To the reaction flask was added 24.3 g (0.069 mol) of compound 11-5, 36.5 g (0.26 mol) of potassium carbonate, 243 ml of ethanol, 6.1 ml (0.044 mole) of triethylamine, heated to about 50 ° C, 0.049 mol) of 2-chloromethylpyridine hydrochloride was maintained at about 50 ° C for 5 hours. The reaction was complete and 750 ml of water was added. The solid was precipitated, filtered and the cake was washed with water and dried to give 17.8 g of compound 1-29. Rate: 63.4%. ‘HNMR (CDC13 . 3 ): [delta] 1.26 (dd, 2H, J = 6.1, 7.6 Hz), 1.35 (brs,. 3 H), 1.49-1.57 (m, 4H), 1.72 (D, 2H, J = 8.6Hz) (T, 2H, J = 7.9 Hz), 3.64 (s, 2H), 6.03 (s, 2H), 2.09 (t, 2H, J = 10.4 Hz), 2.89 (d, 2H, J = 10.7 Hz) , 7.42 (s, 1 H), 7.15 (dd, 1 H, J = 5.2, 6.7 Hz), 7.24 (s, 1 H), 7.41 (d, 1 H, J = 7.7 Hz), 7.64 (td, H, J = 7.6, 1.8 Hz), 8.55 (D,. 1 H, J = 4.2 Hz); the MS (ESI): m / Z 406 [m + H] + .
Example 46: 6- [2- [l- (2-Pyridylmethyl) -4-piperidinyl] ethyl] spiro [[1,3] dioxolo [4,5-f ] Isoindole-7, Γ-cyclopropane] -5-one hydrochloride (Compound No. 1-33)

To the reaction flask was added 5 g (0.012 mol) of compound 1-29 and 25 ml of ethanol, heated at 50 ° C
(0.012 mol) of concentrated hydrochloric acid was added, and 1 g of activated charcoal was added to decolorize for 20 minutes. The filtrate was cooled to room temperature and 50 ml of isopropyl ether was added dropwise. The solid was precipitated, stirred for 1 hour, The ether cake was washed with ether and dried to give 5 g of compound 1-33 in a yield of 91.7%. Ethanol / isopropyl ether can be re-refined, the yield of about 90%. 1H-NMR is (D 2 0): 51.14 (T, 2 H, J-7.0 Hz), 1.38-1.70 (m,. 7 H), 1.96 (D, 2H, J = 13.3 Hz), 2.99-3.14 (m, H. 4 ), 3.50 (d, 2 H, J = 11.0 Hz), 4.37 (s, 2H), 5.93 (s, 2H), 6.28 (s, 1 H), 6.75 (s, 1 H), 7.47 (dd, J = 7.8, 1.7 Hz), 8.58 (d, 1 H, J = 4.4 Hz), 7.55 (d, 1 H, J = 7.8 Hz), 7.91 (td, ; MS (ESI): m / z 406 [M-Cl] & lt; + & gt ; .
Example 48: 6- [2- [l- (2-Pyridylmethyl) -4-piperidinyl] ethyl] spiro [[1,3] dioxolo [4,5-f ] Isoindole-7, Γ-cyclopropan-5-one phosphate (Compound I-3S)

To the reaction flask was added 2 g (0.0049 mole) of compound 1-29 and 40 ml of ethanol, stirred at 60 ° C until all dissolved, 0.57 g (0.0049 mole) of 85% phosphoric acid was added, stirred and solidified,
Liter of ethyl acetate, cooled to room temperature, stirred for 1 hour, filtered, and a small amount of ethyl acetate was used to wash the filter cake and dried to give 2.1 g of compound 1-35 in a yield of 84.7%. 1H-NMR (D 2 0): δ 1.10 (t, 2 H, J = 7.2 Hz), 1.33-1.64 (m, 7 H), 1.92 (d, 2 H, J = 13.4 Hz), 2.95-3.09 (m, (S, 1 H), 6.69 (s, 1 H), 7.45 (s, 2 H), 4.34 (s, (d, 1 H, J-7.8 Hz), 7.88 (td, 1 H, J = 7.7, 1.2 Hz), 8.54 (d, 1 H, J = 4.6 Hz).
PATENT
CN 103524515
https://encrypted.google.com/patents/CN103524515B?cl=en
PATENT
CN 105859732
https://www.google.com/patents/CN105859732A?cl=en
Example 14: 6- [2- [l_ (2- pyridylmethyl) -4-piperidinyl] ethyl] spiro [[1,3] dioxolo [4,5 -f] isoindole-7, prepared Γ- cyclopropane] phosphate 5-one (compound I) is
[0146] Compound was added 2g (4.9 mmol) of formula XI to the reaction flask 50mL, 40mL of ethanol, 60 ~ 70 ° C dissolved by heating, added with stirring square. 57g 85% (4.9mmol) phosphoric acid, and the precipitated solid was added dropwise 40mL of acetic acid ethyl cooled to room temperature, stirred for 1 hour, filtered, the filter cake washed with a small amount of ethyl acetate, dried to give 2.3g white solid (compound I, HPLC purity: 99.8%). Yield: 92.7%, H bandit R (D2O): δ1 · l〇 (t, 2H, J = 7.2Hz), 1.33-1.64 (m, 7H), 1.92 (d, 2H, J = 13.4Hz), 2.95 -3.09 (m, 4H), 3.46 (d, 2H, J = 10.7Hz), 4.34 (s, 2H), 5.89 (s, 2H), 6.20 (s, 1H), 6.69 (s, 1H), 7.45 ( , 7.53 (d, lH, J 7.8Hz dd, lH, J = 5.2,7.4Hz) =), 7.88 (td, lH, J =
PATENT
WO 2017177816
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=WO2017177816&recNum=1&maxRec=&office=&prevFilter=&sortOption=&queryString=&tab=FullText
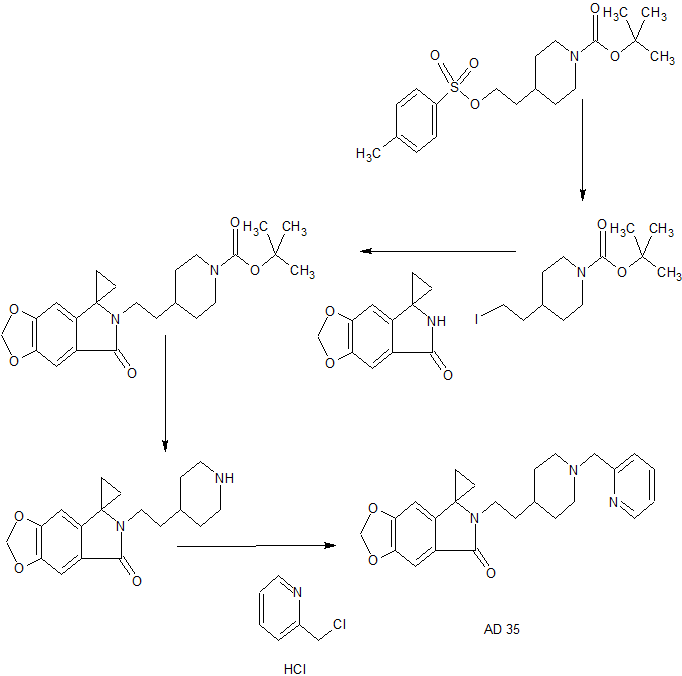
Process for preparing AD-35 and its intermediates – comprising the reaction of a cyano ester with a Grignard reagent, followed by condensation and further manipulative steps.
A novel intermediate of AD-35 is claimed. Also claimed is a processes for preparing 6,7-dihydro-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-f]isoindol-5-one comprising the reaction of a cyano ester compound in an isopropyl ester (Ti(i-Pr)4)) with a Grignard reagent in the presence of an ethyl magnesium halide. Further claimed are processes for preparing synthon of intermediates. A process for preparing a benzodioxole derivative, particularly AD-35 from intermediates is also claimed.
WO2014005421 reports a class of benzodioxole compounds, which have the activity to inhibit acetylcholinesterase and can be used to treat Alzheimer’s disease. Of these compounds, it is particularly noteworthy that 6- [2- [1- (2-pyridylmethyl) -4-piperidinyl] ethyl] spiro [[1,3] dioxole And [4,5-f] isoindole-7,1′-cyclopropane] -5-one phosphate, codon AD-35, whose chemical structure is as follows:
AD-35 is a weaker acetylcholinesterase inhibitor that inhibits acetylcholinesterase activity in vitro is about one tenth of the activity of donepezil, but the compound exhibits comparable efficacy with donepezil in the Morris water maze test , That is, the effect of improving memory and learning ability is comparable to donepezil. This suggests that the AD-35 is likely to also have the effect of improving memory and learning through other mechanisms in the body. A further study of the rat model of Alzheimer’s disease induced by Aβ 25-35 found that AD-35 significantly inhibited the production and release of proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-1β, Small Aβ 25-35 on the nerve cell toxicity, effectively protect the nerve cells.
In addition, AD-35 also exhibits a certain ability to chelate transition metal ions such as Cu 2+ in vitro , while Cu 2+ accelerates the formation of Aβ fibers and enhances the toxicity of Aβ to neuronal cells, thereby promoting neuronal cell death , So excessive Cu 2+ in the brain is also considered to be one of the risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease (Sarell et al. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285 (53), 41533). From the chemical structure point of view, AD-35 molecules in the piperidine ring and pyridine ring on the two nitrogen atoms constitute a structural unit similar to ethylenediamine, which should be able to explain why this compound to a certain extent Chelating transition metal ions. In terms of the safety of the compounds, the acute toxicity of mice showed that the toxicity of AD-35 was much less than that of donepezil. A newly completed clinical single-dose incremental tolerance test (SAD) showed that the subjects taking 90 mg of AD-35 did not have any adverse effects at once, indicating that the compound was safe.
In summary, the AD-35 is promising to be a small side-effect drug for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, and its multiple mechanisms of action are likely to make this compound not only alleviate the symptoms of Alzheimer’s patients , And can delay the process of the disease.
Since the synthesis route of AD-35 and its analogs reported in WO2014005421 is too long, the operation is complicated and the yield is low, and some steps are not suitable for industrial production. Therefore, it is necessary to develop a new process route to overcome the above- Preparation method.
The preferred reaction conditions of the present invention are listed in the following schemes:
Specific implementation plan
The following examples are provided for the purpose of further illustrating the invention, but this is not intended to be limiting of the invention.
Reference Example 1: Preparation of the starting material of tert-butyl 4- [2- (p-toluenesulfonyloxy) ethyl] piperidine-1-carboxylate (Formula VIa)
[0104]
To a 10 L reaction flask was added 800 g (3.49 mol) of tert-butyl 4- (2-hydroxyethyl) piperidine-1-carboxylate, 5 L of dichloromethane, 974 ml of (6.75 mol) of triethylamine and 16 g of 4-dimethyl (3L × 3), the organic phase was collected, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and the reaction mixture was washed with anhydrous sodium sulfate , Filtered and the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure to give 1360.3 g of compound VIa (HPLC purity: 85%). 1 H NMR (DMSO-d 6 ): δ 0.85-0.93 (m, 2H), 1.38 (s, 9H), 1.42-1.52 (m, 5H), 2.43 (s, 3H), 2.59 (br s, 2H (D, 2H, J = 11.3 Hz), 4.05 (t, 2H, J = 6.1 Hz), 7.50 (d, 2H, J = 8.1 Hz), 7.79 (d, 2H, J = 8.3 Hz) MS (ESI): m / z 383 [M + Na] & lt; + & gt ; .
Reference Example 2: Preparation of the starting material 4- (2-iodoethyl) piperidine-1-carboxylate (Formula VIb)
To a 50 mL reaction flask was added 5 g (13.0 mmol) of tert-butyl 4- [2- (p-toluenesulfonyloxy) ethyl] piperidine-1-carboxylate (Formula VIa), 35 mL of acetone and 2.9 g (19.3 mmol The organic phase was washed with 50 mL of water. The organic phase was collected and the aqueous phase was extracted again with 50 mL of ethyl acetate. The organic phase was washed with 50 mL of water and extracted with 50 mL of water and 50 mL of water. The organic phases were combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered and the filtrate was concentrated to dryness to give 3.5 g of compound VIb in a yield of 79.5%. 1 H NMR (DMSO-d 6 ): δ 0.97-1.07 (m, 2H), 1.41 (s, 9H), 1.51-1.58 (m, 1H), 1.63-1.66 (m, 2H), 1.73-1.78 (m, 2H), 2.69 (br s, 2H), 3.31 (t, 2H, J = 7.3Hz), 3.96 (d, 2H, J = 10.3Hz); MS (ESI): m / + H] + .
Example 1: Preparation of 6-bromo-1,3-benzodioxole-5-carboxylic acid (Compound II)
To the 2L reaction flask, 100 g (0.60 mol) of piperine, 29 g (0.725 mol) of sodium hydroxide and 1 L of water were successively added, and 150 g (0.84 mol) of N-bromosuccinimide was added thereto, After the reaction was carried out for 45 min, the reaction was monitored by TLC. The reaction solution was concentrated dropwise with concentrated hydrochloric acid to adjust the pH of the reaction solution to 2 to 3, and the solid was precipitated. The ice was cooled, filtered and washed with water to obtain 117.4 g of compound II (HPLC purity: 82%), Yield 79.5%. 1 H NMR (DMSO-d 6 ): δ 6.15 (s, 2H), 7.30 (s, 1H), 7.32 (s, 1H), 13.17 (s, 1H).
Example 2: Preparation of 6-bromo-1,3-benzodioxole-5-carboxylic acid (Compound II)
To the 2L reaction flask, 100 g (0.60 mol) of piperine, 29 g (0.725 mol) of sodium hydroxide and 1 L of water were successively added, and 150 g (0.84 mol) of N-bromosuccinimide was added thereto, After the reaction was complete for 45 min, the reaction was monitored by TLC. After 1 L of ethyl acetate and 40 mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid were added, the mixture was stirred for 20 min. The organic phase was collected, concentrated to dryness, 200 mL of water and 600 mL of petroleum ether, stirred for 1 h, , And 116 g of compound II (HPLC purity: 92.0%) was dried to a yield of 78.9%. & Lt; 1 & gt ; H NMR data with Example 1.
Example 3: Preparation of ethyl 6-bromo-1,3-benzodioxole-5-carboxylate (Compound IIIa)
To a 2 L reaction flask was added 117.3 g (0.39 mol) of 6-bromo-1,3-benzodioxole-5-carboxylic acid (II), 585 mL of absolute ethanol, opened with a stirrer, (1.4mol) concentrated sulfuric acid, heating reflux reaction 6h, TLC monitoring reaction is completed. Water was added dropwise, and 1.2 L of water was added dropwise to remove the solid, filtered and washed with water, and dried at 35 to 45C to obtain 124.0 g of compound IIIa (HPLC purity: 85%) in a yield of 93.9%. . 1 H NMR (CDCl3 . 3 ): [delta] 1.39 (T, 3H, J = 7.1Hz), 4.34 (Q, 2H, J = 7.1Hz), 6.04 (S, 2H), 7.07 (S, IH), 7.31 ( s, 1H).
Example 4: Preparation of methyl 6-bromo-1,3-benzodioxole-5-carboxylate (Compound IIIb)
To a 1 L reaction flask was added 50 g (0.30 mol) of 6-bromo-1,3-benzodioxole-5-carboxylic acid (II), 500 mL of anhydrous methanol, opened with a stirrer, 33.3 mL (0.60 mol) of concentrated sulfuric acid was added dropwise and heated under reflux for 6 h. TLC test reaction is completed, ice water cooling, precipitation of solids, dropping 500mL of water, filtration, water washing filter cake, 45 ~ 55 ℃ drying 44.4 g compound IIIb, yield: 84.0%. 1 H NMR (DMSO-d 6 ): δ 3.83 (s, 3H), 6.19 (s, 2H), 7.35 (s, 1H), 7.36 (s, 1H).
Example 5: Preparation of 6-cyano-1,3-benzodioxole-5-carboxylate (Compound IVa)
To a 2 L reaction flask was charged 124 g (0.38 mol) of ethyl 6-bromo-1,3-benzodioxole-5-carboxylate (IIIa), 990 mL of N, N-dimethylformamide, After opening the stirrer, 33.1 g (0.09 mol) of potassium ferrocyanide and 103.3 g (0.54 mol) of cuprous iodide were added, heated to 120-140C for 5 h, and the TLC reaction was completed. Cooling, dropping water to precipitate a solid, filtering, and washing the filter cake. The filter cake was stirred in 1.9 L of dichloromethane for 30 min, filtered, the filtrate was added with 9 g of activated charcoal, decolorized for 30 min, filtered and the filtrate was concentrated to a small amount. The solid was precipitated, n-hexane was added dropwise, cooled with ice water, filtered and dried to give 82.8 g of compound IVa (HPLC purity: 99.5%), yield: 83.2%. . 1 H NMR (DMSO-D . 6 ): [delta] 1.34 (T, 3H, J = 7.1Hz), 4.33 (Q, 2H, J = 7.1Hz), 6.29 (S, 2H), 7.51 (S, IH), 7.57 (s, 1H).
Example 6: Preparation of 6-cyano-1,3-benzodioxole-5-carboxylate (Compound IVa)
To a 50 mL reaction flask was added 3.5 g (12.8 mmol) of ethyl 6-bromo-1,3-benzodioxole-5-carboxylate (IIIa), 35 mL of N, N-dimethylformamide , 2.3g (25.7mmol) cuprous cyanide, open stirring, 120 ~ 140 ℃ reaction 30 ~ 60min, TLC detection reaction is completed, cooling, dropping 30mL saturated ammonium chloride aqueous solution, precipitate solid, filter, water washing cake. The filter cake was dissolved in 200 mL of ethyl acetate and washed with saturated aqueous ammonium chloride (30 ml x 2 times). The organic phase was collected and the aqueous phase was extracted again with 100 ml of ethyl acetate. The combined organic phases were dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered , And concentrated to give 2.0 g of compound IVa in a yield of 62.5%. & Lt; 1 & gt ; H NMR data with Example 5.
Example 7: Preparation of 6-cyano-1,3-benzodioxole-5-carboxylate (Compound IVb)
To a 1 L reaction flask was added 40 g (0.15 mol) of methyl 6-bromo-1,3-benzodioxole-5-carboxylate (IIIb), 11.4 g (31.0 mmol) of potassium ferrocyanide , 35.2 g (0.18 mol) of cuprous iodide, 240 mL of N, N-dimethylacetamide, 120 to 140 ° C in an oil bath for 2 to 3 hours, and the TLC reaction was completed. After cooling, 480 mL of water was added dropwise, Ice water cooling, filtration, water washing filter cake. Filter cake was dissolved in 500mL ethyl acetate and 200mL tetrahydrofuran mixture, heated to 80 ℃, adding 2g activated carbon, filtered, the filtrate was concentrated to a small amount, precipitation of solid, dropping 200mL petroleum ether, ice water cooling, filtration, petroleum ether washing filter The cake was dried to give 27.7 g of compound IVb in a yield of 87.6%. 1 H NMR (DMSO-d 6 ): δ 3.87 (s, 3H), 6.28 (s, 2H), 7.49 (s, 1H), 7.55 (s, 1H).
Example 8: Preparation of Spiro [6H- [1,3] dioxolo [4,5-f] isoindole-7,1′-cyclopropane] -5-one (Compound V)
To a 2 L reaction flask was added 16 g (0.072 mol) of compound of formula IVa, 160 mL of dichloromethane, stirred and dissolved under nitrogen. 24 mL (0.080 mol) of isopropyl tetrafis (4) isopropyl ether was added and cooled to 0 to 20 ° C A solution of 73 mL (0.22 mol) of ethylmagnesium bromide in diethyl ether (3M) was added and the reaction was complete after TLC. Slowly drop the water / tetrahydrofuran solution (64 mL water / 240 mL tetrahydrofuran), heat to 50 ° C, decalcinate with 2 g of activated charcoal and stir for 20 min. Filtration, ethyl acetate washing filter residue, the filtrate 40 ~ 50 ° C concentrated under reduced pressure, add 96mL ethyl acetate and 96mL water, stirring solid precipitation, dropping 290mL n-hexane, ice water cooling, filtration, n-hexane washing cake, Dried to give 11.9 g of compound V (HPLC purity: 70%) in a yield of 80.2%. 1 H NMR (DMSO-d 6 ): δ 1.33-1.41 (m, 4H), 6.11 (s, 2H), 6.86 (s, 1H), 7.09 (s, 1H), 8.53 (s, 1H).
Example 9: Preparation of Spiro [6H- [1,3] dioxolo [4,5-f] isoindole-7,1′-cyclopropane] -5-one (Compound V)
To a 500 mL reaction flask was added 10 g (48.8 mmol) of 6-cyano-1,3-benzodioxole-5-carboxylate (IVb), 200 mL of methyl tert-butyl ether, (50.7 mmol) of (IV) isopropyl ester was cooled to 0 to 20 ° C, and 49 mL (0.15 mol) of ethyl magnesium bromide in diethyl ether (3M) was slowly added dropwise. After completion of the drop, the TLC reaction was completed. (10 mL x 2 times), the organic phase was collected and the aqueous phase was extracted again with 100 mL of ethyl acetate. The organic phases were combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and the activated charcoal was dried over 100 mL of ethyl acetate and extracted with 250 mL of ethyl acetate. Decolorization, filtration, the filtrate was concentrated to a small amount, dropping petroleum ether, ice water cooling, filtration, petroleum ether washing cake, drying 2.3g compound V, yield: 23.2%. & Lt; 1 & gt ; H NMR data with Example 8.
Example 10: 4- [2- (5-oxospiro [[1,3] dioxolo [4,5-f] isoindole-7,1′-cyclopropane] -6 Yl) ethyl] piperidine-1-carboxylate (Compound VIIa)
To a 250 mL reaction flask was added 11.9 g (0.041 mol) of compound of formula V, 84 mL of dimethylsulfoxide, 4 g (0.071 mol) of potassium hydroxide, 27.3 g (0.06 mol) of 4- [2- (p-toluenesulfonyloxy ) Ethyl] piperidine-1-carboxylate (Formula VIa), heated to 55-65 ° C for 3 to 4 hours, and the TLC reaction was completed. (150 mL x 2 times), the aqueous phase was extracted again with 200 mL of ethyl acetate, the organic phase was combined, and 3 g of activated charcoal was added to decolorize, stirred for 30 min, filtered, and the mixture was washed with 300 mL of ethyl acetate. The filtrate was concentrated to dryness under reduced pressure to give compound VIIa. 1 H NMR (CDCl 3 ): δ 1.08-1.19 (m, 2H), 1.28 (dd, 2H, J = 6.2, 7.4 Hz), 1.45 (s, 9H), 1.48-1.57 (m, 5H) (d, 2H, J = 12.7 Hz), 2.69 (t, 2H, J = 11.6 Hz), 3.20 (t, 2H, J = 7.6 Hz), 4.07 (d, 2H, J = 13.1 Hz) , 2H), 6.43 (S, IH), 7.23 (S, IH); the MS (ESI): m / Z 437 [m + of Na] + .
Example 11: 4- [2- (5-oxospiro [[1,3] dioxolo [4,5-f] isoindole-7,1′-cyclopropane] -6 Yl) ethyl] piperidine-1-carboxylate (Compound VIIa)
To a 250 mL reaction flask, 6.7 g (33.0 mmol) of compound of formula V, 100 mL of N, N-dimethylformamide, 2.6 g (65.0 mmol) of sodium hydroxide, 14 g (41.3 mmol) of 4- (2-iodoethyl ) Piperidine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester (VIb), 25-30 ° C for 1.5 h, TLC detection reaction was completed, 100 mL of water and 100 mL of ethyl acetate were added and the organic phase was washed with water (50 mL x 2 times) The organic phase was collected and the aqueous phase was extracted again with 100 mL of ethyl acetate. The organic phases were combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered and the filtrate was concentrated to dryness to give compound VIIa. & Lt; 1 & gt ; H NMR data with Example 10.
Example 12: 6- [2- (4-Piperidine) ethyl] spiro [[l, 3] dioxolo [4,5-f] isoindole- Propane] -5-one hydrochloride (Compound VIIIa)
To a 100 mL reaction flask was added the compound of formula VIIa obtained in Example 10, 30 mL of ethanol, 45 mL of ethyl acetate, 10.5 mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid. Open the stirrer, 50 ~ 60 ℃ reaction 3h, TLC detection reaction is completed, stop heating, ice water cooling, filtration, ethyl acetate detergent cake, drying, 8.5g off-white solid (compound VIIIa, HPLC purity: 97%) The Yield: 41.4% (calculated based on the amount of compound V in Example 10). 1 H NMR (D 2 O): δ 1.06 (t, 2H, J = 6.7Hz), 1.32-1.46 (m, 6H), 1.60 (m, 1H), 1.91 (d, 2H, J = 13.5Hz) (M, 4H), 3.39 (d, 2H, J = 12.8 Hz), 5.90 (s, 2H), 6.18 (s, 1H), 6.68 (s, 1H); MS (ESI): m / z 315 [M-Cl] + .
Example 13: 6- [2- [1- (2-Pyridylmethyl) -4-piperidinyl] ethyl] spiro [[1,3] dioxolo [4,5-f ] Isoindole-7,1′-cyclopropane] -5-one (Compound XI)
A solution of 128.6 g (0.35 mol) of the compound of formula VIIIa, 90 g (0.54 mol) of 2-chloromethylpyridine hydrochloride (formula IXa), 965 mL of water, 26 g of activated carbon and 60 to 65C for 30 minutes were charged into a 2 L reaction flask, , And the residue was washed with 643 ml of water and 215 mL of ethanol. The solution was slowly added with 161 g (1.16 mol) of potassium carbonate. The reaction was carried out at 55 to 65 ° C for 4 to 5 hours. After completion of the TLC reaction, the reaction was cooled, filtered and dried to obtain 137 g of crude The crude product was dissolved in 1.37L ethanol and dissolved at 60-65 ° C. After decontamination with activated charcoal (27.4 g / times x 2 times), 4.11 L of water was added dropwise with stirring, the solid was precipitated, the ice was cooled, filtered, And dried to give 118.9 g of compound XI in 80% yield. 1 H NMR (CDCl 3 ): δ 1.26 (dd, 2H, J = 6.1, 7.6 Hz), 1.35 (br s, 3H), 1.49-1.57 (m, 4H), 1.72 (d, 2H, J = 8.6 (T, 2H, J = 7.9 Hz), 3.64 (s, 2H), 6.03 (s, & lt; RTI ID = 0.0 & gt; 2H), 6.42 (s, 1H), 7.15 (dd, 1H, J = 5.2, 6.7 Hz), 7.24 (s, 1H), 7.41 (d, 1H, J = 7.7 Hz), 7.64 (td, 7.6, 1.8 Hz =), 8.55 (D, IH, J = 4.2Hz); the MS (ESI): m / Z 406 [m + H] + .
Example 14: 6- [2- [1- (2-Pyridylmethyl) -4-piperidinyl] ethyl] spiro [[1,3] dioxolo [4,5-f ] Isoindole-7,1′-cyclopropane] -5-one phosphate (Compound I)
To a 50 mL reaction flask was added 2 g (4.9 mmol) of the compound of formula XI, 40 mL of ethanol, dissolved at 60-70 ° C and 0.57 g of 85% (4.9 mmol) of phosphoric acid was added with stirring. The solid was precipitated, 40 mL of ethyl acetate was added dropwise, To room temperature, stirred for 1 hour, filtered, a small amount of ethyl acetate to wash the filter cake, and dried to obtain 2.3 g of a white solid (Compound I, HPLC purity: 99.8%). Yield: 92.7%. 1 H NMR (D 2 O): δ 1.10 (t, 2H, J = 7.2Hz), 1.33-1.64 (m, 7H), 1.92 (d, 2H, J = 13.4Hz), 2.95-3.09 (m, 4H), 3.46 (d, 2H, J = 10.7 Hz), 4.34 (s, 2H), 5.89 (s, 2H), 6.20 (s, 1H), 6.69 (s, 1H), 7.45 (dd, 1H, J = 7.5, 7.4 Hz), 7.53 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz), 7.88 (td, 1H, J = 7.7, 1.2 Hz), 8.54 (d, 1H, J = 4.6 Hz)
Multifunctional compound AD-35 improves cognitive impairment and attenuates the production of TNF-alpha and IL-1beta in an alphabeta25-35-induced rat model of alzheimer’s disease
J Alzheimer’s Dis 2017, 56(4): 1403
| CN101626688A * |
Dec 11, 2007 |
Jan 13, 2010 |
雷维瓦药品公司 |
Compositions, synthesis, and methods of using indanone based cholinesterase inhibitors |
| WO2014005421A1 * |
Jul 3, 2013 |
Jan 9, 2014 |
Zhejiang Hisun Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. |
Benzodioxole derivative and preparation method and use thereof |
////////////Alzheimers disease, Zhejiang Hisun Pharmaceutical, AD 35, PHASE1, IND-120499
O=C5N(CCC2CCN(Cc1ccccn1)CC2)C3(CC3)c4cc6OCOc6cc45






















