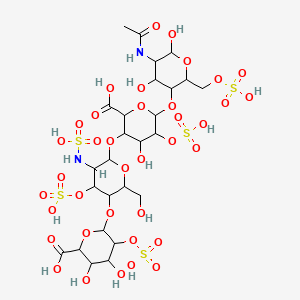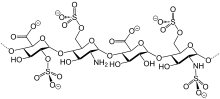

Bemiparin
- AVE 5026
- Adomiparin
- Ardeparin
- Arteven
- Bemiparin
- CY 216
- CY 222
- Centaxarin
- Certoparin
- Clevarin
- Clivarin
- Clivarine
- Dalteparin
- Deligoparin
- F 202
- FR 860
- Fluxum
- Fragmin A
- Fragmin B
- Fraxiparin
- Gammaparin
- H 5284
- H 9399
- Hapacarin
- Heparin subcutan
- Heparin sulfate
- Heparinic acid
- Heparins
- KB 101
- Leparan
- LipoHep Forte
- Livaracine
- M 118
- M 118REH
- M 402
- M 402 (heparin)
- Mono-embolex
- Multiparin
- Nadroparin
- Nadroparine
- Necuparanib
- Novoheparin
- OP 386
- OP 622
- Octaparin
- Pabyrn
- Parnaparin
- Parvoparin
- Reviparin
- Sandoparin
- Semuloparin
- Subeparin
- Sublingula
- Tafoxiparin
- Tinzaparin
- Triofiban
- Vetren
- Vitrum AB
- α-Heparin
cas 91449-79-5
Bemiparin (trade names Ivor and Zibor, among others) is an antithrombotic and belongs to the group of low molecular weight heparins (LMWH).[1]
Bemiparin is an ultra-low molecular weight heparin (ultra-LMWH) used to prevent thromboembolism following surgery and extracorporeal clotting during dialysis.
Rovi and Archimedes (a wholly owned subsidiary of ProStrakan), have developed and launched bemiparin, a Factor Xa inhibitor for the injectable treatment and prevention of thrombosis.
low or very low molecular weight heparins (eg bemiparin sodium) with a high anti-factor Xa activity for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis.
Bemiparin is an antithrombotic and belongs to the group of drugs known as the low molecular weight heparins (LMWH). Like semuloparin, bemiparin is classified as an ultra-LMH because of its low mean molecular mass of 3600 daltons, which is a unique property of this class 1. These heparins have lower anti-thrombin activity than the traditional low molecular weight heparins and act mainly on factor-Xa, reducing the risk of bleeding due to selectivity for this specific clotting factor. Interestingly, current research is underway for the potential benefit of bemiparin in the treatment of tumors and diabetic foot ulcers 12,1.
Laboratorios Farmaceuticos Rovi has developed and launched Enoxaparina Rovi, a biosimilar version of enoxaparin sodium, an injectable low-molecular-weight fraction of heparin, for the prophylaxis of venous thromboembolism.
PATENT
WO2018015463
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=WO2018015463
claiming a method for analyzing glycosaminoglycans, heparins and their derivatives in a compound comprising a monosaccharide residues present in heparin (eg bemiparin sodium) chains by identification and relative quantification of its characteristic signals by1H NMR one-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance and/or 1H-13C HSQC two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance, using dimethylmalonic acid as internal reference
PATENT
CN-110092848
https://patents.google.com/patent/CN110092848A/en
| Serial number | Project | Control standard | Testing result |
| 1 | Weight average molecular weight | 3000~4200 | 3650 |
| 2 | Molecular weight is greater than 6000 constituent content | < 15% | 12.9% |
| 3 | Constituent content of the molecular weight less than 2000 | < 35% | 36.7% |
| 4 | Molecular weight is between 2000~6000 constituent contents | 50%~75% | 50.4% |
| 5 | Anti-Xa activity | 80~120IU/mg | 116IU/mg |
| 6 | Anti- IIa activity | 5~20IU/mg | 14.6IU/mg |
| 7 | The anti-anti- IIa of Xa/ | ≥7 | 7.95 |
PATENT
WO-2021152192
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf;jsessionid=9D96E01E1CE8B8107A83A95B4B344DD3.wapp2nC?docId=WO2021152192&tab=PCTDESCRIPTION
Use of a composition comprising low or very low molecular weight heparins (eg bemiparin sodium) with a high anti-factor Xa activity for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis.
Heparin belongs to the glycosaminoglycan family and is a polysaccharide of animal origin, which is extracted from the intestine or lungs of mammals (cow, lamb, pig) and is used in human therapies for the prevention and treatment of thromboembolic diseases . It is well known that the use of heparin is accompanied by very annoying bleeding effects and its daily administration, three subcutaneous or intravenous injections, constitutes a very considerable inconvenience.
During the course of the last few years, different chemical methods have been used to depolymerize heparin, such as:
– treatment with sodium nitrite in an acid medium,
– alkaline treatment of asters,
– use of free radicals generated in the presence of hydrogen peroxide,
– treatment of a quaternary ammonium salt of heparin in a non-aqueous medium with a strong base according to a beta elimination mechanism.
These methods make it possible to obtain, with variable yields, mixtures of heparin fragments in which the average molecular weight and anticoagulant activity vary according to the procedure and operating conditions. Low molecular weight heparins (LMWH) described in the state of the art or commercialized are obtained according to different depolymerization procedures. Their average molecular weights (Mw) are in the range of 3,600 and 7,500 Daltons.
It is now recognized that the antithrombotic activity of LMWH is mainly due to its ability to activate antithrombin III, a plasma protein and potent inhibitor of activated factor X and thrombin. In this way, it is possible to measure the antithrombotic activity of heparin by means of specific tests to determine the inhibition of these factors.
Research carried out by different authors shows that heparin fragments or oligosaccharides, with short chains of average molecular weight <4,800 Daltons, have a selective action on activated factor X and not on thrombin, in determinations using methods of the Pharmacopoeia. .
It has been found that if very low molecular weight fragments are required that have strong anti-factor Xa activity, it is preferable to use a selective depolymerization technique in non-aqueous medium, as described in US patent 9,981,955, which respects the antithrombin III binding site.
The document EP 1070503 A1 describes the controlled depolymerization of heparin using a process in a non-aqueous medium that makes it possible to obtain a family of LMWH that are obtained enriched in low molecular weight oligosaccharides that have a high anti-factor Xa activity and a low anti-factor lia activity, and which can be represented by the general formula:
in which:
n can vary between 1 and 12,
Ri = H or S0 3 Na,
R 2 = SOsNao COCH 3 ,
Said very low molecular weight heparin is obtained by selective depolymerization of heparin in a non-aqueous medium according to a beta elimination procedure.
Medical uses
Bemiparin is used for the prevention of thromboembolism after surgery, and to prevent blood clotting in the extracorporeal circuit in haemodialysis.[2]
Contraindications
The medication is contraindicated in patients with a history of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia with or without disseminated intravascular coagulation; acute bleeding or risk of bleeding; injury or surgery of the central nervous system, eyes or ears; severe liver or pancreas impairment; and acute or subacute bacterial endocarditis.[2]
Interactions
No interaction studies have been conducted. Drugs that are expected to increase the risk of bleeding in combination with bemiparin include other anticoagulants, aspirin and other NSAIDs, antiplatelet drugs, and corticosteroids.[2]
Chemistry
Like semuloparin, bemiparin is classified as an ultra-LMWH because of its low molecular mass of 3600 g/mol on average.[3] (Enoxaparin has 4500 g/mol.) These heparins have lower anti-thrombin activity than classical LMWHs and act mainly on factor Xa, reducing the risk of bleeding.[4]
References
- ^ Chapman TM, Goa KL (2003). “Bemiparin: a review of its use in the prevention of venous thromboembolism and treatment of deep vein thrombosis”. Drugs. 63 (21): 2357–77. doi:10.2165/00003495-200363210-00009. PMID 14524738.
- ^ Jump up to:a b c Austria-Codex (in German). Vienna: Österreichischer Apothekerverlag. 2018. Ivor 2500 IE Anti-Xa/0,2 ml Injektionslösung in Fertigspritzen.
- ^ Planès A (September 2003). “Review of bemiparin sodium–a new second-generation low molecular weight heparin and its applications in venous thromboembolism”. Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy. 4 (9): 1551–61. doi:10.1517/14656566.4.9.1551. PMID 12943485. S2CID 13566575.
- ^ Jeske WP, Hoppensteadt D, Gray A, Walenga JM, Cunanan J, Myers L, Fareed J, Bayol A, Rigal H, Viskov C (October 2011). “A common standard is inappropriate for determining the potency of ultra low molecular weight heparins such as semuloparin and bemiparin”. Thrombosis Research. 128 (4): 361–7. doi:10.1016/j.thromres.2011.03.001. PMID 21458847.
External links
- bemiparin at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Badyket, Ivor, Hibor, Zibor, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration |
Subcutaneous injection (except for haemodialysis) |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 96% (estimated) |
| Elimination half-life | 5–6 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Molar mass | 3600 g/mol (average) |
| |
|
- Chapman TM, Goa KL: Bemiparin: a review of its use in the prevention of venous thromboembolism and treatment of deep vein thrombosis. Drugs. 2003;63(21):2357-77. [Article]
- Planes A: Review of bemiparin sodium–a new second-generation low molecular weight heparin and its applications in venous thromboembolism. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2003 Sep;4(9):1551-61. [Article]
- Jeske WP, Hoppensteadt D, Gray A, Walenga JM, Cunanan J, Myers L, Fareed J, Bayol A, Rigal H, Viskov C: A common standard is inappropriate for determining the potency of ultra low molecular weight heparins such as semuloparin and bemiparin. Thromb Res. 2011 Oct;128(4):361-7. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2011.03.001. Epub 2011 Apr 2. [Article]
- Sanchez-Ferrer CF: Bemiparin: pharmacological profile. Drugs. 2010 Dec 14;70 Suppl 2:19-23. doi: 10.2165/1158581-S0-000000000-00000. [Article]
- Hoffman M, Monroe DM: Coagulation 2006: a modern view of hemostasis. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2007 Feb;21(1):1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.hoc.2006.11.004. [Article]
- Antonijoan RM, Rico S, Martinez-Gonzalez J, Borrell M, Valcarcel D, Fontcuberta J, Barbanoj MJ: Comparative pharmacodynamic time-course of bemiparin and enoxaparin in healthy volunteers. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2009 Dec;47(12):726-32. [Article]
- Irish Medicines Board: Bemiparin [Link]
- Hibor-Bemiparin Sodium [Link]
- Zibor 2,500 IU Solution for Injection [Link]
- Injectable drugs guide [Link]
- Thrombosis Advisors- Factor Xa inhibitor [Link]
- Anti-tumor effects of bemiparin in HepG2 and MIA PaCa-2 cells [Link]
- Bemiparin, an effective and safe low molecular weight heparin: a review [Link]
- Bemiparin sodium [Link]
Patent
////////////Bemiparin sodium, Bemiparin