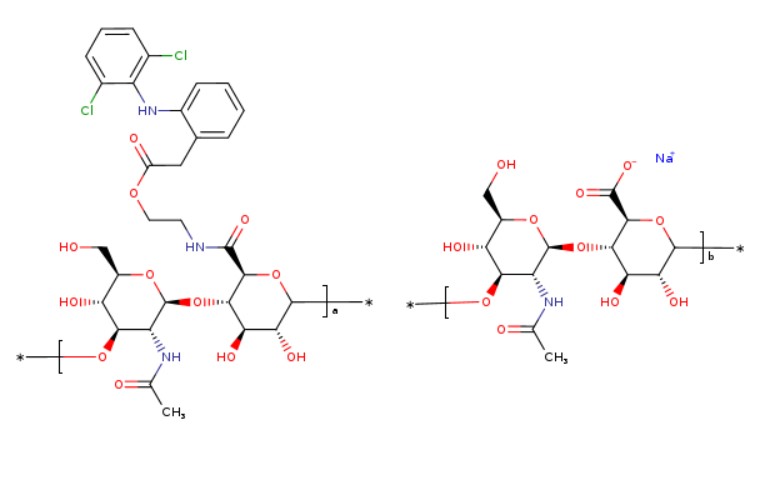
Diclofenac etalhyaluronate sodium
RN: 1398396-25-2
UNII: LG1II3835L
Molecular Formula, [(C30-H35-Cl2-N3-O12)a-(C14-H20-N-Na-O11)b]n-H2-O
Molecular Weight, 1101.8195
HYALURONIC ACID PARTLY AMIDIFIED WITH 2-(2-(2-((2,6-DICHLOROPHENYL)AMINO)PHENYL)ACETYLOXY)ETHANAMINE, SODIUM SALT
HYALURONAMIDE, N-(2-((2-(2-((2,6-DICHLOROPHENYL)AMINO)PHENYL)ACETYL)OXY)ETHYL), SODIUM SALT
SI 613
APPROVED PMDA JAPAN 2021/3/23, Joycle
Anti-inflammatory, Joint function improving agent
Treatment of Signs and Symptoms of Osteoarthritis of the Knee
![Chemical structure of N-[2-[[2-[2-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino]phenyl]acetyl]oxy]ethyl]hyaluronamide (diclofenac etalhyaluronate, SI-613)](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/325304331/figure/fig1/AS:669091362766859@1536535220444/Chemical-structure-of.png)
Diclofenac Etalhyaluronate Sodium
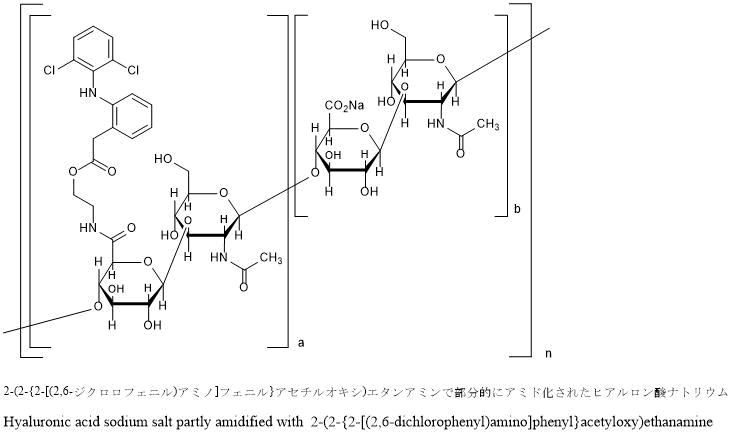
Sodium hyaluronate partially amidated with 2- (2- {2-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl) amino] phenyl} acetyloxy) ethaneamine
Hyaluronic acid sodium salt partly amidified with 2- (2- {2-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl) amino] phenyl} acetyloxy) ethanamine
[(C 30 H 35 Cl 2 N 3 O 12 ) a (C 14 H 20 NNaO 11 ) b ] n
[ 1398396-25-2 ]
Hyaluronic acid/non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug; Hyaluronic acid/NSAID; JOYCLU; ONO 5704; ONO-5704/SI-613; SI-613
- OriginatorSeikagaku Corporation
- DeveloperOno Pharmaceutical; Seikagaku Corporation
- ClassAmides; Analgesics; Antirheumatics; Drug conjugates; Glycosaminoglycans; Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatories
- Mechanism of ActionCyclooxygenase inhibitors
- RegisteredOsteoarthritis
- Phase IITendinitis
- 23 Mar 2021Registered for Osteoarthritis in Japan (Intra-articular)
- 25 Sep 2020Phase II for Osteoarthritis is still ongoing in USA (Seikagaku Corporation pipeline, September 2020)
- 25 Sep 2020Phase II for Tendinitis is still ongoing in Japan (Seikagaku Corporation pipeline, September 2020)
Currently, preparations using hyaluronic acid and its derivatives are used as medicines for arthropathy such as osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthropathy. Hyaluronic acid preparations are usually formulated as injections, and for the purpose of improving dysfunction due to arthropathy and suppressing pain through the lubricating action, shock absorption action, cartilage metabolism improving action, etc. of hyaluronic acid, the affected knee, It is administered directly to joints such as the shoulders. Commercialized hyaluronic acid preparations include, for example, those containing purified sodium hyaluronate as an active ingredient (for example, Alz (registered trademark) and Svenir (registered trademark)). The preparation requires continuous administration of 3 to 5 times at a frequency of once a week.
PATENT
WO 2018168920
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=WO2018168920
<Synthesis Example>
Aminoethanol-diclofenac-introduced sodium hyaluronate (test substance) was synthesized according to the method described in Examples of International Publication No. 2005/066241 (hyaluronic acid weight average molecular weight: 800,000, introduction rate). : 18 mol%).
More specifically, it was synthesized by the following method.
2.155 g (10.5 mmol) of 2-bromoethylamine hydrobromide is dissolved in 20 mL of dichloromethane, 1.436 mL (10.5 mmol) of triethylamine is added under ice-cooling, and di-tert-butyl-dicarbonate (Boc) is added. 2 O) 2.299 g (10.5 mmol) of a dichloromethane solution of 5 mL was added and stirred. After stirring at room temperature for 90 minutes, ethyl acetate was added, and the mixture was washed successively with 5 wt% citric acid aqueous solution, water and saturated brine. After dehydration with sodium sulfate, the solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure to obtain Boc-aminoethyl bromide.
5 mL of a dimethylformamide (DMF) solution of 2.287 g (10.2 mmol) of Boc-aminoethyl bromide obtained above is ice-cooled, 6 mL of a DMF solution of 3.255 g (10.2 mmol) of diclofenac sodium is added, and the mixture is added at room temperature. Stirred overnight. The mixture was stirred at 60 ° C. for 11 hours and at room temperature overnight. Ethyl acetate was added, and the mixture was sequentially separated and washed with a 5 wt% aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution, water, and saturated brine. After dehydration with sodium sulfate, ethyl acetate was distilled off under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (toluene: ethyl acetate = 20: 1 (v / v), 0.5% by volume triethylamine) to obtain Boc-aminoethanol-diclofenac.
2.108 g (4.80 mmol) of Boc-aminoethanol-diclofenac obtained above was dissolved in 5 mL of dichloromethane, 20 mL of 4M hydrochloric acid / ethyl acetate was added under ice-cooling, and the mixture was stirred for 2.5 hours. Diethyl ether and hexane were added and precipitated, and the precipitate was dried under reduced pressure. As a result, aminoethanol-diclofenac hydrochloride was obtained. Structure 1 was identified by-NMR
H: 1 H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl 3 ) [delta] (ppm) = 3.18 (2H, t, NH 2 CH 2 CH 2 O-), 3.94 (2H, s, Ph-CH 2 -CO), 4.37 (2H, t, NH 2 CH 2 CH 2 O-), 6.47-7.31 (8H, m, Aromatic H, NH).
After dissolving 500 mg (1.25 mmol / disaccharide unit) of hyaluronic acid having a weight average molecular weight of 800,000 in 56.3 mL of water / 56.3 mL of dioxane, imide hydroxysuccinate (1 mmol) / 0.5 mL of water, water-soluble carbodiimide Hydrochloride (WSCI / HCl) (0.5 mmol) / water 0.5 mL, aminoethanol-diclofenac hydrochloride (0.5 mmol) / (water: dioxane = 1: 1 (v / v), 5 mL obtained above ) Was added in sequence, and the mixture was stirred all day and night. 7.5 mL of a 5 wt% sodium hydrogen carbonate aqueous solution was added to the reaction mixture, and the mixture was stirred for about 4 hours. 215 μL of a 50% (v / v) acetic acid aqueous solution was added to the reaction solution for neutralization, and then 2.5 g of sodium chloride was added and the mixture was stirred. 400 ml of ethanol was added to precipitate, and the precipitate was washed twice with an 85% (v / v) aqueous ethanol solution, twice with ethanol, and twice with diethyl ether, dried under reduced pressure overnight at room temperature, and aminoethanol-diclophenac. Introduction Sodium hyaluronate (test substance) was obtained. The introduction rate of diclofenac measured by a spectrophotometer was 18 mol%.
PATENT
WO 2018168921
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=WO2018168921
//////////Diclofenac etalhyaluronate sodium, JOYCLU, ONO 5704, ONO-5704/SI-613, SI 613, JAPAN 2021, Joycle, APPROVALS 2021
#Diclofenac etalhyaluronate sodium, #JOYCLU, #ONO 5704, #ONO-5704/SI-613, #SI 613, #JAPAN 2021, #Joycle, #APPROVALS 2021















