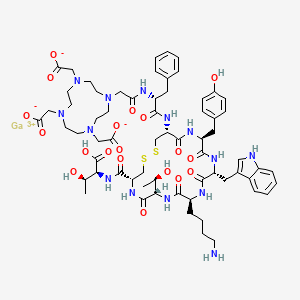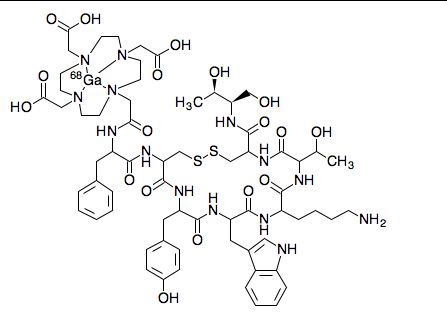
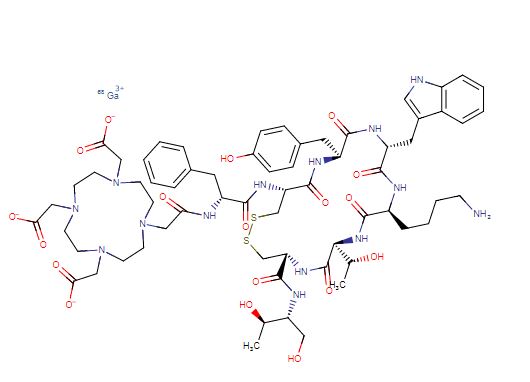
Edotreotide gallium Ga-68
エドトレオチドガリウム (68Ga);
- Edotreotide Gallium Ga-68
- Gallium (68Ga) edotreotide
- Gallium edotreotide Ga-68
- Gallium Ga 68-dotatoc
- Gallium Ga 68-edotreotide
- Gallium Ga-68 edotreotide
gallium;2-[4-[2-[[(2R)-1-[[(4R,7S,10S,13R,16S,19R)-10-(4-aminobutyl)-4-[[(1S,2R)-1-carboxy-2-hydroxypropyl]carbamoyl]-7-[(1R)-1-hydroxyethyl]-16-[(4-hydroxyphenyl)methyl]-13-(1H-indol-3-ylmethyl)-6,9,12,15,18-pentaoxo-1,2-dithia-5,8,11,14,17-pentazacycloicos-19-yl]amino]-1-oxo-3-phenylpropan-2-yl]amino]-2-oxoethyl]-7,10-bis(carboxylatomethyl)-1,4,7,10-tetrazacyclododec-1-yl]acetate
L-threonine, N-[[(4R,7S,10S,13
| Formula |
C65H92N14O18S2. Ga
|
|---|---|
| CAS |
1027785-90-5
|
| Mol weight |
1491.362
|
FDA, 2019/8/21 APPROVED Ga-68-dotatoc
UNII Y68179SY2L
Indicated for use with positron emission tomography (PET) for the localization of somatostatin receptor positive neuroendocrine tumors (NETs)
|
Diagnostic aid (tumor), Radioactive agent
|
Edotreotide gallium Ga-68 is an 8 amino acid peptide bound to the chelator 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid (DOTA).8 Edotreotide gallium Ga-68 is indicated for localizing somatostatin receptor positive neuroendocrine tumors by positron emission tomography.7 Dotatate gallium Ga-68 is used for a similar indication.2 Dotatate gallium Ga-68 has lower tumor uptake but this data is highly variable between patients.2
Edotreotide gallium Ga-68 was granted FDA approval on 21 August 2019.7
Indication
Edotreotide gallium Ga-68 is a radioactive diagnostic compound used in positron emission tomography (PET) for diagnose somatostatin receptor positive neuroendocrine tumors in pediatrics and adults.7
Associated Conditions
Pharmacodynamics
Edotreotide gallium Ga-68 binds to somatostatin receptors where it emits beta particle radiation for detection by positron emission tomography.7 The duration of action is short as it has short radioactive and biological half lives.4,8 Patients should hydrate before and after the administration of this medication to encourage frequent urination and rapid clearance.7
Mechanism of action
Edotreotide gallium Ga-68 binds to somatostatin receptors, with higher affinity for somatostatin receptor type 2, where it emits beta particle radiation for detection by positron emission tomography (PET).7
Absorption
Edotreotide gallium Ga-68 reaches 80% activity in tumors within 30 minutes,4 and reaches its highest activity in tumors 70±20min post injection.8 Edotreotide is mostly taken up into the spleen, followed by kidneys, liver, pituitary, thyroid, and adrenal gland.3,4,8 Accumulation in non-tumor tissue reaches a maximum within 40 minutes.4
Volume of distribution
Data regarding the volume of distribution of this medication is not readily available.7
Protein binding
Data suggests edotreotide gallium-Ga 68 may bind to proteins in serum.6 The extent of serum protein binding and which proteins it binds to are not described in the literature.
Metabolism
Edotreotide gallium Ga-68 is largely unmetabolized.8 4 hours post injection there are no metabolites or degradation products detectable in serum.4
Route of elimination
16% of a Edotreotide gallium Ga-68 dose is eliminated in the urine within 2h.1,7 It is expected that Edotreotide gallium Ga-68 is exclusively eliminated in the urine.1,7 In animal studies, edotreotide Y-90 was >80% eliminated in the urine within 24h, with 95.6±3.4% being unmetabolized.3,8 <1% of a dose is detected in the feces.5
Half life
Edotreotide gallium Ga-68 has a radioactive half life of 68 minutes.4,8 Edotreotide gallium Ga-68 has two half lives, 2.0±0.3min and 48±7min for its removal from blood.4,8
Clearance
Data regarding the clearance of this medication is not readily available.7
Toxicity
The LD50 of this medication is not readily available.7
In the event of an overdose, give patients plenty of fluids and diuretics if necessary to encourage frequent urination.7 If possible, an estimation of radioactive dose should be performed.7
General References
- Hartmann H, Zophel K, Freudenberg R, Oehme L, Andreeff M, Wunderlich G, Eisenhofer G, Kotzerke J: [Radiation exposure of patients during 68Ga-DOTATOC PET/CT examinations]. Nuklearmedizin. 2009;48(5):201-7. doi: 10.3413/nukmed-0214. Epub 2009 Jul 28. [PubMed:19639164]
- Poeppel TD, Binse I, Petersenn S, Lahner H, Schott M, Antoch G, Brandau W, Bockisch A, Boy C: 68Ga-DOTATOC versus 68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT in functional imaging of neuroendocrine tumors. J Nucl Med. 2011 Dec;52(12):1864-70. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.111.091165. Epub 2011 Nov 9. [PubMed:22072704]
- de Jong M, Bakker WH, Krenning EP, Breeman WA, van der Pluijm ME, Bernard BF, Visser TJ, Jermann E, Behe M, Powell P, Macke HR: Yttrium-90 and indium-111 labelling, receptor binding and biodistribution of [DOTA0,d-Phe1,Tyr3]octreotide, a promising somatostatin analogue for radionuclide therapy. Eur J Nucl Med. 1997 Apr;24(4):368-71. doi: 10.1007/bf00881807. [PubMed:9096086]
- Hofmann M, Maecke H, Borner R, Weckesser E, Schoffski P, Oei L, Schumacher J, Henze M, Heppeler A, Meyer J, Knapp H: Biokinetics and imaging with the somatostatin receptor PET radioligand (68)Ga-DOTATOC: preliminary data. Eur J Nucl Med. 2001 Dec;28(12):1751-7. doi: 10.1007/s002590100639. Epub 2001 Oct 31. [PubMed:11734911]
- Kwekkeboom DJ, Kooij PP, Bakker WH, Macke HR, Krenning EP: Comparison of 111In-DOTA-Tyr3-octreotide and 111In-DTPA-octreotide in the same patients: biodistribution, kinetics, organ and tumor uptake. J Nucl Med. 1999 May;40(5):762-7. [PubMed:10319747]
- Bangard M, Behe M, Guhlke S, Otte R, Bender H, Maecke HR, Biersack HJ: Detection of somatostatin receptor-positive tumours using the new 99mTc-tricine-HYNIC-D-Phe1-Tyr3-octreotide: first results in patients and comparison with 111In-DTPA-D-Phe1-octreotide. Eur J Nucl Med. 2000 Jun;27(6):628-37. doi: 10.1007/s002590050556. [PubMed:10901448]
- FDA Approved Drug Products: Gallium Dotatoc GA 68 [Link]
- EMA Assessment Report: SomaKit TOC [Link]
///////////Edotreotide gallium Ga-68, FDA 2019, エドトレオチドガリウム (68Ga),
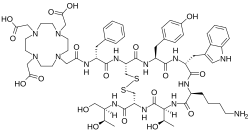 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-[4-[2-[[(2R)-1-[[(4R,7S,10S,13R,16S,19R)-10-(4-aminobutyl)-4-[[(2R,3R)-1,3-dihydroxybutan-2-yl]carbamoyl]-7-[(1R)-1-hydroxyethyl]-16-[(4-hydroxyphenyl)methyl]-13-(1H-indol-3-ylmethyl)-6,9,12,15,18-pentaoxo-1,2-dithia-5,8,11,14,17-pentazacycloicos-19-yl]amino]-1-oxo-3-phenylpropan-2-yl]amino]-2-oxoethyl]-7,10-bis(carboxymethyl)-1,4,7,10-tetrazacyclododec-1-yl]acetic acid
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| Properties | |
| C65H92N14O18S2 | |
| Molar mass | 1421.65 g·mol−1 |
| Pharmacology | |
| License data | |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
Edotreotide (USAN, codenamed SMT487, also known as (DOTA0–Phe1–Tyr3)octreotide, or DOTATOC) is a substance which, when bound to various radionuclides, is used in the treatment and diagnosis of certain types of cancer.[1]
Yttrium-90 labeled edoteotide has been the subject of a trial by the National Cancer Institute to determine its effects in young cancer patients (up to 25 years of age) for its ability to locate malignant cancer cells without harming normal cells. Specific cancers being included in the trial include neuroblastoma, childhood brain tumours and gastrointestinal cancer.[2][3]
-
Yttrium-90 labeled edotreotide
References
- ^ Martindale, The Extra Pharmacopoeia, 30th ed, p1161.
- ^ Bushnell, D. L.; O’Dorisio, T. M.; O’Dorisio, M. S.; Menda, Y.; Hicks, R. J.; Van Cutsem, E.; Baulieu, J. -L.; Borson-Chazot, F.; Anthony, L.; Benson, A. B.; Oberg, K.; Grossman, A. B.; Connolly, M.; Bouterfa, H.; Li, Y.; Kacena, K. A.; Lafrance, N.; Pauwels, S. A. (2010). “90Y-Edotreotide for Metastatic Carcinoid Refractory to Octreotide”. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 28 (10): 1652–1659. doi:10.1200/JCO.2009.22.8585. PMC 4872330. PMID 20194865.
- ^ Radiolabeled Octreotide in Treating Children With Advanced or Refractory Solid Tumors