Octamoxin
- Molecular FormulaC8H20N2
- Average mass144.258 Da
Octan-2-ylhydrazine
Octomoxine
UNII:0HXY3M6S54
UNII:2NJ66SLA5C
UNII:895PL98ZMY
CAS Registry Number: 4684-87-1
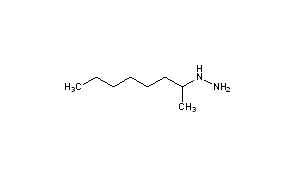
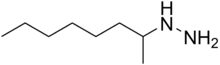
CAS Name: (1-Methylheptyl)hydrazine
Additional Names: 2-hydrazinooctane; octomoxine
Trademarks: Ximaol
Molecular Formula: C8H20N2
Molecular Weight: 144.26
Percent Composition: C 66.61%, H 13.97%, N 19.42%
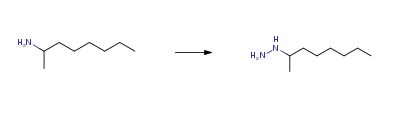
Literature References: Monoamine oxidase inhibitor. Prepd by condensation of methyl hexyl ketone and hydrazine hydrate followed by hydrogenation under pressure: Michel-Ber et al., GB 899385 (1962 to Soc. Civile Auguil).
Derivative Type: Sulfate
CAS Registry Number: 3845-07-6
Trademarks: Nimaol
Molecular Formula: C8H20N2.H2SO4
Molecular Weight: 242.34
Percent Composition: C 39.65%, H 9.15%, N 11.56%, S 13.23%, O 26.41%
Properties: Crystals, mp 78-80°.
Melting point: mp 78-80°
Therap-Cat: Antidepressant.
Keywords: Antidepressant; Hydrazides/Hydrazines; Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor.
Octamoxin (trade names Ximaol, Nimaol), also known as 2-octylhydrazine, is an irreversible and nonselective monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine class that was used as an antidepressant in the 1960s but is now no longer marketed.[2][3][4][5]
CLIP
OXIME TO AMINO TO PRODUCT
Zhurnal Russkago Fiziko-Khimicheskago Obshchestva1899vol. 31p. 878Ch emisches Zentralblatt 1900 vol. 71 Ip. 653
References
- ^ “Octamoxin – Compound Summary”. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 26 March 2005. Identification and Related Records. Retrieved 31 May 2012.
- ^ “Dictionary of pharmacological agents – Google Books”.
- ^ “13-06781. Octamoxin [Archived]: The Merck Index”.
- ^ Levy J, Michel-Ber E (1966). “[Relations between the antidepressive effects of octamoxine revealed by 3 pharmacological tests and inhibition of cerebral monoamine oxidase in mice]”. Thérapie (in French). 21 (4): 929–45. PMID 5925088.
- ^ Gayral L, Stern H, Puyuelo R (1966). “[Indications and results of the treatment of mental depression by octamoxine (ximaol)]”. Thérapie (in French). 21 (5): 1183–90. PMID 5976767.
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-Methylheptylhydrazine[citation needed]
|
|
| Systematic IUPAC name
Octan-2-ylhydrazine[1]
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| Properties | |
| C8H20N2 | |
| Molar mass | 144.262 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.831 g/mL |
| Boiling point | 228 °C (442 °F; 501 K) |
| Pharmacology | |
| Oral | |
| Related compounds | |
|
Related compounds
|
Tuaminoheptane |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
///////////Octamoxin, Ximaol, Nimaol, 2-octylhydrazine, октамоксин , أوكتاموكسين , 奥他莫辛 ,














