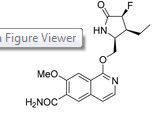

PF-06650833
1-{[(2S,3S,4S)-3-ethyl-4-fluoro-5-oxopyrrolidin-2-yl]methoxy}-7-methoxyisoquinoline-6-carboxamide
CAS 1817626-54-2
Chemical Formula: C18H20FN3O4
Molecular Weight: 361.3734
- Originator Pfizer
- Class Anti-inflammatories; Antirheumatics
- Mechanism of Action Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase inhibitors
- Phase II Rheumatoid arthritis
- Phase I Lupus vulgaris
- 01 Aug 2018 Pfizer completes a phase II trial in Rheumatoid arthritis (Treatment-experienced) in USA, Ukraine, Taiwan, Serbia, Russia, Romania, Poland, Mexico, South Korea, Georgia, Bosnia-Herzegovina, Australia, Croatia, Spain, Slovakia, Czech Republic, Hungary, Germany, Bulgaria (PO) (NCT02996500)
- 28 Jul 2018 No recent reports of development identified for phase-I development in Lupus(In volunteers) in USA (PO, Controlled release)
- 28 Jul 2018 No recent reports of development identified for phase-I development in Lupus(In volunteers) in USA (PO, Immediate release)
- PF-06650833 is an inhibitor of Interleukin-1 receptor associated kinase 4 (IRAK4). RAK4 is located proximal to TLR/IL-1 receptors, and in preclinical studies, inhibits downstream signaling from these receptors. The development of novel small molecule inhibitors of this kinase has the potential to lead to new therapeutics to treat diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and lymphomas.
Interleukin-1 receptor associated kinase 4 (IRAK-4) is a serine threonine kinases that plays a key role in innate immune signaling. IRAK-4 is activated by the interleukin (IL-1) family receptors (IL-1R, IL-18R, and IL-33R), as well as the Toll-like receptors (TLRs). Inhibition of IRAK-4 blocks the production of inflammatory cytokines such as type I interferons, tumor necrosis factor (TNF), IL-1, IL-6, and IL-12 that are key drivers of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. IRAK-4 is an attractive therapeutic target for diseases associated with dysregulated inflammation, such as systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis.


Conditions: (a) LDA (1.2 equiv), TMSCl (1.3 equiv), THF, −60 °C, 30 min; (b) allyl methyl carbonate (1.1 equiv), Pd(OAc)2 (0.05 equiv), THF, 65 °C, 2 h, 73% (2 steps); (c) LiThCN (1.5 equiv), EtMgCl (1.5 equiv), TMSCl (2.0 equiv), THF, −78 °C, 6 h, 90%; (d) LDA (1.8 equiv), NFSI (1.25 equiv), THF, −78 °C, 1 h, 23% (8), 45% (9); (e) pTsOH (0.05 equiv), MeCN, H2O, 90 °C, 2 h, 97%; (f) 3 (0.9 equiv), KHMDS (2.0 equiv), DMF, THF, −10 °C, 30 min, 84%; (g) H2O2 (10 equiv), K2CO3 (4.0 equiv), DMSO, 20 °C, 2 h, 97%.
CLIP
Target: Interleukin-1 receptor associated kinase 4 (IRAK4): This kinase is important in innate immunity, and its inhibition is predicted to be beneficial in treating inflammatory diseases.
Disease: Rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disorder
Notes: PF06650833 came from a screening assay that used nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy to determine binding between molecular fragments and IRAK4. The initial hit, which bound weakly to IRAK4, was optimized with structure- and property-based medicinal chemistry to generate a series of potent inhibitors, said Katherine Lee, an associate research fellow at Pfizer.
Paper
Improvements to Enable the Large Scale Synthesis of 1-{[(2S,3S,4S)-3-Ethyl-4-fluoro-5-oxopyrrolidin-2-yl]methoxy}-7-methoxyisoquinoline-6-carboxamide (PF-06650833)


https://pubs.acs.org/doi/suppl/10.1021/acs.oprd.8b00386/suppl_file/op8b00386_si_001.pdf
An improved process for the large scale synthesis of 1-{[(2S,3S,4S)-3-ethyl-4-fluoro-5-oxopyrrolidin-2-yl]methoxy}-7-methoxyisoquinoline-6-carboxamide (1), a candidate currently in clinical development, was developed. Key objectives were to eliminate chromatographic purifications, to maximize the reproducibility of each step, and to improve the yield and efficiency of each step relative to the previous discovery syntheses of 1. This work was focused on improvements to the synthesis of the stereochemically complex lactam 2. Steps of particular concern were the preparation of the unsaturated lactam 6, the cuprate conjugate addition reaction to produce 7, and the conversion of 7 to 8 with a high degree of diastereoselection. The solutions to these challenges have permitted the synthesis of 2 in excess of 100 kg, which in turn has permitted 1 to be prepared in sufficient amounts to support further development.
1 (31.3 kg, 91%, 82% overall) as a white, free-flowing powder.
1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO): δ 8.86 (s, 1H), 8.16 (s, 1H), 7.90 (d, J = 5.9 Hz, 1H), 7.84 (br. s., 1H), 7.74 (s, 1H), 7.70 (br. s., 1H), 7.42 (d, J = 5.9 Hz, 1H), 4.90 (dd, J = 5.9, 53.8 Hz, 1H), 4.54 (dd, J = 3.5, 11.1 Hz, 1H), 4.26 (dd, J = 6.4, 11.0 Hz, 1H), 4.13–4.05 (m, 1H), 3.97 (s, 3H), 2.69–2.54 (m, 1H), 1.68–1.53 (m, 2H), 1.02 (t, J = 7.3 Hz, 3H).
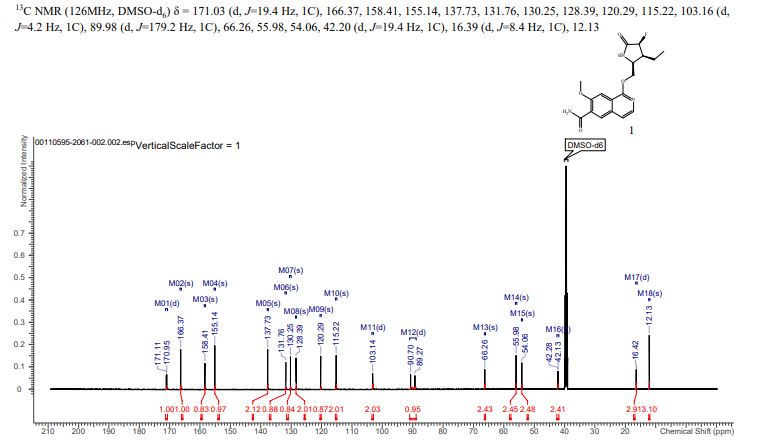
13C NMR{1H} (126 MHz, DMSO): δ 171.0 (d, J = 19.4 Hz), 166.4, 158.4, 155.1, 137.7, 131.8, 130.3, 128.4, 120.3, 115.2, 103.2 (d, J = 4.2 Hz), 90.0 (d, J = 179.2 Hz), 66.3, 56.0, 54.1, 42.2 (d, J = 19.4 Hz), 16.4 (d, J = 8.4 Hz), 12.1.
19F NMR (H decoupled, 376 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ −199.26.
LCMS: 362 (MH+).

//////////////PF-06650833, PF 06650833, PF06650833, PF-6650833, PF 6650833, PF6650833.
O=C(C1=CC2=C(C(OC[C@H]([C@H](CC)[C@@H]3F)NC3=O)=NC=C2)C=C1OC)N
















