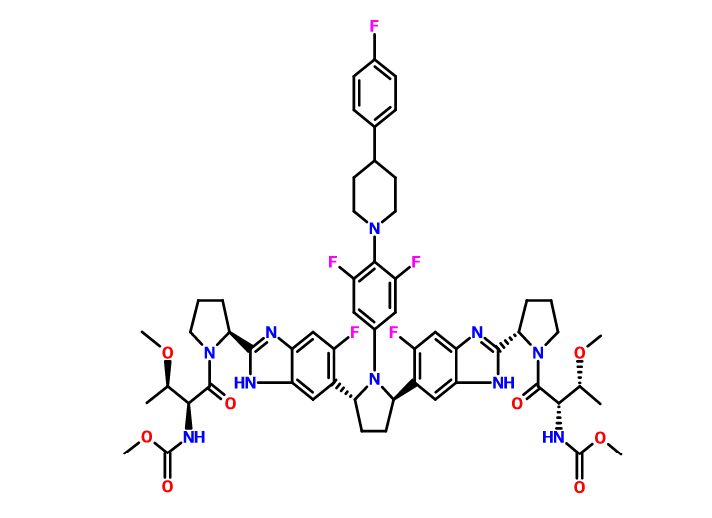
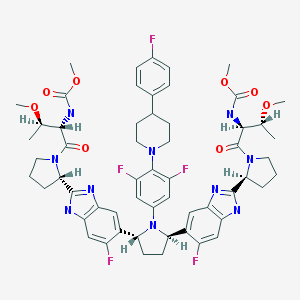
Pibrentasvir
ABT-530, Pibrentasvir, A 1325912.0
Dimethyl N,N’-([(2R,5R)-1-{3,5-difluoro-4-[4-(4-fluorophenyl)piperidin-1-yl]phenyl}pyrrolidine-2,5-diyl]bis{(6-fluoro-1H-benzimidazole-5,2-diyl)[(2S)-pyrrolidine-2,1-diyl][(2S,3R)-3-methoxy-1-oxobutane-1,2-diyl]})biscarbamate
Methyl {(2S,3R)-1-[(2S)-2-{5-[(2R,5R)-1-{3,5-difluoro-4-[4-(4-fluorophenyl)piperidin-1-yl]phenyl}-5-(6-fluoro-2-{(2S)-1-[N-(methoxycarbonyl)-O-methyl-L-threonyl]pyrrolidin-2-yl}-1H-benzimidazol-5-yl)pyrrolidin-2-yl]-6-fluoro-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl}pyrrolidin-1-yl]-3-methoxy-1-oxobutan-2-yl}carbamate
Dimethyl N,N’-(((2R,5R)-1-(3,5-difluoro-4-(4-(4-fluorophenyl)piperidin-1-yl)phenyl)pyrrolidine-2,5-diyl)bis((6-fluoro-1H-benzimidazole-5,2-diyl)((2S)-pyrrolidine-2,1-diyl)((2S,3R)-3-methoxy-1-oxobutane-1,2-diyl)))biscarbamate
Methyl ((2S,3R)-1-((2S)-2-(5-((2R,5R)-1-(3,5-difluoro-4-(4-(4-fluorophenyl)piperidin-1-yl)phenyl)-5-(6-fluoro-2-((2S)-1-(N-(methoxycarbonyl)-O-methyl-L-threonyl)pyrrolidin-2-yl)-1H-benzimidazol-5-yl)pyrrolidin-2-yl)-6-fluoro-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)pyrrolidin-1-yl)-3-methoxy-1-oxobutan-2-yl)carbamate
Phase III
Abbott Laboratories INNOVATOR
A protease inhibitor potentially for the treatment of HCV infection.
Hepatitis C virus NS 5 protein inhibitors
![]()
CAS No. 1353900-92-1
| MF | C57H65F5N10O8 |
|---|
MW 1113.1925 MW
Pibrentasvir
- UNII-2WU922TK3L
- CLINICAL https://clinicaltrials.gov/search/intervention=A-1325912.0%20OR%20ABT-530%20OR%20Pibrentasvir
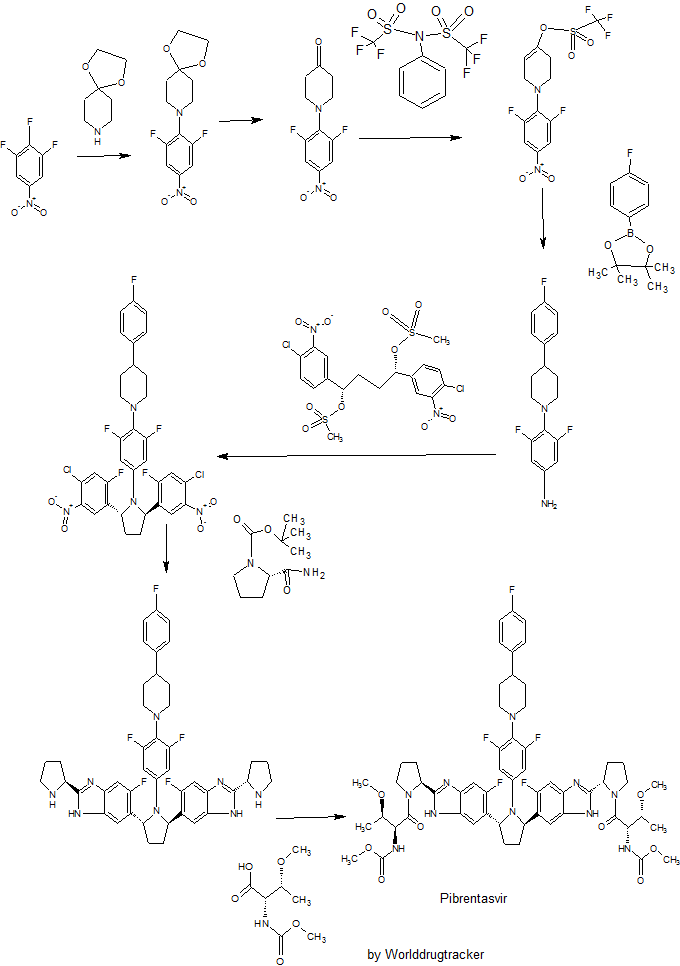
SYNTHESIS
PATENT
WO 2012051361
http://www.google.com/patents/WO2012051361A1?cl=en
Example 3.52 methyl {(2S,3R)-l-[(2S)-2-{5-[(2R,5R)-l-{3,5-difluoro-4-[4-(4- fluorophenyl)piperidin-l-yl]phenyl}-5-(6-fluoro-2-{(2.S)-l-[A^-(methoxycarbonyl)-0-methyl-L- threonyl]pyiTolidin-2-yl}-l f-benzimidazol-5-yl)pyiTolidin-2-yl]-6-fluoro-l f-benzimidaz yl}pyrrolidin-l-yl]-3-methoxy-l-oxobutan-2-yl}carbamatelH NMR (400 MHz, DMSO) δ 12.36 – 12.06 (m, 2H), 7.41 (dd, J = 11.2, 6.3, 1H), 7.34 (dd, J = 10.4, 4.8, 1H), 7.30 – 7.20 (m, 3H), 7.17 – 6.98 (m, 5H), 5.98 – 5.82 (m, 2H), 5.65 – 5.47 (m, 2H), 5.17 – 5.06 (m, 2H), 4.25 (dd, J = 15.6, 8.1, 2H), 3.88 – 3.74 (m, 3H), 3.53 (d, J = 1.3, 6H), 3.49 – 3.38 (m, 2H), 3.31 (d, 1H), 3.25 (d, J = 3.7, 1H), 3.13 (d, J = 1.3, 3H), 3.03 (d, J = 2.3, 3H), 3.00 – 2.84 (m, 3H), 2.60 – 2.53 (m, J = 2.5, 2H), 2.26 – 1.55 (m, 14H), 1.28 – 1.13 (m, 1H), 1.10 – 0.88 (m, 6H). MS (ESI; M+H) m/z = 1113.4.
PATENT
The present invention features crystalline polymorphs of methyl {(2S,3R)-1- [(2S)-2-{5-[(2R,5R)-l-{3,5-difluoro-4 4-(4-fluorophenyl)piperidin-l-yl]phenyl}-5-(6-fluoro-2-{(2S)- 1 -[N-(methoxycarbonyl)-0-methyl-L-threonyl]pyrrolidin-2-yl} – 1 H-benzimidazol-5-yl)pyrrolidin- -yl] -6-fluoro- 1 H-benzimidazol-2-yl} pyrrolidin- 1 -yl] -3 -methoxy- 1 -oxobutan-2-
yl} carbamate 
, herein “Compound I”). Compound I is a potent HCV NS5A inhibitor and is described in U.S. Patent Application Publication No. 2012/0004196, which is incorporated herein by reference in its entirety.
//////////1353900-92-1, PHASE 3, ABT-530, Pibrentasvir, ABT 530, A 1325912.0, breakthrough therapy designation
C[C@H]([C@@H](C(=O)N1CCC[C@H]1c2[nH]c3cc(c(cc3n2)[C@H]4CC[C@@H](N4c5cc(c(c(c5)F)N6CCC(CC6)c7ccc(cc7)F)F)c8cc9c(cc8F)[nH]c(n9)[C@@H]1CCCN1C(=O)[C@H]([C@@H](C)OC)NC(=O)OC)F)NC(=O)OC)OC
C[C@H]([C@@H](C(=O)N1CCC[C@H]1c2[nH]c3cc(c(cc3n2)[C@H]4CC[C@@H](N4c5cc(c(c(c5)F)N6CCC(CC6)c7ccc(cc7)F)F)c8cc9c(cc8F)[nH]c(n9)[C@@H]1CCCN1C(=O)[C@H]([C@@H](C)OC)NC(=O)OC)F)NC(=O)OC)OC
oct 2016
US FDA grants breakthrough therapy designation to AbbVie’s G/P to treat HCV
AbbVie’s investigational, pan-genotypic regimen of glecaprevir (ABT-493) / pibrentasvir (ABT-530) (G/P) has received breakthrough therapy designation from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV).
AbbVie’s investigational, pan-genotypic regimen of glecaprevir (ABT-493) / pibrentasvir (ABT-530) (G/P) has received breakthrough therapy designation from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV).
The HCV is a bloodborne virus commonly transmitted through injecting drug use due to the sharing of injection equipment, reuse or inadequate sterilisation of medical equipment, and the transfusion of unscreened blood and blood products.
The designation facilitates the use of AbbVie’s G/P to treat chronic HCV patients who failed previous therapy with direct-acting antivirals (DAAs) in genotype 1 (GT1), including therapy with an NS5A inhibitor and / or protease inhibitor.
AbbVie research and development executive vice-president Michael Severino said: “AbbVie is committed to advancing HCV care and addressing areas of continued unmet need for people living with chronic HCV.
“The FDA’s breakthrough therapy designation is an important step in our effort to bring our pan-genotypic regimen to market, which we are also investigating as an eight-week path to virologic cure for the majority of patients.”
AbbVie said that G/P is currently in Phase III trials evaluating the safety and efficacy of the regimen across all major HCV genotypes (genotypes 1-6).
Figures released by the World Health Organisation revealed that an estimated 700,000 people die each year from hepatitis C-related liver diseases.
There is currently no vaccine for hepatitis C, although research in this area is underway at present.