
4-Fluoropyrazoles are accessible in a single step from readily available aldehyde-derived N-alkylhydrazones through double C–H fluoroalkylation with tribromofluoromethane (CBr3F). RuCl2(PPh3)3 has been proven to be the most efficient catalyst for this transformation when compared to a range of other Cu-, Pd-, or Fe-based catalyst systems.

Univ Lyon, Université Claude Bernard Lyon 1, Institut de Chimie et Biochimie Moléculaires et Supramoléculaires (ICBMS, CNRS UMR 5246), F-69622 Villeurbanne, France
J. Org. Chem., 2017, 82 (6), pp 3311–3316
DOI: 10.1021/acs.joc.7b00085
*E-mail: didier.bouyssi@univ-lyon1.fr., *E-mail: nuno.monteiro@univ-lyon1.fr.
Ruthenium-Catalyzed Tandem C–H Fluoromethylation/Cyclization of N-Alkylhydrazones with CF3BR: Access to 4-Fluoropyrazoles
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.joc.7b00085
The importance of fluorine-containing pyrazoles to the pharmaceutical and agrochemical industries has been steadily increasing in recent years. As a consequence, the development of methods suitable for the incorporation of fluorine or fluoroalkyl groups into the pyrazole ring continues to be the subject of intense research.
Predicated on their previous copper-catalyzed synthesis of 4-substituted pyrazoles, Bouyssi, Monteiro and their co-worker from the Institut de Chemie et Biochemie Moléculaires et Supramoléculaires reported a ruthenium-catalyzed synthesis of substituted-4-fluoropyrazoles ( J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 3311). The requisite starting materials, aldehyde derived N,N-dialkylhydrazones, were readily synthesized. Tribromofluoromethane served as the source of fluorine.
The commercially available and inexpensive ruthenium complex, RuCl2(PPh3)3, was discovered to be a very effective catalyst for this transformation. Diglyme was the preferred solvent for the reaction. The reaction displayed good tolerance for a variety of functional groups, including cyano, ester, formyl, and halide.
In general, higher yields were obtained with electron-withdrawing substituents. This novel methodology affords substituted-4-fluoropyrazoles in good yields in one step from readily available starting materials.

2K
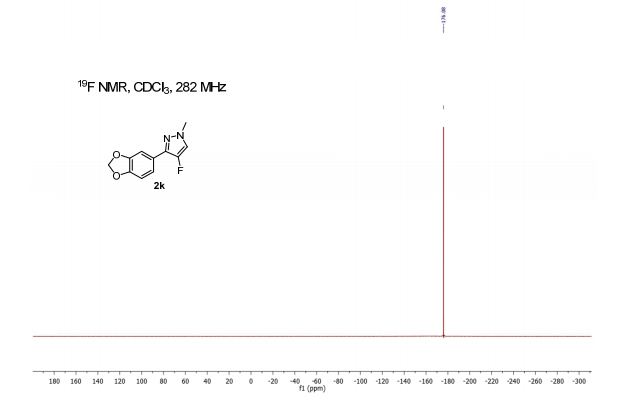
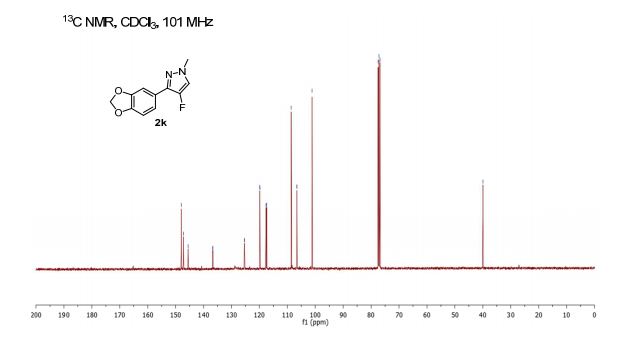
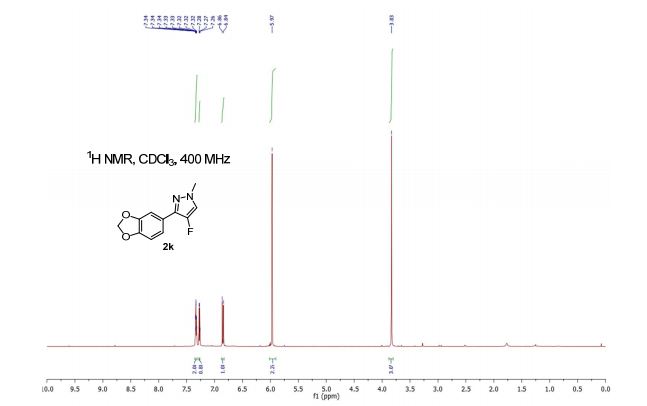
3-(Benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)-4-fluoro-1-methyl-1H-pyrazole (2k)
Chromatography using ethyl acetate/cyclohexane (gradient elution 30:70 to 50:50) gave the title compound as a pale yellow solid (79 mg, 60%).
Mp = 82–85 °C.
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.35–7.31 (m, 2H), 7.27 (d, J = 4.8 Hz, 1H), 6.85 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 5.97 (s, 2H), 3.83 (s, 3H).
13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 148.0, 147.2, 146.8 (d, J = 248.0 Hz), 136.7 (d, J = 6.2 Hz), 125.3 (d, J = 4.2 Hz), 119.8 (d, J = 4.7 Hz), 117.5 (d, J = 28.6 Hz), 108.6, 106.6 (d, J = 3.7 Hz), 101.1, 40.0 (s).
19F NMR (282 MHz, CDCl3) δ −178.2 (s). HRMS (ESI): Calcd for C11H10FN2O2 [M + H+]: 221.0721, found 221.0728.


Alexis prieto
Chercheur postdoctoral chez Melchiorre group, ICIQ
Melchiorre group, ICIQ

Univ Lyon, Université Claude Bernard Lyon 1, Institut de Chimie et Biochimie Moléculaires et Supramoléculaires (ICBMS, CNRS UMR 5246), F-69622 Villeurbanne, France
//////////////















