CAS 1313725-88-0, Molecular Formula, C17-H15-N9, Molecular Weight, 345.3685
1H-1,2,3-Triazolo(4,5-b)pyrazine, 1-((1S)-1-imidazo(1,2-a)pyridin-6-ylethyl)-6-(1-methyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-
- AZD-6094
- AZD6094
- HMPL-504
- HMPL504
- Savolitinib
- Savolitinib [INN]
- UNII-2A2DA6857R
- Volitinib
- HM 5016504
Hutchison China MediTech (Chi-Med), Cancer, kidney (renal cell carcinoma, papillary)
A c-Met kinase inhibitor with antineoplastic activity.
NCI: volitinib. An orally bioavailable inhibitor of the c-Met receptor tyrosine kinase with potential antineoplastic activity. Volitinib selectively binds to and inhibits the activation of c-Met in an ATP-competitive manner, and disrupts c-Met signal transduction pathways. This may result in cell growth inhibition in tumors that overexpress the c-Met protein. C-Met encodes the hepatocyte growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase and plays an important role in tumor cell proliferation, survival, invasion, and metastasis, and tumor angiogenesis; this protein is overexpressed or mutated in a variety of cancers.(NCI Thesaurus)
Savolitinib is an experimental small molecule inhibitor of c-Met. It is being investigated for the treatment of cancer by AstraZeneca.[1] It is in phase II clinical trials for adenocarcinoma, non-small cell lung cancer, and renal cell carcinoma.[2]
Savolitinib is a first-in-class inhibitor of c-Met in phase III clinical development at at Hutchison China MediTech (Chi-Med) and AstraZeneca for the treatment of patients with MET-driven, unresectable and locally advanced or metastatic papillary renal cell carcinoma. Phase II trials are also under way for the oral treatment of locally advanced or metastatic pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinoma. AstraZeneca is conducting phase II clinical trials for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Phase I/II trials are ongoing at Samsung Medical Center for the second-line treatment of advanced gastric adenocarcinoma patients with MET amplification.
In 2011, the drug was licensed to AstraZeneca by at Hutchison China MediTech (Chi-Med) for worldwide codevelopment and marketing rights for the treatment of cancer.

SYNTHESIS
PAPER
Journal of Organic Chemistry (2018),
A multidisciplinary approach covering synthetic, physical, and analytical chemistry, high-throughput experimentation and experimental design, process engineering, and solid-state chemistry is used to develop a large-scale (kilomole) Suzuki–Miyaura process. Working against clear criteria and targets, a full process investigation and optimization package is described highlighting how and why key decisions are made in the development of large-scale pharmaceutical processes.
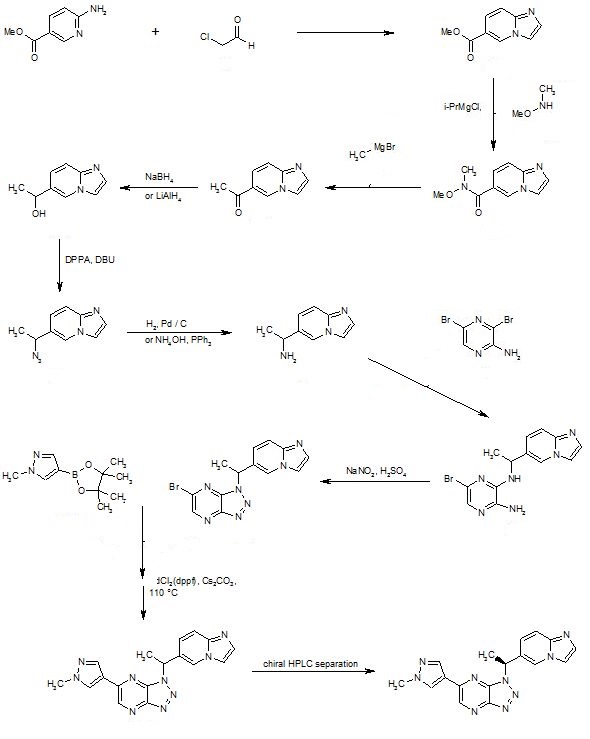
Process Design and Optimization in the Pharmaceutical Industry: A Suzuki–Miyaura Procedure for the Synthesis of Savolitinib
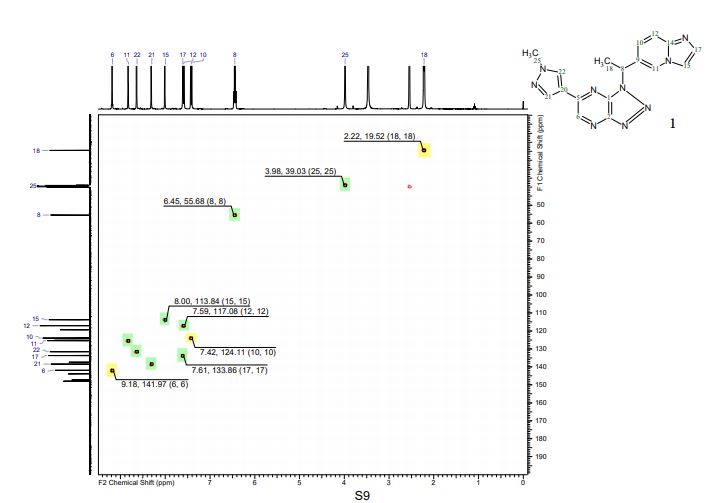
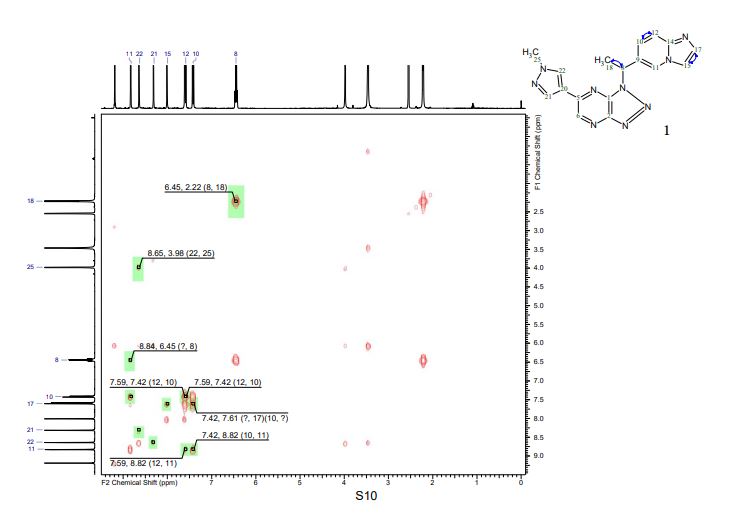
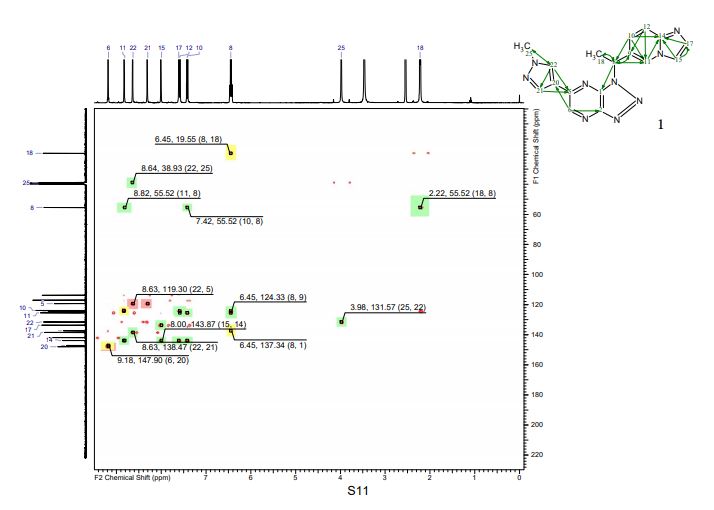
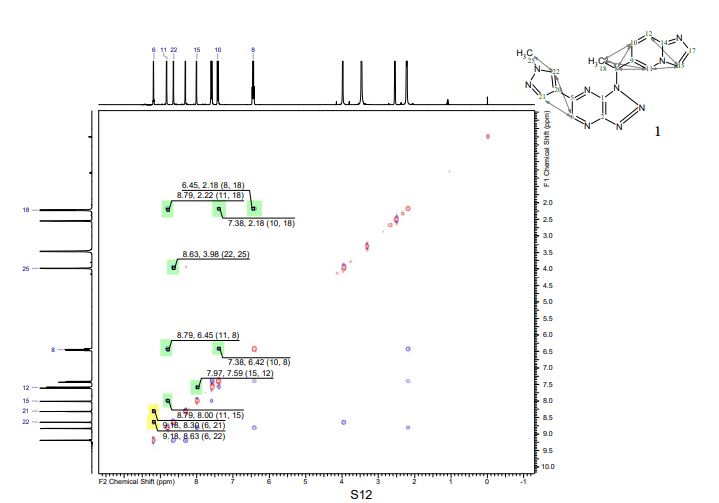
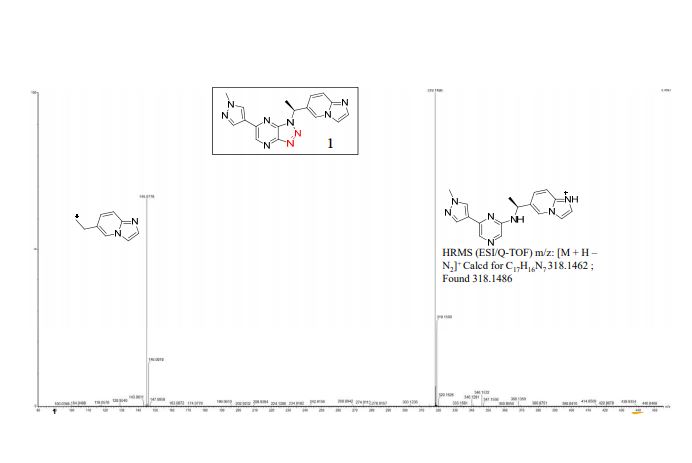
PAPER
Journal of Medicinal Chemistry (2014), 57(18), 7577-7589
HGF/c-Met signaling has been implicated in human cancers. Herein we describe the invention of a series of novel triazolopyrazine c-Met inhibitors. The structure–activity relationship of these compounds was investigated, leading to the identification of compound 28, which demonstrated favorable pharmacokinetic properties in mice and good antitumor activities in the human glioma xenograft model in athymic nude mice.
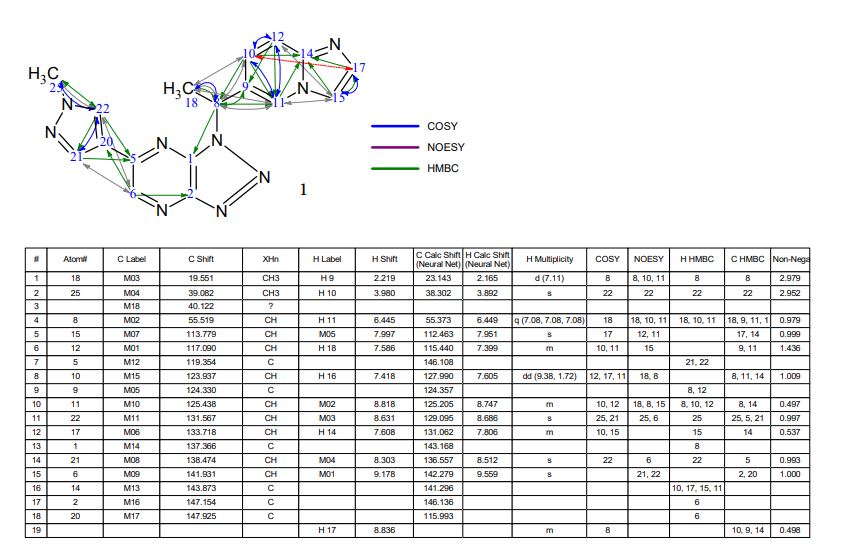
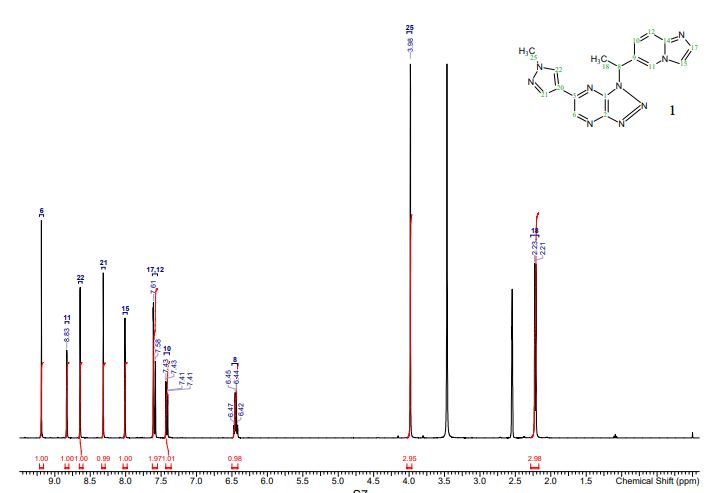
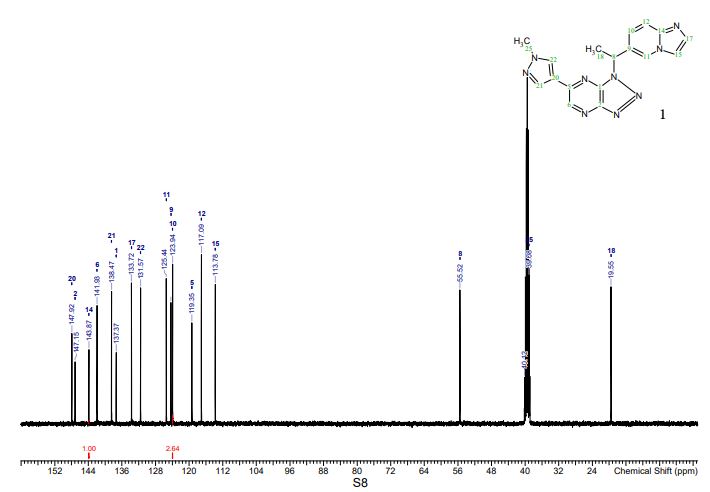
Discovery of (S)-1-(1-(Imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-6-yl)ethyl)-6-(1-methyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-1H-[1,2,3]triazolo[4,5-b]pyrazine (Volitinib) as a Highly Potent and Selective Mesenchymal–Epithelial Transition Factor (c-Met) Inhibitor in Clinical Development for Treatment of Cancer
Preparation of (S)-2-(4-(1-(1-(pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyridin-5-yl)ethyl)-1H-[1,2,3]triazolo[4,5-b]pyrazin-6-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)ethanol (30) and (R)-2-(4-(1-(1-(pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyridin-5-yl)ethyl)-1H-[1,2,3]triazolo[4,5-b]pyrazin-6-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)ethanol (31)
PATENT
WO 2018175251
WO 2018055029
WO 2018024608
WO 2016087680
WO 2016081773
PATENT
JP 2016069348
PATENT
The present invention provides a triazolopyrazine derivatives, the chemical name (S) -1- (l_ (imidazo [l, 2_a] pyrazin-6-yl) ethane-yl) -6-α _ -1H- pyrazol-4-yl-methyl) -1Η- [1,2,3] triazolo [4,5-b] pyrazine, of formula (I), the
[0005] This compound is an inhibitor of the activity c -Me t, may be used for treatment or prevention of inhibition of c -Me t sensitive cancers. In the Chinese patent CN 102906092A (W02011 / 079804), discloses the synthesis and use triazolopyrazine derivatives. Prepared by repeating the above patent, the compound powder obtained by detecting an amorphous state. As those skilled in the art, although amorphous higher solubility and dissolution rate than polymorph in most cases, but it is unstable, hygroscopic, readily converted to stable crystalline form.Thus, without the presence of processing stability and poor storage stability shaped, and in the production process, the smaller the bulk density of the particles of amorphous, high surface free energy, are likely to cause aggregation, poor flowability, and a series of powerful elastic deformation of the formulation problem seriously affecting the clinical value of amorphous Drug triazolopyrazine derivatives.
PATENT
PATENT
WO 2014174478
CN 102127096
PATENT
References
- ^ https://searchusan.ama-assn.org/usan/documentDownload?uri=%2Funstructured%2Fbinary%2Fusan%2Fsavolitinib.pdf
- ^ adisinsight.springer.com/drugs/800035893
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Volitinib |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H15N9 |
| Molar mass | 345.37 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
///////////////Savolitinib, Phase III, AZD-6094, AZD6094, HMPL-504, HMPL504, UNII-2A2DA6857R, Volitinib, HM 5016504
C[C@@H](c1ccc2nccn2c1)
In some embodiments, the c-Met inhibitor is ARQ197 (Tivantinib). Tivantinib has the IUPAC name (3R,4R)-3-(5,6-Dihydro-4H-pyrrolo[3,2,1-ij]quinolin-1-yl)-4-(1H-indol-3-yl)-2,5-pyrrolidinedione and the following chemical structure:
[0058] In some embodiments, the c-Met inhibitor is EMD1214063 (MSC2156119J; Tepotinib).
Tepotinib has the IUPAC name 3-(1-(3-(5-((1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)methoxy)pyrimidin-2-yl)benzyl)-1,6-dihydro-6-oxopyridazin-3-yl)benzonitrile and the following chemical structure:
[0059] In some embodiments, the c-Met inhibitor is GSK/1363089/XL880 (Foretinib). Foretinib has the IUPAC name N1’-[3-fluoro-4-[[6-methoxy-7-(3-morpholinopropoxy)-4-quinolyl]oxy]phenyl]-N1-(4-fluorophenyl)cyclopropane-1,1-dicarboxamide and the following chemical structure:
[0060] In some embodiments, the c-Met inhibitor is XL184 (Cabozantinib). Cabozantinib has the IUPAC name N-(4-((6,7-Dimethoxyquinolin-4-yl)oxy)phenyl)-N-(4-fluorophenyl)cyclopropane-1,1-dicarboxamide and the following chemical structure:
[0061] In some embodiments, the c-Met inhibitor is HMPL-504/AZD6094/volitinib (Savolitinib). Volitinib has the IUPAC name (S)-1-(1-(imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-6-yl)ethyl)-6-(1-methyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-1H-[1,2,3]triazolo[4,5-b]pyrazine and the following chemical structure:
[0062] In some embodiments, the c-Met inhibitor is MSC2156119J (EMD 1214063, Tepotinib).
Tepotinib has the IUPAC name Benzonitrile, 3-[1,6-dihydro-1-[[3-[5-[(1-methyl-4-piperidinyl)methoxy]-2-pyrimidinyl]phenyl]methyl]-6-oxo-3-pyridazinyl]- and the following chemical structure:
[0063] In some embodiments, the c-Met inhibitor is LY2801653 (Merestinib). Merestinib has the IUPAC name N-(3-fluoro-4-{[1-methyl-6-(1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-1H-indazol-5 yl]oxy}phenyl)-1-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-methyl-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyridine-3-carboxamide and the following chemical structure:
[0064] In some embodiments, the c-Met inhibitor is AMG 337. AMG 337 has the IUPAC name 7-methoxy-N-((6-(3-methylisothiazol-5-yl)-[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazin-3-yl)methyl)-1,5-naphthyridin-4-amine and the following chemical structure:
[0065] In some embodiments, the c-Met inhibitor is INCB28060 (Capmatinib). Capmatinib has the IUPAC name 2-fluoro-N-methyl-4-[7-(quinolin-6-ylmethyl)imidazo[1,2-b][1,2,4]triazin-2-yl]benzamide and the following chemical structure:
[0066] In some embodiments, the c-Met inhibitor is AMG 458. AMG 458 has the IUPAC name 1-(2-hydroxy-2-methylpropyl)-N-(5-((7-methoxyquinolin-4-yl)oxy)pyridin-2-yl)-5-methyl-3-oxo-2-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxamide and the following chemical structure:
[0067] In some embodiments, the c-Met inhibitor is PF-04217903. PF-04217903 has the IUPAC name 2-(4-(1-(quinolin-6-ylmethyl)-1H-[1,2,3]triazolo[4,5-b]pyrazin-6-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)ethanol and the following chemical structure:
[0068] In some embodiments, the c-Met inhibitor is PF-02341066 (Crizotinib). Crizotinib has the IUPAC name (R)-3-(1-(2,6-dichloro-3-fluorophenyl)ethoxy)-5-(1-(piperidin-4-yl)-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)pyridin-2-amine and the following chemical structure:
[0069] In some embodiments, the c-Met inhibitor is E7050 (Golvatinib). Golvatinib has the IUPAC name N-(2-fluoro-4-((2-(4-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)piperidine-1-carboxamido)pyridin-4-yl)oxy)phenyl)-N-(4-fluorophenyl)cyclopropane-1,1-dicarboxamide and the following chemical structure:
[0070] In some embodiments, the c-Met inhibitor is MK-2461. MK-2461 has the IUPAC name N-((2R)-1,4-Dioxan-2-ylmethyl)-N-methyl-N’-[3-(1-methyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-5-oxo-5H-benzo[4,5]cyclohepta[1,2-b]pyridin-7-yl]sulfamide and the following chemical structure:
[0071] In some embodiments, the c-Met inhibitor is BMS-777607. BMS-777607 has the IUPAC name N-(4-((2-amino-3-chloropyridin-4-yl)oxy)-3-fluorophenyl)-4-ethoxy-1-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyridine-3-carboxamide and the following chemical structure:
[0072] In some embodiments, the c-Met inhibitor is JNJ-38877605. JNJ-38877605 has the IUPAC name 6-(difluoro(6-(1-methyl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazin-3-yl)methyl)quinoline and the following chemical structure:


















