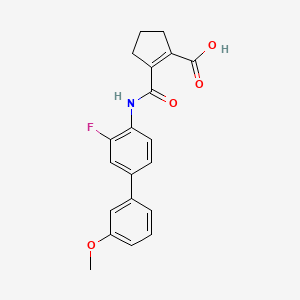
Vidofludimus
2-[[2-fluoro-4-(3-methoxyphenyl)phenyl]carbamoyl]cyclopentene-1-carboxylic acid
355.4 g/mol, C20H18FNO4
CAS 717824-30-1
4SC-101
UNII-8Y1PJ3VG81
SC12267
Vidofludimus calcium anhydrous
RN: 1354012-90-0
UNII: FW5VY7926X
IM-90838
IMU-838
Molecular Formula, 2C20-H17-F-N-O4.Ca, Molecular Weight, 748.7886
1-Cyclopentene-1-carboxylic acid, 2-(((3-fluoro-3′-methoxy(1,1′-biphenyl)-4-yl)amino)carbonyl)-, calcium salt (2:1)
Inflammatory Bowel Disease,
Immunosuppressants
Multiple Sclerosis,
Rheumatoid Arthritis,
Liver and Biliary Tract Disorders,
Antipsoriatics
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus,
Dihydroorotate Dehydrogenase (DHODH) Inhibitors
phase II clinical development at Immunic (previously Immunic AG) as an induction and maintenance therapy for patients with moderate to severe ulcerative colitis, as well as for the treatment of patients with relapsed-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS). Immunic is also conducting early clinical evaluation of the drug as a potential treatment for Crohn’s disease, whereas a phase II clinical trial is ongoing at the Mayo Clinic in patients suffering from primary sclerosing cholangitis.
In 2016, Immunic acquired the product from 4SC.
Vidofludimus is under investigation in clinical trial NCT03722576 (Vidofludimus Calcium for Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis).
Ca salt of vidofludimus (designated as form A) as dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH) inhibitor eg graft versus host disease, rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis
Immunic AG (a subsidiary of Immunic Inc ), following an asset acquisition from 4SC, is developing vidofludimus an orally available, small molecule DHODH inhibitor and IL-17 blocker which inhibits pyrimidine biosynthesis, for the treatment of autoimmune and inflammatory disorders including ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease and multiple sclerosis
PAPER
Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters (2005), 15(21), 4854-4857
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0960894X05010127
PRODUCT PATENT
WO 03006424
SPC protection in most of the EU states until 2021 and expire in the US in January 2022 with US154 extension
PATENT
WO2019101888 claiming composition comprising vidofludimus
PATENT
WO 2012001151
WO 2016200778
WO 2018177151
PATENT
WO2012001148 claiming similar compound (assigned to 4SC Ag ) naming the inventor Daniel Vitt. Immunic AG (a subsidiary of Immunic Inc ),
Example 4: Preparation of the calcium salts
300.4 mg of Vidofludimus free acid was dissolved in 18 mL of DCM/MeOH (3:1) and sonicated for 8 minutes. 31.5 mg of calcium hydroxide was suspended in 3 mL of DCM/MeOH (3:1); this was slowly added to the Vidofludimus free acid solution. The slight suspension was stirred overnight at 25°C. The solvent was partially evaporated under nitrogen flow at 25°C. A thick light yellow suspension was observed. The solid was recovered by filtration and washed with DCM/MeOH (3:1). The material was dried for 15 min under vacuum at 25°C. The material was shown to be crystalline using the methods described in the following.
From elemental analysis, the ratio of fluorine to calcium was calculated. The elemental composition is essentially consistent with a hemi-calcium-salt.
The Raman spectrum of the newly formed compound demonstrated differences to that of the free acid (see Figure 3 for both spectra.). Note that a Raman spectrum that is not simply the superposition of the free acid, the salt former and the solvent spectra, e.g., a Raman spectrum where new peaks or shifted peaks are observed, may correspond to a salt.
However, from the Raman spectrum alone, it cannot be determined whether crystalline salt formation has occurred. Peak shifts could also be due, in principle, to complexation of the free acid and salt former as an amorphous product, to polymorphs of either the free acid or salt former, to impurities, or to degradation products. Therefore, the integrity of the molecular structure was confirmed by 1H-NMR.
In addition, the powder X-ray diffraction shown in Figure 5 show that crystalline material was obtained, however with a pattern different from that of the free acid (see Figure 6). With light microscopy the crystals were visualized (Figure 4), DSC (differential scanning calorimetry) demonstrated a melting point of about 155°C (indicating a melting of a solvate and of a non-solvated form), TG-FTIR (thermogravimetric analyzer-coupled Fourier-Transform Infrared) indicates that probably a methanol solvate and a hydrate were formed and dynamic vapor sorption revealed desolvation followed by 0.3% water uptake at about 85% r.h. and 0.4% water uptake at 95% r.h. (not reversible).
PATENT
WO-2019175396
Novel white crystalline calcium salt of vidofludimus and its solvates and hydrates (designated as polymorph A), process for its preparation, composition comprising it and its use for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, inflammatory bowel disease, psoriasis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, lupus erythematosus, fibrosis, uveitis, rhinitis and Pneumocystis carinii are claimed. Vidofludimus is known to be an IL-17 antagonist, immunosuppressant and dihydroorotate dehydrogenase inhibitor.
Novel calcium salt polymorphs as Anti-Inflammatory, Immunomodulatory and Anti- Proliferatory Agents
Subject matter of the present invention is a white crystalline polymorph A of the Ca salt of a compound according to formula I or a solvate and/or a hydrate thereof with a molar ratio of a compound according to formula 1 or a solvate and/or a hydrate thereof to calcium which is 2±0.3. Subject matter of the present invention is in particular a compound according to formula I or a solvate and/or a hydrate thereof which is characterized by an X-ray powder diffraction pattern having characteristic peaks expressed in degrees 2theta at ±0.2 of the values shown below: 2 theta = 5.91°, 9.64°, 16.78°, 17.81°, 19.81°, 25.41° In particular the invention refers to new polymorphs of calcium salts of the Ca salt of a compound according to formula I or a solvate and/or a hydrate thereof which inhibits dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH), a process for their manufacture, pharmaceutical compositions containing them and to their use for the treatment and prevention of diseases, in particular their use in diseases where there is an advantage in inhibiting dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH). Examples of relevant diseases are given below.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) is a group of inflammatory conditions of the colon and small intestine. With Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis as principal types thereof. Crohn’s disease can affect the small intestine and large intestine, as well as the mouth, esophagus, stomach and the anus. Ulcerative colitis primarily affects the colon and the rectum.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a disease that is quite common especially among elder people. Its treatment with usual medications as for example non-steroid anti-inflammatory agents is not satisfactory. In view of the increasing ageing of the population, especially in the developed Western countries or in Japan the development of new medications for the treatment of RA is urgently required.
WO 2003/006425 describes certain specific compounds, which are reported to be useful for treatment and prevention of diseases where there is an advantage in inhibiting dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH). However, the specific salts according to the present invention are not disclosed. WO 2012/001148 describes the calcium salts of said compounds. However, the specific polymorphs according to the present invention are not disclosed.
WO 99/38846 and EP 0 646 578 disclose compounds which are reported to be useful for treatment of RA.
A medicament against rheumatoid arthritis with a new mechanism of action, leflunomide, was put on the market by the company Aventis under the tradename ARAVA [EP 780128, WO 97/34600]. Leflunomide has immunomodulatory as well as anti-inflammatory properties [EP 217206, DE 2524929]. The mechanism of action is based upon the inhibition of dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH), an enzyme of the pyrimidine biosynthesis.
De Julian-Ortiz (J. Med. Chem. 1999, 42, 3308-3314) describes certain potential Anti-Herpes compounds with cyclopentenoic acid moieties.
DE 33 46 814 A1 describes certain carbonic acid amide derivatives for the treatment, prevention and amelioration of diseases connected to cerebral dysfunction and symptoms caused thereby.
In the human body, DHODH catalyzes the synthesis of pyrimidines, which are in particular necessary for cellular metabolism. An inhibition of DHODH leads to block of transcription of sensitive genes in metabolically activated cells, whereas cells with normal metabolic activity obtain their required pyrimidine building blocks from the pyrimidine salvage pathway and show normal transcriptional activity. Disease relevant activated lymphocytes rely on de novo pyrimidine syntheses and react particularly sensitively to DHODH inhibition. Some substances that inhibit DHODH are important medicaments for the treatment of chronic inflammatory and auto-immune diseases.
A compound named leflunomide (ARAVA) has been the first approved inhibitor of DHODH and is used for the treatment of human diseases, in particular rheumatoid arthritis. WO 99/45926 is a further reference that discloses compounds which act as inhibitors of DHODH. Another drug which is targeting DHODH is teriflunomide (AUBAGIO®) is the metabolite of leflunomide. Teriflunomide is approved for the treatment of multiple sclerosis in some countries.
JP-A-50-121428 discloses N-substituted cyclopentene-l,2-dicarboxylic acid monoamides as herbicides and their syntheses. For example, N-(4-chlorophenyl)-l-cyclopentene-l,2-dicarboxylic acid monoamide is produced by reacting l-cyclopentene-l,2-dicarboxylic anhydride with 4- chloroaniline.
In the Journal of Med. Chemistry, 1999, Vol. 42, pages 3308-3314, virtual combinatorial syntheses and computational screening of new potential Anti-Herpes compounds are described. In Table 3 on page 3313 experimental results regarding IC50 and cytotoxicity are presented for 2-(2,3-difluorophenylcarbamoyl)-l -cyclopentene- 1 -carboxylic acid, 2-(2,6-difluorophenylcarbamoyl)-l -cyclopentene-l -carboxylic acid and 2-(2,3,4-trifluorophenyl-carbamoyl)- 1 -cyclopentene- 1 -carboxylic acid.
DE 3346814 and US 4661630 disclose carboxylic acid amides. These compounds are useful for diseases attended with cerebral dysfunction and also have anti-ulcer, anti-asthma, anti-inflammatory and hypo-cholesterol activities.
In EP 0097056, JP 55157547, DE 2851379 and DE 2921002 tetrahydrophthalamic acid derivatives are described.
It is an object of the present invention to provide effective agents, specifically in the form of certain polymorphs of their calcium salts, which can be used for the treatment of diseases which require the inhibition of DHODH.
It was also an object of the present invention to provide compounds that inhibit DHODH in a range similar to the compounds disclosed in W02003/006425 and WO 2012/001148 and at the same time show a white colour in order to facilitate double blind placebo controlled clinical studies.
It was also an object of the present invention to provide compounds and composition comprising that compounds that inhibit DHODH in a range similar to the compounds disclosed in
W02003/006425 and WO 2012/001148 and are characterized by having a THF content below
720 ppm in order to be in compliance with guidelines of the European Medicines Agency (e.g. with the version 6 December 2016 ; EMA/CHMP/ICH/82260/2006)
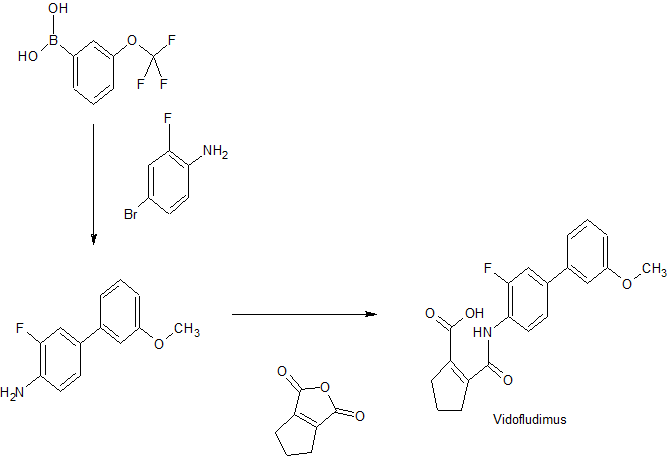
Particularly, it has previously been found that certain compounds of the general formula (I) shown herein below, such as 2-(3-Fluoro-3′-methoxy-biphenyl-4-ylcarbamoyl)-cyclopent-l-enecarboxylic acid (INN Vidofludimus), exhibit good anti-inflammatory activity and their usability in the oral therapy for the treatment of autoimmune diseases such as for example rheumatoid arthritis or inflammatory bowel diseases had been addressed.
Accordingly, a novel white polymorph of Calcium- vidofludimus named polymorph A with an inhibitory effect on DHODH, in particular human DHODH, was provided. Furthermore, a composition was provided comprising said white polymorph of Calcium-vidofludimus named polymorph A characterized by having a Tetrahydroduran (THF) content below 720 ppm.
[I,I ‘ – biphenyl] – 4 – yl}carbamoyl)cyclopent – 1 – ene – 1 – carboxylic acid) according to formula (I) or a solvate and/or a hydrate thereof, CAS-No 717824-30-1white crystalline calcium salt of 2 – ({3 – fluoro – 3’ – methoxy –
Thus, subject matter of the present invention is a white crystalline calcium salt of vidofludimus with a molar ratio of vidofludimus to calcium is 2±0.3 or a solvate and/or a hydrate thereof. In contrast to the pale yellow polymorph as described in EP 2588446B1, e.g. example 4, subject matter of the present invention is of white color.
White crystal can be defined as crystals with pure white color similar to the RAL color code RAL9010 that is equal or similar to the US Federal Standard 595 color code“White 506”, #27885.
A solvate for all embodiments of the invention maybe selected from the group comprising ethanol, propanol, isopropanol, butanol, ΊΊ IF, water. In a preferred embodiment for all embodiments of the invention the solvate is a hydrate. In one preferred embodiment the solvate is a calcium dihydrate for all embodiments of the invention.
In particular, subject matter of the present invention is a white crystalline polymorph A of the Ca salt of a compound according to formula I (vidofludimus) or a solvate and/or a hydrate thereof thereof which is characterized by an X-ray powder diffraction pattern having characteristic peaks expressed in degrees 2theta at ±0.2 of the values shown below:
2 theta = 5.91°, 9.64°, 16.78°, 17.81°, 19.81°, 25.41 °
PATENT
https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2012001151A1/en
/////////vidofludimus, PHASE 2, Inflammatory Bowel Disease, (IBD), Crohn’s Disease, Ulcerative Colitis, 4SC-101, UNII-8Y1PJ3VG81, SC12267, IM-90838, IMU-838, Immunic, 4SC,
COC1=CC=CC(=C1)C2=CC(=C(C=C2)NC(=O)C3=C(CCC3)C(=O)O)F
[Ca+2].COc1cccc(c1)