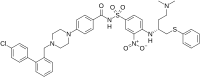
ABT-737
| Molecular Weight |
813.43 |
|---|---|
| Formula |
C42H45ClN6O5S2 |
| CAS No. |
852808-04-9 |
ABT-737 is a small molecule drug that inhibits Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL, two members of the Bcl-2 family of evolutionarily-conserved proteins that share Bcl-2 Homology (BH) domains. First developed as a potential cancer chemotherapy,[1] it was subsequently identified as a senolytic (a drug that selectively induces cell death in senescent cells).[2]
The Bcl-2 family is most notable for their regulation of apoptosis, a form of programmed cell death, at the mitochondrion; Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL are anti-apoptotic proteins. Because many cancers have mutations in these genes that allow them to survive, scientists began working to develop drugs that would inhibit this pathway in the 1990s.[1] ABT-737 was one of the earliest of a series of drugs developed by Abbott Laboratories (now Abbvie) to target this pathway, based on their resolution of the 3D structure of Bcl-xL and studies using high-field solution nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) that revealed how the BH domains of these proteins interacted with their targets.[1]
ABT-737 was superior to previous BCL-2 inhibitors given its higher affinity for Bcl-2, Bcl-xL and Bcl-w. In vitro studies showed that primary cells from patients with B-cell malignancies are sensitive to ABT-737.[3] In animal models, it improved survival, caused tumor regression, and cured a high percentage of mice.[4] In preclinical studies utilizing patient xenografts, ABT-737 showed efficacy for treating lymphoma and other blood cancers.[5]
Unfortunately, ABT-737 is not bioavailable after oral administration, leading to the development of navitoclax (ABT-263) as an orally-available derivative with similar activity on small cell lung cancer (SCLC) cell lines.[1][6] Navitoclax entered clinical trials,[1][6] and showed promise in haematologic cancers, but was stalled when it was found to cause thrombocytopenia (severe loss of platelets), which was discovered to be caused by the platelets’ requirement for Bcl-xL for survival.[1]
Subsequently, it was reported that ABT-737 specifically induces apoptosis in senescent cells in vitro and in mouse models.[2]
ABT-737, a BH3 mimetic, is a potent Bcl-2, Bcl-xL and Bcl-w inhibitor with EC50s of 30.3 nM, 78.7 nM, and 197.8 nM, respectively. ABT-737 induces the disruption of the BCL-2/BAX complex and BAK-dependent but BIM-independent activation of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway. ABT-737 induces autophagy and has the potential for acute myeloid leukemia (AML) research.
PATENT
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=WO2022246929&_cid=P10-LB5WBS-20634-1
PATENT
CN113248415
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=CN334799516&_cid=P22-LB8RFE-22163-1
PATENT
US20070015787
Journal of Medicinal Chemistry (2007), 50(4), 641-662
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jm061152t
////////

AS ON DEC2021 3,491,869 VIEWS ON BLOG WORLDREACH AVAILABLEFOR YOUR ADVERTISEMENT

join me on Linkedin
Anthony Melvin Crasto Ph.D – India | LinkedIn
join me on Researchgate
RESEARCHGATE

join me on Facebook
Anthony Melvin Crasto Dr. | Facebook
join me on twitter
Anthony Melvin Crasto Dr. | twitter
+919321316780 call whatsaapp
EMAIL. amcrasto@amcrasto
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
4-{4-[(4′-Chloro[1,1′-biphenyl]-2-yl)methyl]piperazin-1-yl}-N-(4-{[(2R)-4-(dimethylamino)-1-(phenylsulfanyl)butan-2-yl]amino}-3-nitrobenzene-1-sulfonyl)benzamide
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| Properties | |
| C42H45ClN6O5S2 | |
| Molar mass | 813.43 g·mol−1 |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
References
- ^ Jump up to:a b c d e f Croce, Carlo M; Reed, John C (October 2016). “Finally, An Apoptosis-Targeting Therapeutic for Cancer”. Cancer Research. 76 (20): 5914–5920. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-1248. PMC 5117672. PMID 27694602.
- ^ Jump up to:a b Yosef, Reut; Pilpel, Noam; Tokarsky-Amiel, Ronit; Biran, Anat; Ovadya, Yossi; Cohen, Snir; Vadai, Ezra; Dassa, Liat; Shahar, Elisheva; Condiotti, Reba; Ben-Porath, Ittai; Krizhanovsky, Valery (2016). “Directed elimination of senescent cells by inhibition of BCL-W and BCL-XL”. Nature Communications. 7: 11190. Bibcode:2016NatCo…711190Y. doi:10.1038/ncomms11190. PMC 4823827. PMID 27048913.
- ^ Vogler, Meike, et al. “Bcl-2 inhibitors: small molecules with a big impact on cancer therapy.” Cell Death & Differentiation 16.3 (2008): 360–367.
- ^ Oltersdorf, Tilman; Elmore, Steven W.; Shoemaker, Alexander R.; Armstrong, Robert C.; Augeri, David J.; Belli, Barbara A.; Bruncko, Milan; Deckwerth, Thomas L.; Dinges, Jurgen; Hajduk, Philip J.; Joseph, Mary K.; Kitada, Shinichi; Korsmeyer, Stanley J.; Kunzer, Aaron R.; Letai, Anthony; Li, Chi; Mitten, Michael J.; Nettesheim, David G.; Ng, ShiChung; Nimmer, Paul M.; O’Connor, Jacqueline M.; Oleksijew, Anatol; Petros, Andrew M.; Reed, John C.; Shen, Wang; Tahir, Stephen K.; Thompson, Craig B.; Tomaselli, Kevin J.; Wang, Baole; Wendt, Michael D.; Zhang, Haichao; Fesik, Stephen W.; Rosenberg, Saul H. (2005). “An inhibitor of Bcl-2 family proteins induces regression of solid tumours”. Nature. 435 (7042): 677–81. Bibcode:2005Natur.435..677O. doi:10.1038/nature03579. PMID 15902208. S2CID 4335635.
- ^ Hann CL, Daniel VC, Sugar EA, Dobromilskaya I, Murphy SC, Cope L, Lin X, Hierman JS, Wilburn DL, Watkins DN, Rudin CM (April 2008). “Therapeutic efficacy of ABT-737, a selective inhibitor of BCL-2, in small cell lung cancer”. Cancer Research. 68 (7): 2321–8. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-07-5031. PMC 3159963. PMID 18381439.
- ^ Jump up to:a b Hauck P, Chao BH, Litz J, Krystal GW (April 2009). “Alterations in the Noxa/Mcl-1 axis determine sensitivity of small cell lung cancer to the BH3 mimetic ABT-737”. Mol Cancer Ther. 8 (4): 883–92. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-1118. PMID 19372561. Retrieved 9 September 2019.
///////////ABT-737, ABT 737
CN(CC[C@@H](NC1=CC=C(C=C1[N+]([O-])=O)S(NC(C2=CC=C(C=C2)N3CCN(CC3)CC4=CC=CC=C4C5=CC=C(C=C5)Cl)=O)(=O)=O)CSC6=CC=CC=C6)C















