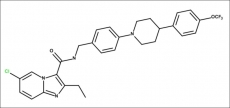
Telacebec
- Molecular FormulaC29H28ClF3N4O2
- Average mass557.006 Da
Telacebec, IAP6, CAS No. 1334719-95-7
Qurient Therapeutics and Russia licensee Infectex are developing telacebec, an oral formulation which targets QcrB subunit of the cytochrome bc1 complex, for treating multi drug resistant or extensively drug resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Qurient is also investigating telacebec for treating buruli ulcer (an infection caused by Mycobacterium ulcerans ). In January 2021, a global phase II trial was expected to begin by December 2021 for the treatment of buruli ulcer.
syn
Angewandte Chemie, International Edition, 57(4), 1108-1111; 2018
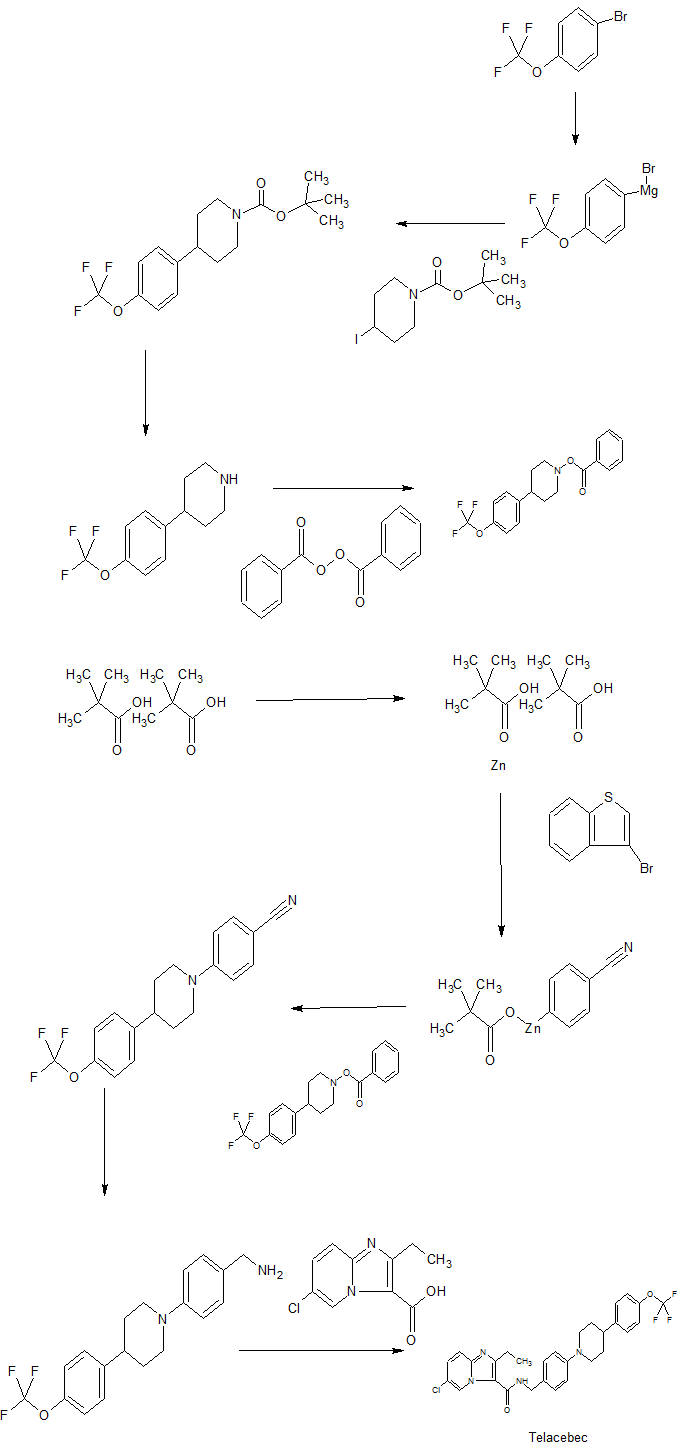
PATENT
WO-2021018387
Novel crystalline forms of telacebec , processes for their preparation and compositions comprising them are claimed. Also claimed is their use for treating bacterial infection.
Different forms of 6-chloro-2-ethyl-AT-(4-(4-(4- (trifluoromethoxy)phenvDpiperidine-i-vDbenzvDimidazolT.2-alpyridine- 3-carboxamide
The present invention relates to different forms of the compound 6-chloro-2-ethyl-lV-(4-(4-(4-(trifhioromethoxy)phenyl)piperidine-i-yl)benzyl)imidazo[i,2-a]pyridine-3-carboxamide and to methods of making such forms/compounds. The present invention furthermore relates to mono-acid addition salts thereof, to methods of making such mono-acid addition salts and to pharmaceutical compositions comprising any of the aforementioned compounds. Furthermore, the present invention relates to uses of any of these compounds.
Tuberculosis as a disease continues to result in millions of deaths each year. Inadequate use of chemotherapy has led to an increasing number of drug resistant cases. This situation is likely to worsen with the emergence of extremely resistant strains to all currently known drugs. Current chemotherapy consists of compounds that directly target Mycobacterium tuberculosis, either by neutralizing general information pathways and critical processes such as RNA polymerization and protein synthesis inhibition or by interfering with mycobacterial specific cell envelop synthesis. The most widely used dedicated anti-tubercular drugs isoniazid, ethionamide, and pyriazin amide are pro-drugs that first require activation. They are administered to a patient for a course of several months. Patients infected with multi-drug resistant strains of M. tuberculosis may have to undergo combination therapies for extended periods of time.
WO 2011/113606 describes various anti-tubercular compounds and their use in the treatment of bacterial infections, including compound“Q203” which chemically is 6-chloro-2-ethyl-!V-(4-(4-(4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl)piperidine-i-yl)benzyl)imidazo[i,2-a]pyridine-3-carboxamide. In a publication by Pethe et al. (Nature Medicine, 19, 1157-1160 (2013), this compound is reported to be active against tuberculosis by interfering with the bacterial energy metabolism, inhibiting cytochrome bci activity which is an essential component of the electron transport chain required for synthesis of ATP.
Whilst the compound shows promise for future therapy of tuberculosis and related infections, there continues to be a need for forms thereof that are particularly suitable for pharmaceutical administration. In particular there is a need to provide forms that are showing an improved solubility in comparison to the free base of this compound. Furthermore, there is a need in the art to provide for forms that show an improved stability.
In a first aspect the present invention relates to a compound 6-chloro-2-ethyl-N-(4-(4-(4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl)piperidine-i-yl)benzyl)imidazo[i,2-a]pyridine-3-carboxamide ditosylate having the structure
PATENT
WO2011113606 .
WO 2017049321
WO 2012143796
PAPER
Scientific reports (2019), 9(1), 8608.
Angewandte Chemie, International Edition (2018), 57(4), 1108-1111.
European journal of medicinal chemistry (2017), 136, 420-427.
European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry (2017), 136, 420-427.
European journal of medicinal chemistry (2017), 125, 807-815.
Nature communications (2016), 7, 12393.
Nature medicine (2013), 19(9), 1157-60
PAPER
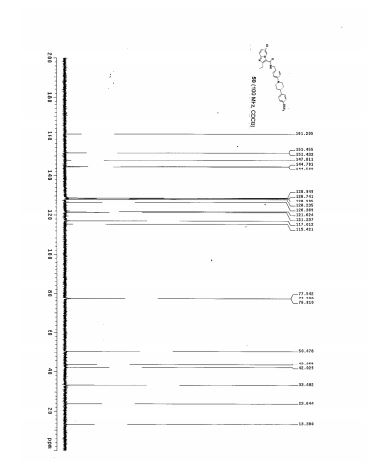
Journal of Medicinal Chemistry (2014), 57(12), 5293-5305.
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jm5003606
Publication Date:May 28, 2014

6-Chloro-2-ethyl-N-(4-{4-[4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl]piperidin-1-yl}benzyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-3-carboxamide (50)


CLIP
June 3, 2019. Qurient press release:
SEONGNAM-SI, South Korea–(BUSINESS WIRE)– Qurient Co. Ltd. today announced positive results from the Phase 2a EBA (early bactericidal activity) clinical trial for telacebec (Q203), a first-in-class, orally-available antibiotic for the treatment of tuberculosis (TB). Telacebec is a selective inhibitor with high specificity for the cytochrome bc1 complex of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This complex is a critical component of the electron transport chain, and inhibition disrupts the bacterium’s ability to generate energy.
The EBA trial assessed the pharmacokinetics, safety, and activity of telacebec in three dose strength (100 mg, 200 mg and 300 mg) in the treatment of adult patients with pulmonary TB. Telacebec met the primary objective of rate of change in the time to positivity (TTP) in sputum over days 0 to 14. Telacebec was safe and well tolerated throughout the different dose strengths. Full results from EBA trial are expected to be presented at future scientific meetings.
Phase 2. EBA began July 2018 in South Africa. As of March 2019, study is active, not enrolling.
June 2018. Q203 has a non-proprietary name assigned: telacebec. USAN: -cebec Cytochrome bc1 complex inhibitors in Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Phase 1. Description from clinicaltrials.gov: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-escalation study in healthy male and female volunteers. Subjects randomly assigned to 1 of 7 treatment cohorts (Cohorts 1 – 7) of 8 subjects each, receiving either Q203 or placebo (6 active treatment : 2 placebo) in a fasting state. Dose escalation to the next cohort may be considered when at least 6 out of 8 subjects, in a cohort, completes all procedures and none of the subjects has a clinically significant adverse event (AE) that is being followed, or at the discretion of the PI if no drug-related serious adverse events (SAEs) have occurred. A food effect cohort will be enrolled to test administration of Q203 in a fed state, at 100 mg dose level (this dose level may change based on PK analysis results). Subjects who received 100mg dose in a fasting state will return and receive the second dose, with food. Subjects will be followed up for AEs, SAE or pregnancy for 30 days postdrug administration.
Related Links
- Qurient website
- 2013 Pethe K–Nature Medicine–Discovery of Q203, a potent clinical candidate for the treatment of tuberculosis
- 2014 Kang S — JMC – Lead Optimization of a Novel Series of Imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine Amides Leading to a Clinical Candidate (Q203) as a Multi- and Extensively-Drug-Resistant Anti-tuberculosis Agent
//////////////Telacebec, IAP6, 1334719-95-7, PHASE 2, QURIENT, TUBERCULOSIS, телацебек , تيلاسيبيك , 特雷贝克 , Q 203