AZD2716
- Antiplaque candidate drug
AstraZeneca INNOVATOR
(R)-7(AZD2716) a novel, potent secreted phospholipase A2 (sPLA2) inhibitor with excellent preclinical pharmacokinetic properties across species, clear in vivo efficacy, and minimized safety risk. Based on accumulated profiling data, (R)-7 was selected as a clinical candidate for the treatment of coronary artery disease.
Chiral HPLC using a Chiralcel OJ 5 μm 20×250 mm
column with heptane/EtOH/formic acid ((10:90:0.1; 15 ml/min, 40 °C, 260 nm) as mobile
phase to yield (S)-7 and (R)-7
(R)-7:tR=5.8 min [α]D20 15.4 (c 0.5, ACN), 99.7 %ee. desired
(S)-7: tR=9.2 min. 99.0 % ee. undesired
LINK
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/suppl/10.1021/acsmedchemlett.6b00188

SYNTHESIS
1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 1.04 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, 3H), 2.55–2.68 (m, 2H), 2.95 (dd, J = 6.1, 12.8 Hz, 1H), 4.00 (s, 2H), 7.13–7.37 (m, 13H), 7.49–7.54 (m, 1H), 12.2 (s, br, 1H).
13C NMR (151 MHz, DMSO): δ 16.7, 39.1, 40.7, 41.0, 126.3, 126.4, 127.3, 127.8, 128.0, 128.2, 128.7, 128.9, 129.2, 130.3, 135.3, 139.2, 139.5, 140.5, 141.2, 142.7, 171.3, 177.1.
HRMS (ESI): [M + H]+ m/z calcd for C24H24NO3 374.1751, found 374.1748.
1H NMR
13C NMR
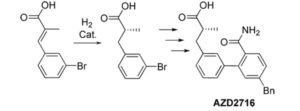
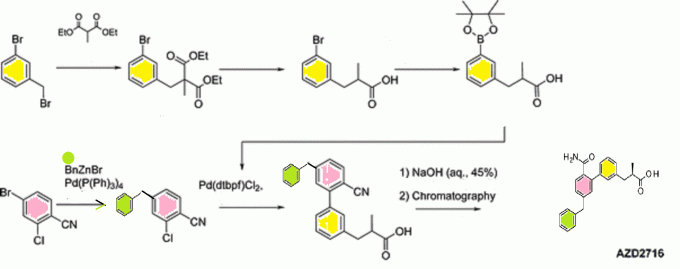
An Enantioselective Hydrogenation of an Alkenoic Acid as a Key Step in the Synthesis of AZD2716
A classical resolution of a racemic carboxylic acid through salt formation and an asymmetric hydrogenation of an α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acid were investigated in parallel to prepare an enantiomerically pure alkanoic acid used as a key intermediate in the synthesis of an antiplaque candidate drug. After an extensive screening of rhodium- and ruthenium-based catalysts, we developed a rhodium-catalyzed hydrogenation that gave the alkanoic acid with 90% ee, and after a subsequent crystallization with (R)-1-phenylethanamine, the ee was enriched to 97%. The chiral acid was then used in sequential Negishi and Suzuki couplings followed by basic hydrolysis of a nitrile to an amide to give the active pharmaceutical ingredient in 22% overall yield.
Paper
Expedited structure-based optimization of the initial fragment hit 1 led to the design of (R)-7(AZD2716) a novel, potent secreted phospholipase A2 (sPLA2) inhibitor with excellent preclinical pharmacokinetic properties across species, clear in vivo efficacy, and minimized safety risk. Based on accumulated profiling data, (R)-7 was selected as a clinical candidate for the treatment of coronary artery disease.
Discovery of AZD2716: A Novel Secreted Phospholipase A2 (sPLA2) Inhibitor for the Treatment of Coronary Artery Disease
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acsmedchemlett.6b00188


akenoic acid as a key step in the sysnthesis of AZD2716. Org. Proc. Res. Dev. 2016, 20(2),
262-269).
/////////atherosclerosis, coronary artery disease, fragment screening, fragment-based drug discovery, Secreted phospholipase A2, sPLA2, AZD2716, AZD-2716, AZD 2716, PRECLINICAL, astrazeneca
c1c(cc(c(c1)C(=O)N)c2cccc(c2)CC(C(=O)O)C)Cc3ccccc3